本文全退指南🙃
-
css 变量在JS中的使用
-
一些边框划入特效
-
css部分属性应用,例如
filter
,
counter
,
mix-blend-mode
,
clip-path
如果上面几点你都不关心,可以
离开了
(点个赞再走),老铁🐶。
全部代码已上传 至压缩包(scdn资源包)。需要的可以
下载 | css-border-effects.zip⇲
。
不建议
大家下载,文中已给出了支持效果的代码。也建议去实操一下。
先介绍中文变量。
意思就是利用中文作为变量在css 中使用。
主要是安利两个库
渐变,代码就只需要一行


布局
/* 这个是固定写法,必须先指定display为grid */
display: grid;
/* grid属性需要指定哪种布局 */
grid: var(--九宫格);
/* 加入一点间距,让九个元素相互之间有一定的距离 */
gap: 10px;
ul {
display: grid;
grid: var(--九宫格);
gap: 10px;

挺好玩的吧
<html lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/chinese-layout">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/chinese-gradient">
</head>
<div class="item">
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
</div>
</body>
body {
--boder——width: 5px
body .item {
display: inline-block;
margin: 10px;
width: 300px;
height: 150px;
ul {
display: grid;
grid: var(--九宫格);
gap: 1px;
li {
height: 30px;
background: var(--极光绿);
border: var(--boder——width) solid black;
本节内容主要来自于 掘金 | Vue超好玩的新特性:在CSS中引入JS变量
主要利用的就是 css in js
案例我用的 scss(后面样式为了节省篇幅也用的scss);
推荐大家一个 vscode 插件
作用就如名字一样,实时遍历sass文件

body .item {
display: inline-block;
margin: 10px;
width: 300px;
height: 150px;
.item > div {
margin: auto;
width: 90%;
height: 90%;
<div class="item">
<div></div>
</div>
// scss
.item div{
position: relative;
border: 1px solid #03A9F3;
&::before,
&::after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
transition: .3s ease-in-out;
&::before {
top: -5px;
left: -5px;
border-top: 1px solid var(--borderColor);
border-left: 1px solid var(--borderColor);
&::after {
right: -5px;
bottom: -5px;
border-bottom: 1px solid var(--borderColor);
border-right: 1px solid var(--borderColor);
&:hover::before,
&:hover::after {
width: calc(100% + 9px);
height: calc(100% + 9px);
<div class="item" info="虚线边框动画">
<div></div>
</div>
.item div{
background:
linear-gradient(90deg, #333 50%, transparent 0) repeat-x,
linear-gradient(90deg, #333 50%, transparent 0) repeat-x,
linear-gradient(0deg, #333 50%, transparent 0) repeat-y,
linear-gradient(0deg, #333 50%, transparent 0) repeat-y;
background-size: 4px 2px, 4px 2px, 2px 4px, 2px 4px;
background-position: 0 0, 0 100%, 0 0, 100% 0;
&:hover {
animation: linearGradientMove .3s infinite linear;
@keyframes linearGradientMove {
100% {
background-position: 4px 0, -4px 100%, 0 -4px, 100% 4px;
<div class="item" info="实线过渡到虚线边框动画">
<div></div>
</div>
div.item:nth-child(5) div{
outline: 1px solid #333;
outline-offset: -1px;
transition: all .3s linear;
&:hover {
border: none;
background:
linear-gradient(90deg, #333 50%, transparent 0) repeat-x,
linear-gradient(90deg, #333 50%, transparent 0) repeat-x,
linear-gradient(0deg, #333 50%, transparent 0) repeat-y,
linear-gradient(0deg, #333 50%, transparent 0) repeat-y;
background-size: 4px 2px, 4px 2px, 2px 4px, 2px 4px;
background-position: 0 0, 0 100%, 0 0, 100% 0;
animation: linearGradientMove .3s infinite linear;
outline: none;
@keyframes linearGradientMove {
100% {
background-position: 4px 0, -4px 100%, 0 -4px, 100% 4px;
其实是四个色块再转,然后把中间部分遮挡。
注意,这个色块已经偏离原来大的位置,看到的边框不再是原来元素的边框,纯粹是为了秀而秀。你懂我意思吧😀
<div class="item" info="彩虹边框">
<div></div>
</div>
div.item div{
--borderWidth: 12px;
--bRadius: 5px;
width: 60%;
height: 60%;
position: relative;
z-index: 0;
overflow: hidden;
padding: 2rem;
z-index: 0;
border-radius: --bRadius;
&::after, &::before {
box-sizing: border-box;
&::before {
content: '';
position: absolute;
left: -50%;
top: -50%;
width: 200%;
height: 200%;
z-index: -2;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: 50% 50%, 50% 50%;
background-position: 0 0, 100% 0, 100% 100%, 0 100%;
background-image: linear-gradient(#399953, #399953), linear-gradient(#fbb300, #fbb300), linear-gradient(#d53e33, #d53e33), linear-gradient(#377af5, #377af5);
animation: rotate 4s linear infinite;
@keyframes rotate {
100% {
transform: rotate(1turn);
&::after {
content: '';
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
left: calc(var(--borderWidth) / 2);
top: calc(var(--borderWidth) / 2);
width: calc(100% - var(--borderWidth));
height: calc(100% - var(--borderWidth));
background: white;
border-radius: --bRadius;
animation: opacityChange 3s infinite alternate;
@keyframes opacityChange {
50% {
opacity:1;
100% {
opacity: .5;

利用的 conic-gradient⇲ | MDN, 思路和上面差不多,坏处也是一样。实用性不强,我就问你,帅不帅吧?
<div class="item" info="质感边框">
<div></div>
</div>
@keyframes opacityChange {
50% {
opacity:.5;
100% {
opacity: 1;
@keyframes rotate {
100% {
transform: rotate(1turn);
div.item {
background-color: #000;
padding: 20px;
div{
--borderWidth: 12px;
--bRadius:
10px;
width: 60%;
height: 60%;
position: relative;
z-index: 0;
overflow: hidden;
padding: 2rem;
z-index: 0;
border-radius: --bRadius;
&::after, &::before {
box-sizing: border-box;
&::before {
content: '';
position: absolute;
z-index: -2;
left: -50%;
top: -50%;
width: 200%;
height: 200%;
background-color: #1a232a;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: 0 0;
background-image: conic-gradient(transparent, rgba(168, 239, 255, 1), transparent 30%);
animation: rotate 4s linear infinite;
&::after {
content: '';
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
left: calc(var(--borderWidth) / 2);
top: calc(var(--borderWidth) / 2);
width: calc(100% - var(--borderWidth));
height: calc(100% - var(--borderWidth));
background: #000;
border-radius: 5px;
div.item:nth-child(9) div::after {
animation: opacityChange 5s infinite linear;
利用的是 clip-path ⇲ | MDN , 放个对比图
<div class="item" info="转动的边框线(单条)">
<div></div>
</div>
div.item {
div{
width: 80%;
position: relative;
text-align: center;
font-size: 24px;
&::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
border: 2px solid rgb(17, 36, 100);
transition: all .5s;
animation: clippath 3s infinite linear;
@keyframes clippath {
0%, 100% { clip-path: inset(0 0 95% 0); }
25% { clip-path: inset(0 95% 0 0); }
50% { clip-path: inset(95% 0 0 0); }
75% { clip-path: inset(0 0 0 95%); }

原理和上面一样,只是弄了两条,加了圆角。
<div class="item" info="转动的边框线(两条)">
<div></div>
</div>
// 转动的边框线(两条)
div.item {
--bRadius: 10px;
div{
position: relative;
text-align: center;
font-size: 24px;
border: 2px solid rgb(179, 191, 231);
border-radius: var(--bRadius);
transition: all .3s;
background-color: #eee;
&::before, &::after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: -10px;
left: -10px;
right: -10px;
bottom: -10px;
border: 2px solid rgb(17, 36, 100);
transition: all .5s;
border-radius: var(--bRadius);
animation: clippath 3s infinite linear;
&::after {
animation: clippath 3s infinite -1.5s linear;
@keyframes clippath {
0%, 100% { clip-path: inset(0 0 98% 0); }
25% { clip-path: inset(0 98% 0 0); }
50% { clip-path: inset(98% 0 0 0); }
75% {
clip-path: inset(0 0 0 98%); }
主要是利用 overflow (隐藏其它元素用)实现, 用另外一个元素盖过来。

<div class="item" info="扩散的边框线">
<div></div>
</div>
div.item {
margin-top: 200px;
padding: 10px;
--bColor: rgb(17, 36, 100);
background-color: #000;
display: inline-flex;
div{
position: relative;
overflow: hidden;
width: 12%;
height: 50%;
&::after {
content: "After";
position: absolute;
top: 4px;
bottom: 4px;
right: 4px;
left: 4px;
border-radius: 5px;
background: #fff;
border: 2px solid var(--bColor);
// 旋转块
&::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 0px;
bottom: 0px;
right: -30%;
left: 0px;
background: #fff;
//border-radius: 50%;
transform: rotateZ(-90deg) translate(-100%, -100%);
transform-origin: top left;
transition: transform .3s;
transition-timing-function: linear;
&:hover {
filter: contrast(1.2);
&:hover::before {
transform: rotateZ(0deg) translate(0%, -0%);
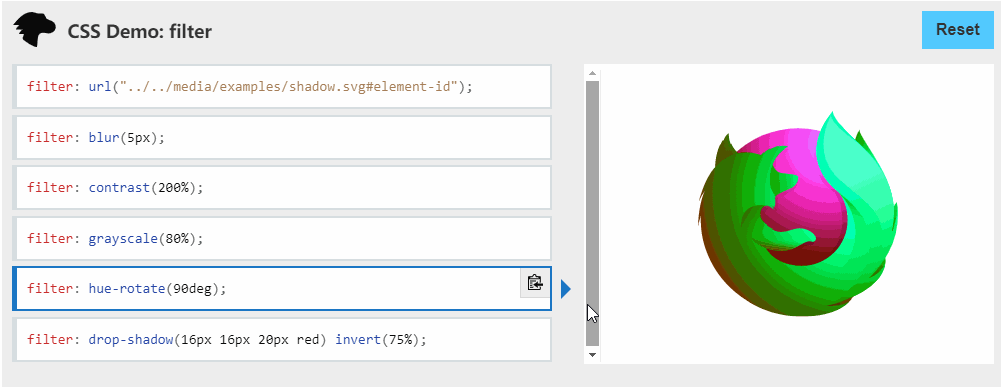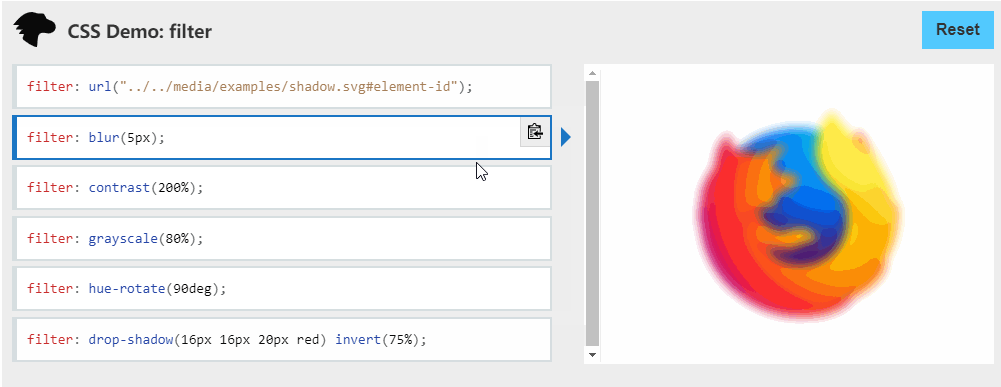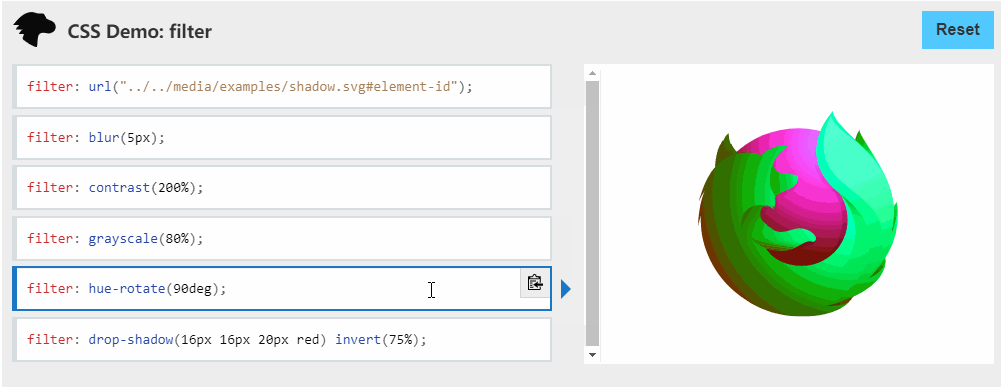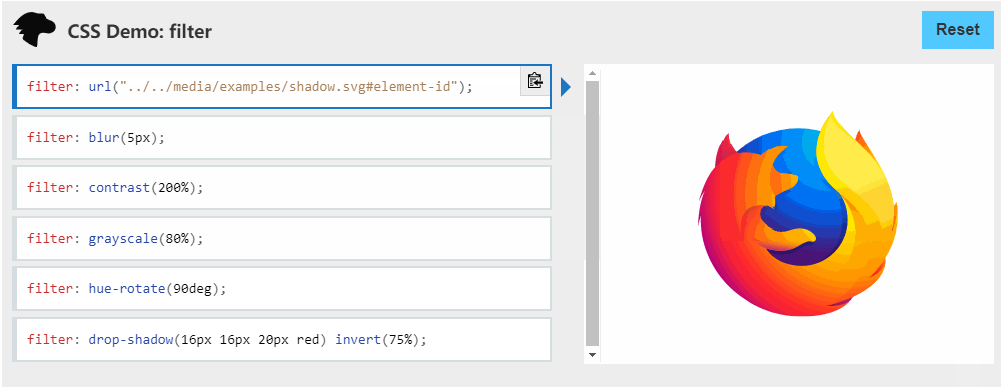
这和前面那彩虹边框一样(只是为了帅),主要利用的是 filter: hue-rotate(360deg) ,之前我也不知道🤣,建议大家去了解一下css-filter⇲。
filter
CSS属性将模糊或颜色偏移等图形效果应用于元素。滤镜通常用于调整图像,背景和边框的渲染。
<div class="item" info="颜色渐变边框">
<div></div>
</div>
div.item {
div{
border: 10px solid;
border-image: linear-gradient(45deg, gold, deeppink) 1;
clip-path: inset(0px round 10px);
animation: huerotate 6s infinite linear;
hue-rotate() (en-US) 函数在输入图像上应用色相旋转。
angle 一值设定图像会被调整的色环角度值。值为 0deg,则图像无变化。
若值未设置值,默认为 0deg。该值虽然没有最大值,超过 360deg 的值相当于又绕一圈。
svg 元素 失效!!
filter: hue-rotate(360deg);
@keyframes huerotate {
0% {
filter: hue-rotate(0deg);
100% {
filter: hue-rorate(360deg);
本节主要参考 CSS 奇思妙想边框动画⇲, 原文我看了应该来自 掘金⇲,还是💥爆💥文💥
主要介绍 css 与 js 如何 结合
基础 JS,后面都要用的。
document.addEventListener('mousedown', function (event) {
var target = event.target;
var body = document.body;
var html = document.documentElement;
body.style.setProperty('--pagex', event.pageX);
body.style.setProperty('--pagey', event.pageY);
html.style.setProperty('--clientx', event.clientX);
html.style.setProperty('--clienty', event.clientY);
html.style.setProperty('--scrolly', window.pageYOffset);
target.style.setProperty('--offsetx', event.offsetX);
target.style.setProperty('--offsety', event.offsetY);
target.parentElement.style.setProperty('--target-width', target.clientWidth);
target.parentElement.style.setProperty('--target-height', target.clientHeight);
target.parentElement.style.setProperty('--target-left', target.offsetLeft);
target.parentElement.style.setProperty('--target-top', target.offsetTop);
});
<div class="process">
<label>进度1:</label>
<div class="bar" style="--percent: 60;"></div>
<label>进度2:</label>
<div class="bar" style="--percent: 40;"></div>
</div>
.process {
.bar {
margin: 5px 0 10px;
height: 20px; width: 300px;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
border-radius: 4px;
overflow: hidden;
.bar::before {
counter-reset: progress var(--percent);
content: counter(progress) '%\2002';
display: block;
height: 100%;
width: calc(300px * var(--percent) / 100);
font-size: 12px;
color: #fff;
background-color: #2486ff;
text-align: right;
white-space: nowrap;
overflow: hidden;
进度条中间的数字比例 用到了 counter 与 counter-reset 。
想要理解更多 推荐阅读张鑫旭 14年🤣 的文章 CSS counter计数器(content目录序号自动递增)详解⇲

(点击文字下一小节会讲)
需要 上节说过需要的基础 JS
另外
// 利用的就是css 变量 ,每次切换left 都保存着上一次的值
.yw-tab-tab {
position: relative;
display: flex;
max-width: 414px;
justify-content: space-between;
border-bottom: 1px solid #717678;
background-color: #fff;
margin: 30px auto;
&::before,
&::after {
position: absolute;
width: calc(var(--target-width, 0) * 1px);
// 因为第一次始终是左边第一个菜单,所以left初始值为负数
left: calc(var(--target-left, -299) * 1px);
color: #2a80eb;
&[style]::before,
&[style]::after {
content: '';
&::before { // 字体变色
background-color: currentColor;
height: calc(var(--target-height) * 1px);
// mix-blend-mode 属性描述了元素的内容需要与父元素的背景颜色进行混合 (overlay 覆盖)
// https://www.runoob.com/try/try.php?filename=trycss_mix-blend-mode-all
// svg 不支持
mix-blend-mode: overlay;
&::after {// 下划线
border-bottom: solid;
bottom: -2px;
transition: left .2s, width .2s;
.yw-tab-a {
color: #717678;
padding: 10px 0;
主要利用变量,另外还有css属性 mix-blend-mode ,
mix-blend-mode:
CSS 属性描述了元素的内容应该与元素的直系父元素的内容和元素的背景如何混合
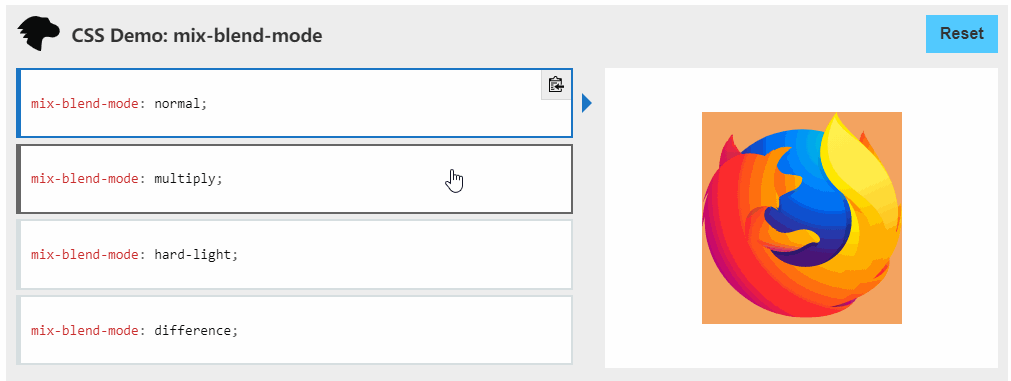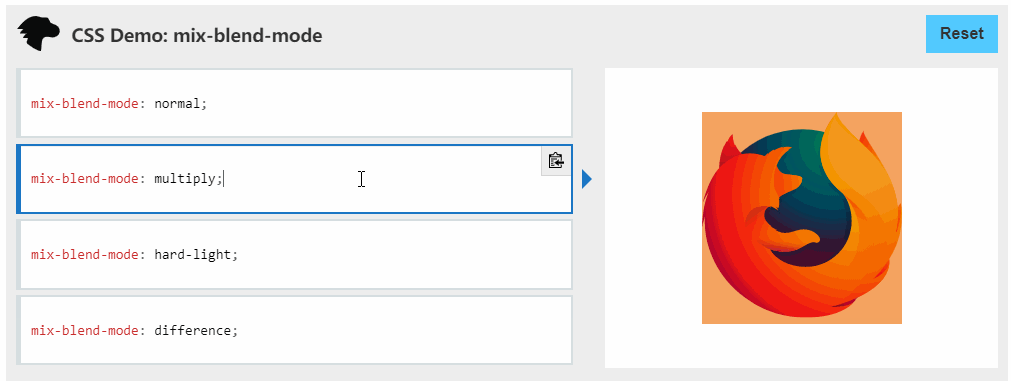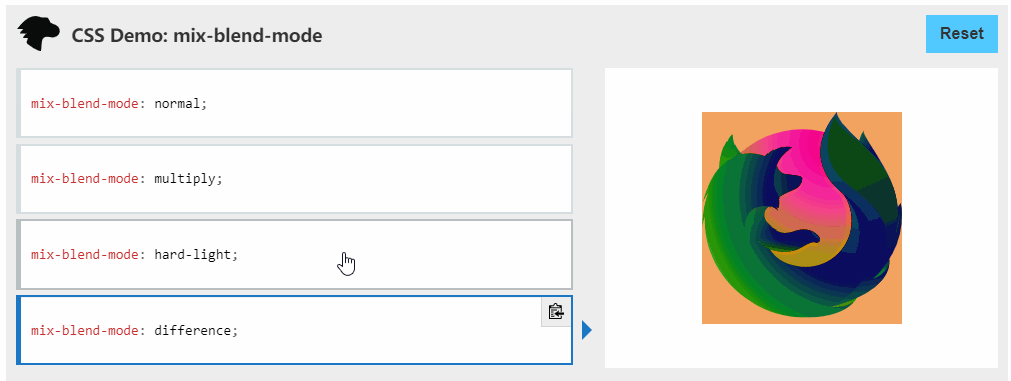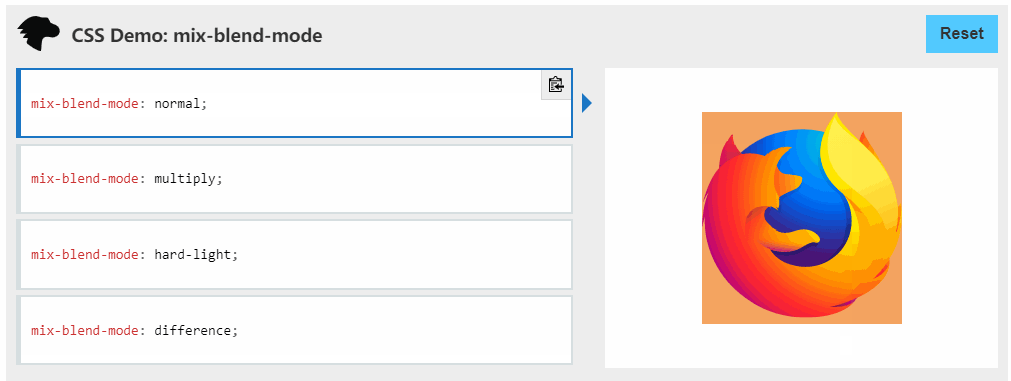
挺有意思的建议了解一下。
需要 上节说过需要的基础 JS
另外
body{
&:active::after {
transform: scale(.8) translate(-50%, -100%);
opacity: 0.5;
transition: 0s;
left: -999px;
&::after {
content: '💥💥 💖💖💖 💥💥';
position:fixed;
z-index: 999;
left: calc(var(--clientx, -999) * 1px);
top: calc(var(--clienty, -999) * 1px);
transform: scale(1.1) translate(-50%, calc(-100% - 20px));
opacity: 0;
transition: transform 2.3s, opacity 4.5s;
本节主要参考 张鑫旭大神 ⇲ 的文章 CSS变量对JS交互组件开发带来的提升与变革⇲
好啦,文章终于水完了啦😜😜😜,哈哈哈~~~
其实文章中基本都贴了,再贴一遍吧
掘金 | Vue超好玩的新特性:在CSS中引入JS变量
公众号 | CSS 奇思妙想边框动画⇲
个人博客 | CSS变量对JS交互组件开发带来的提升与变革⇲
一、半透明的边框实现
加入我们有这样一个需求:在一个背景图片的区域中,定义一个带有半透明白色边框的白色div。这个的实现方法最先想到的就是可以为边框定义透明度,代码如下:
background:white;
border:20px solidhsla(0,0%,100%,.5);
这里hsla为一种定义颜色的方法,它的各个参数含义如下:
H:Hue(色调)。0(
来给它做个动画!
我们可以对我们的边框进行动画化处理,甚至在不改变元素大小的情况下也可以进行动画化处理,非常简单。
要做到这一点,我们只需要为动画创建一个自定义的关键帧(keyframe),并在元素的CSS代码中的动画(animation)参数中使用它。
让我们看一个例子,HTML如下
<div id="box">
在网上查阅相关资料后,发现目前的动态渐变色边框的实现方式大部分为使用伪元素比内容区域大一圈然后横向移动渐变色背景的方式实现,而没有渐变色边框围绕内容区域进行旋转的效果,于是我做了一个这样的demo供大家参考。
首先将内容区域嵌套进一个DIV盒子中并设置overflow:hidden;。这个盒子的大小是内容区域的大小加上你希望实现的渐变边框的宽度,然后将内容区域居中,这样内容区域和父元素之间就有一个看似是边框的空白区域。
现在在这个空白区域加一个比父元素更大,背景为渐变色的盒子,将层级设置为最低z-index: -1;。再将这个渐变色背景的盒子加入旋转动画就完成了
今天的这个卡片边框动画效果,主要应用在一些重要信息上,想引起用户注意的时候,我们才会增加这样的效果,一般情况不会添加这样的动效,但是,我们还是需要学会怎么实现它,现在我们就一起来看看这个项目的最终效果:HTML代码:<!DOCTYPE html>
<title>【每日一练】34—CSS实现边框动画...













