爱可可AI前沿推介(12.27)
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 GR - 图形学
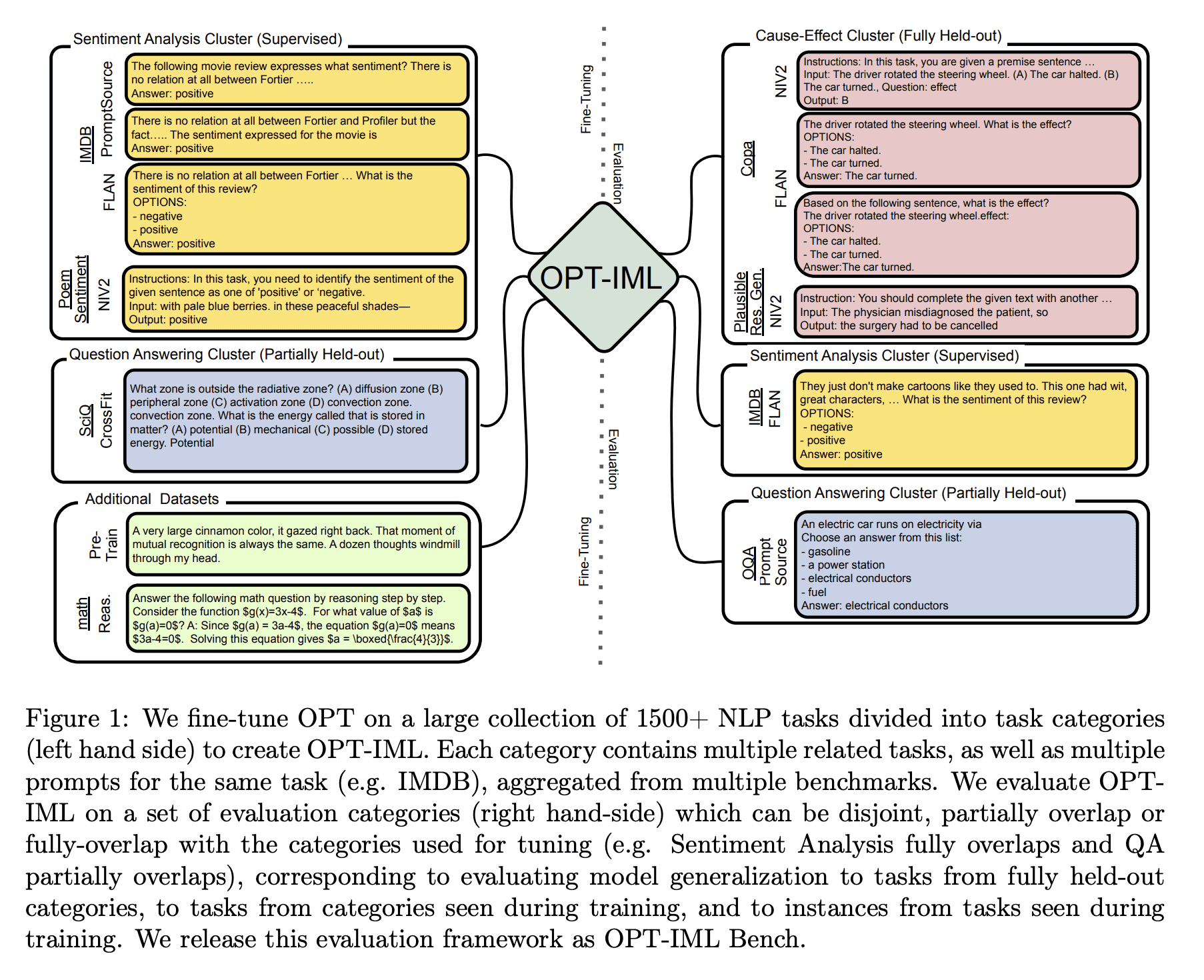
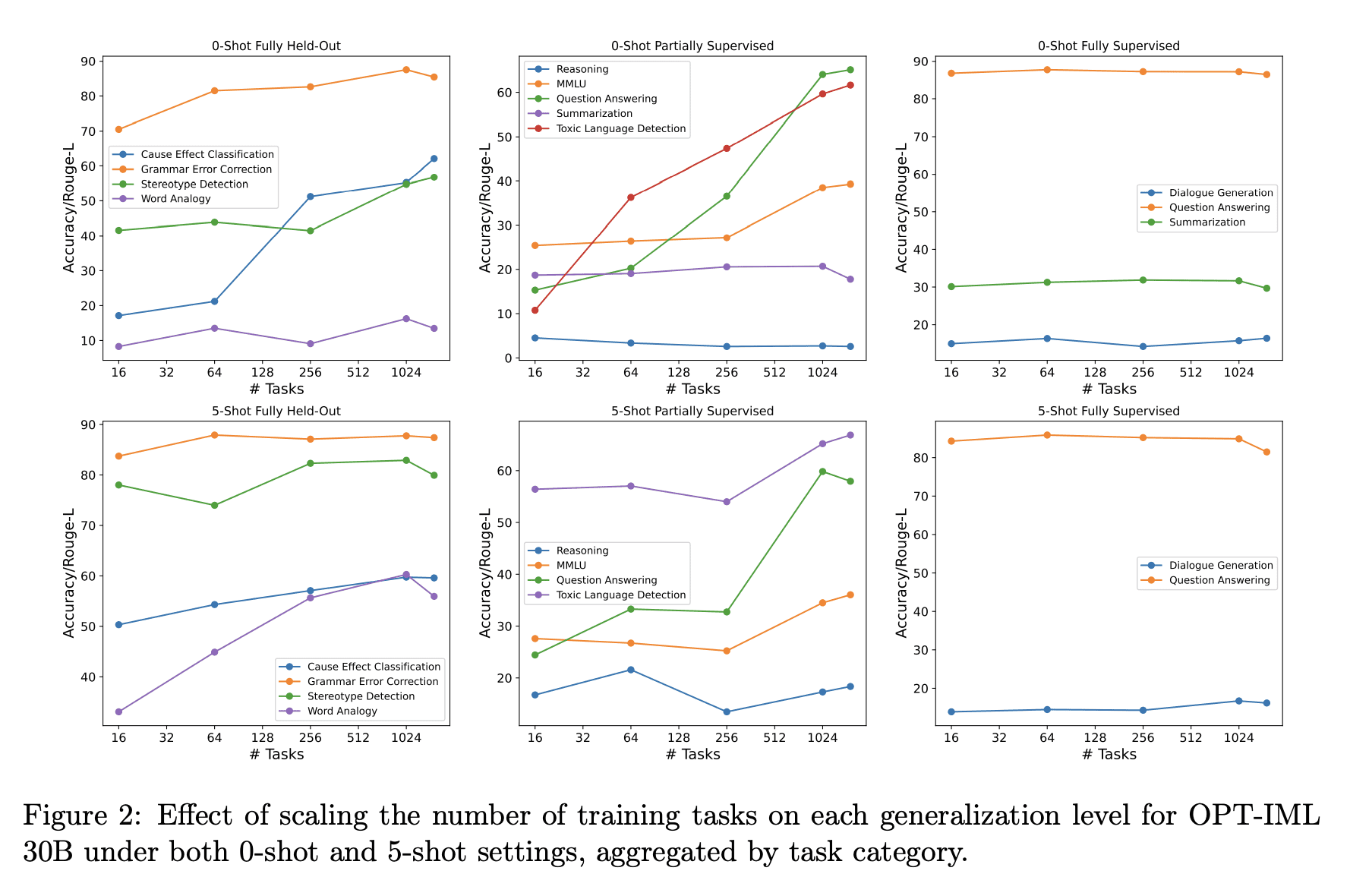
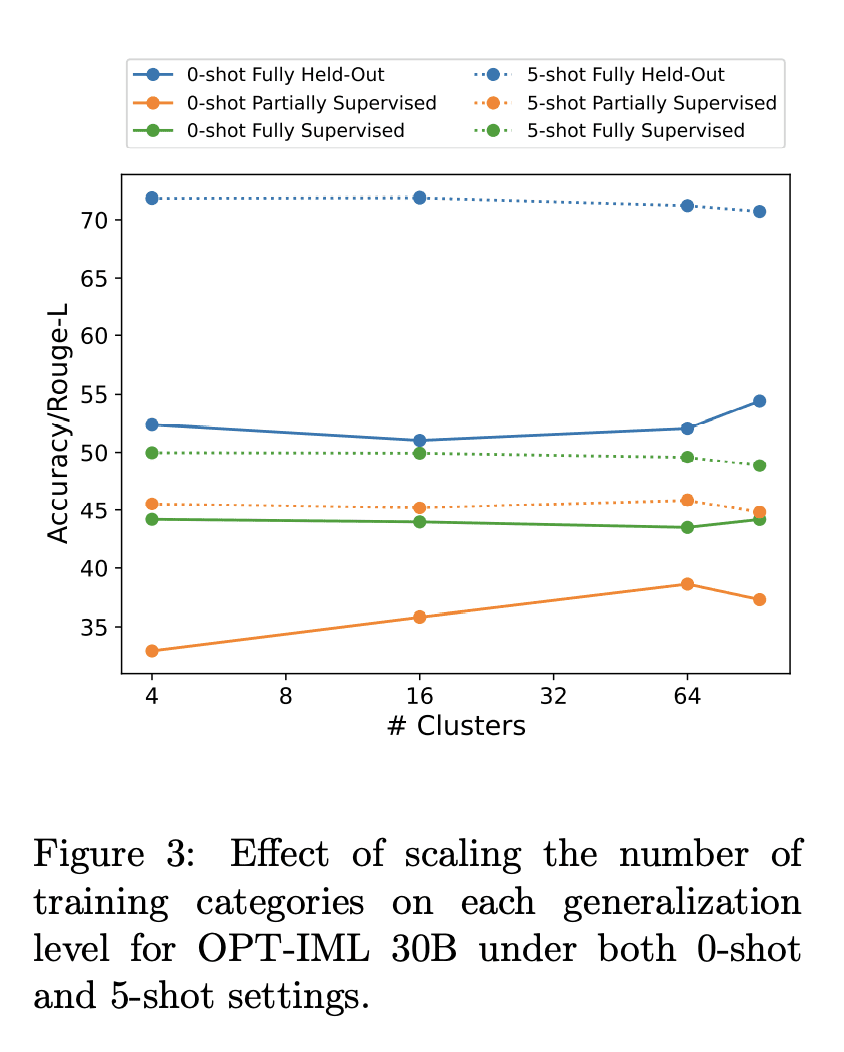
1、[CL] OPT-IML: Scaling Language Model Instruction Meta Learning through the Lens of Generalization
2、[CL] Beyond Contrastive Learning: A Variational Generative Model for Multilingual Retrieval
3、[CL] Ontologically Faithful Generation of Non-Player Character Dialogues
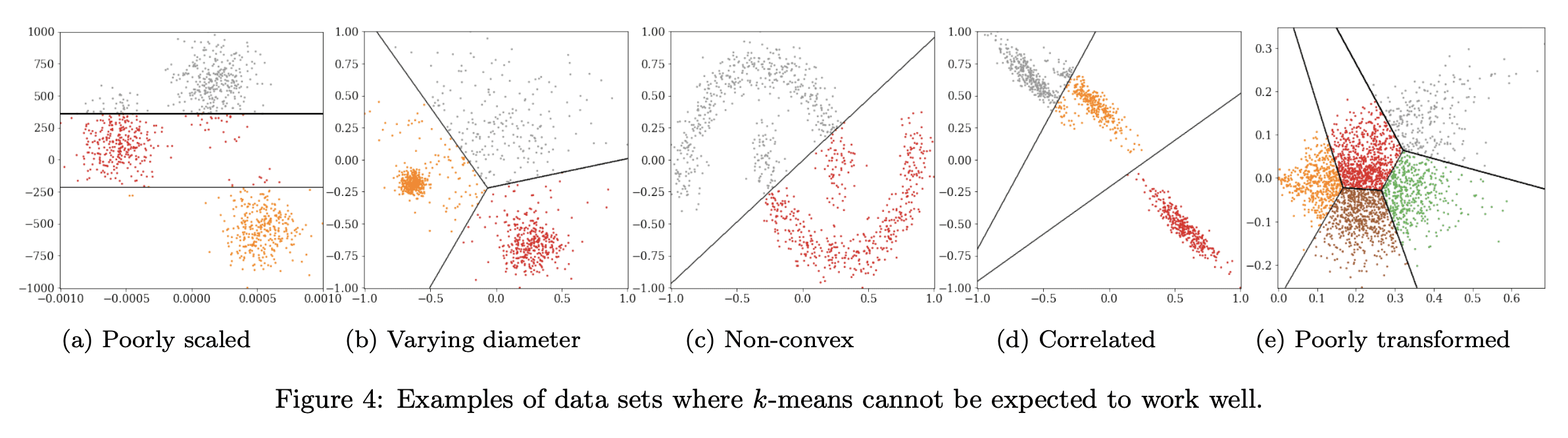
4、[LG] Stop using the elbow criterion for k-means and how to choose the number of clusters instead
5、[CV] Do DALL-E and Flamingo Understand Each Other?
[CV] FFNeRV: Flow-Guided Frame-Wise Neural Representations for Videos
[CV] ClimateNeRF: Physically-based Neural Rendering for Extreme Climate Synthesis
[CV] SparsePose: Sparse-View Camera Pose Regression and Refinement
[CL] SODA: Million-scale Dialogue Distillation with Social Commonsense Contextualization
摘要:泛化视角的语言模型指令元学习扩展、面向多语言检索的变分生成模型、非玩家人物本体忠实对话生成、K-均值聚类应停止使用肘部准则以及替代的聚类数选择方法、文本到图像和图像到文本的统一改进框架、视频流引导框架感知神经表示、面向极端气候合成的基于物理神经渲染、稀疏视图相机姿态回归与细化、基于社会常识背景化的百万级对话蒸馏
1、[CL] OPT-IML: Scaling Language Model Instruction Meta Learning through the Lens of Generalization
S Iyer, X V Lin, R Pasunuru, T Mihaylov, D Simig...
[Meta AI]
OPT-IML: 泛化视角的语言模型指令元学习扩展
要点:
- 收集了一个大型的基于指令微调的基准,包括来自8个数据集集合的2000个NLP任务;
- 建立了指令微调的多方面的权衡和最佳实践;
- 训练发布了基于OPT的OPT-IML 30B和175B指令微调模型。
摘要:
最近的工作表明,在通过指令描述的任务集合上微调大型预训练语言模型,即指令微调,可以改善其对未见任务的零样本和少样本的泛化。然而,对指令微调过程中做出的不同决策的性能权衡的理解有限。这些决定包括指令微调基准的规模和多样性,不同的任务采样策略,有演示和没有演示的微调,使用专门数据集进行推理和对话的训练,最后是微调目标本身。本文描述了在模型大小和基准大小进行扩展时,指令微调决策对下游任务性能的影响。本文创建了OPT-IML基准:2000个NLP任务的指令元学习(IML)的大型基准,从8个现有基准整合到任务类别中,并准备了一个评估框架来衡量三种类型的模型泛化:从完全留出类的任务,到从可见类到留出任务,再到从可见任务中留出实例。通过该框架的视角,本文首先提出适用于OPT-30B的指令微调决策的见解,并进一步利用这些见解来训练OPT-IML 30B和175B,它们是OPT的指令微调版本。OPT-IML在具有不同任务和输入格式(PromptSource、FLAN、Super-NaturalInstructions和UnifiedSKG)的四个不同评估基准上展示了两种规模的所有三个泛化能力。它不仅在所有基准上的表现都明显优于OPT,而且与在每个特定基准上微调的现有模型具有高度竞争力。在两个规模上发布OPT-IML,以及OPT-IML Bench评估框架。
Recent work has shown that fine-tuning large pre-trained language models on a collection of tasks described via instructions, a.k.a. instruction-tuning, improves their zero and few-shot generalization to unseen tasks. However, there is a limited understanding of the performance trade-offs of different decisions made during the instruction-tuning process. These decisions include the scale and diversity of the instruction-tuning benchmark, different task sampling strategies, fine-tuning with and without demonstrations, training using specialized datasets for reasoning and dialogue, and finally, the fine-tuning objectives themselves. In this paper, we characterize the effect of instruction-tuning decisions on downstream task performance when scaling both model and benchmark sizes. To this end, we create OPT-IML Bench: a large benchmark for Instruction Meta-Learning (IML) of 2000 NLP tasks consolidated into task categories from 8 existing benchmarks, and prepare an evaluation framework to measure three types of model generalizations: to tasks from fully held-out categories, to held-out tasks from seen categories, and to held-out instances from seen tasks. Through the lens of this framework, we first present insights about instruction-tuning decisions as applied to OPT-30B and further exploit these insights to train OPT-IML 30B and 175B, which are instruction-tuned versions of OPT. OPT-IML demonstrates all three generalization abilities at both scales on four different evaluation benchmarks with diverse tasks and input formats -- PromptSource, FLAN, Super-NaturalInstructions, and UnifiedSKG. Not only does it significantly outperform OPT on all benchmarks but is also highly competitive with existing models fine-tuned on each specific benchmark. We release OPT-IML at both scales, together with the OPT-IML Bench evaluation framework.
https://
arxiv.org/abs/2212.1201
7

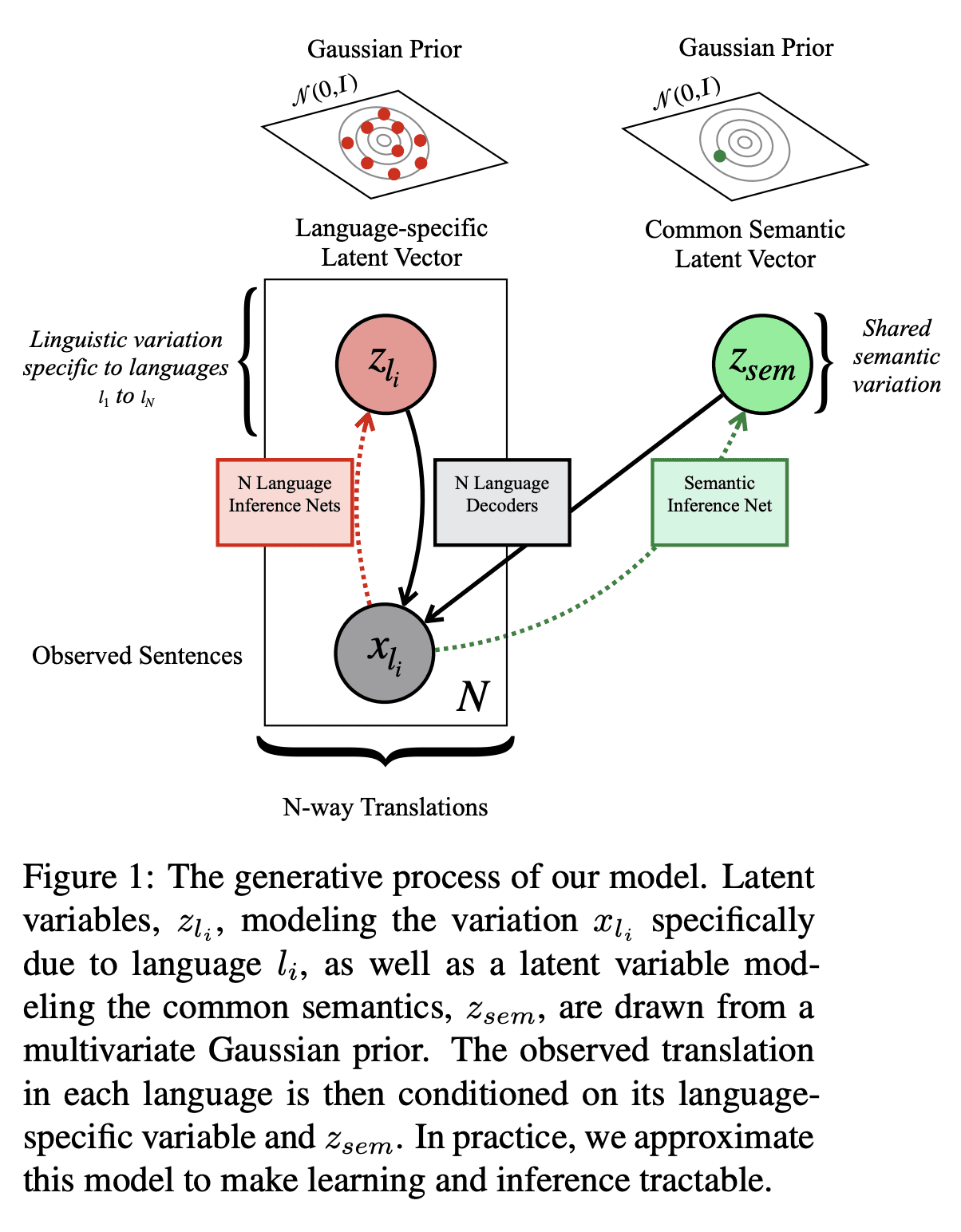
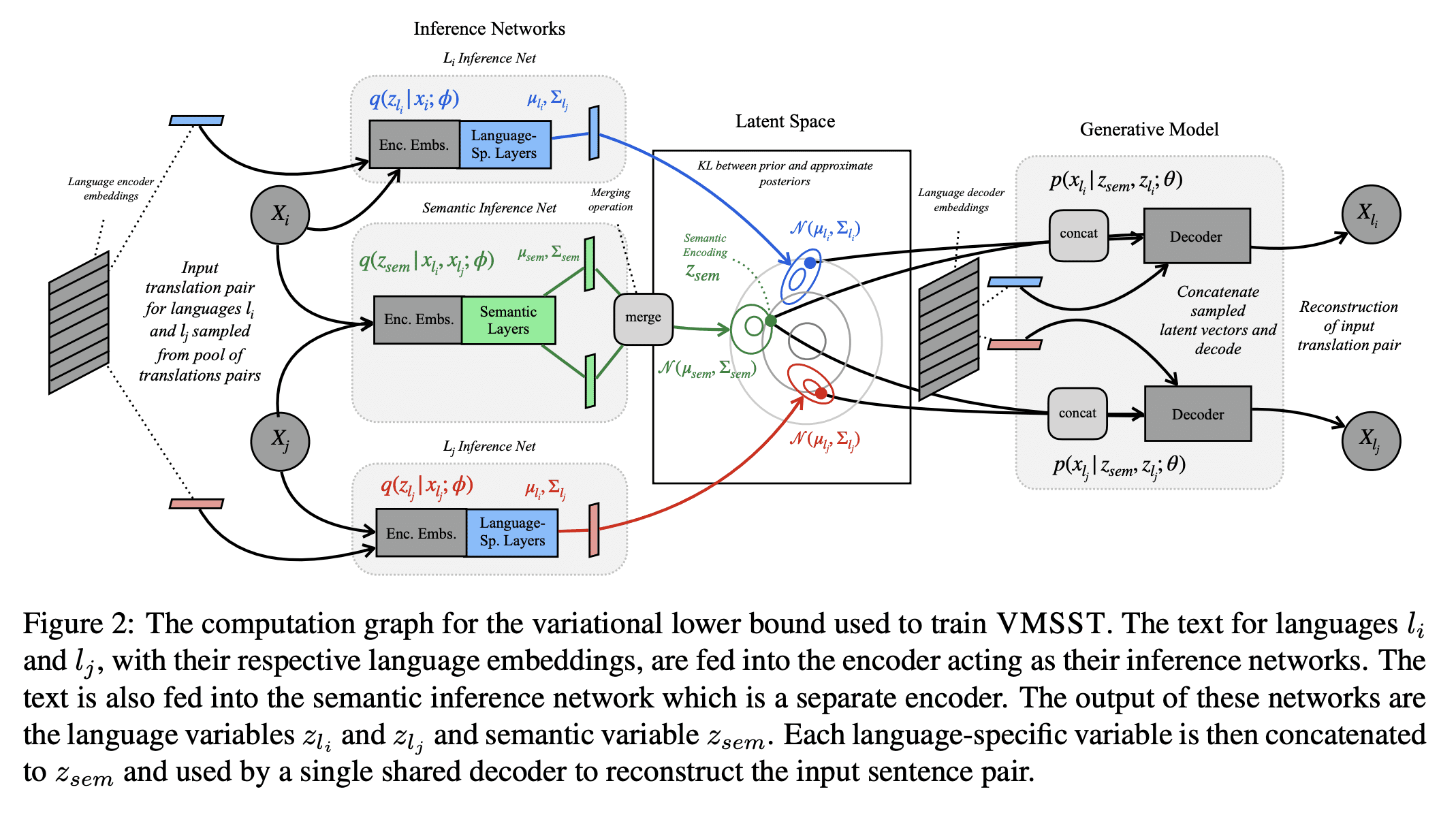
2、[CL] Beyond Contrastive Learning: A Variational Generative Model for Multilingual Retrieval
J Wieting, J H. Clark, W W. Cohen, G Neubig...
[Google Research & CMU & University of California San Diego, San Diego]
超越对比学习:面向多语言检索的变分生成模型
要点:
- 提出一种生成模型,用于学习多语言文本嵌入,可用于检索或句对评分;
- 该模型有效鼓励了这种多语言环境中的源分离,将翻译间共享的语义信息与文体或语言特定的变化区分开来;
- 提出VMSST,一种生成式大规模多语言文本嵌入模型,旨在将语义信息与语言特定信息分离。
摘要:
对比学习已成功用于检索语义对齐的句子,但它通常需要大的批量大小或仔细的工程才能正常工作。本文提出一种用于学习多语言文本嵌入的生成模型,可用于检索或句对评分。该模型对N种语言的并行数据进行操作,并通过本文提出的近似值,有效地鼓励在这种多语言环境中进行源分离,将翻译之间共享的语义信息与文体或特定语言变化分开。本文在学习多语种文本嵌入的对比和基于代际的方法之间进行了仔细的大规模比较,尽管这些方法很受欢迎,但这种比较尚未尽得到深入理解。本文在一系列任务上评估了这种方法,包括语义相似性、双文挖掘和跨语言问题检索——最后一项任务是本文提出的。总体而言,本文提出的变分多语言源分离Transformer(VMSST)模型在这些任务上的表现优于强大的对比和生成基线。
Contrastive learning has been successfully used for retrieval of semantically aligned sentences, but it often requires large batch sizes or careful engineering to work well. In this paper, we instead propose a generative model for learning multilingual text embeddings which can be used to retrieve or score sentence pairs. Our model operates on parallel data in N languages and, through an approximation we introduce, efficiently encourages source separation in this multilingual setting, separating semantic information that is shared between translations from stylistic or language-specific variation. We show careful large-scale comparisons between contrastive and generation-based approaches for learning multilingual text embeddings, a comparison that has not been done to the best of our knowledge despite the popularity of these approaches. We evaluate this method on a suite of tasks including semantic similarity, bitext mining, and cross-lingual question retrieval -- the last of which we introduce in this paper. Overall, our Variational Multilingual Source-Separation Transformer (VMSST) model outperforms both a strong contrastive and generative baseline on these tasks.
https://
arxiv.org/abs/2212.1072
6

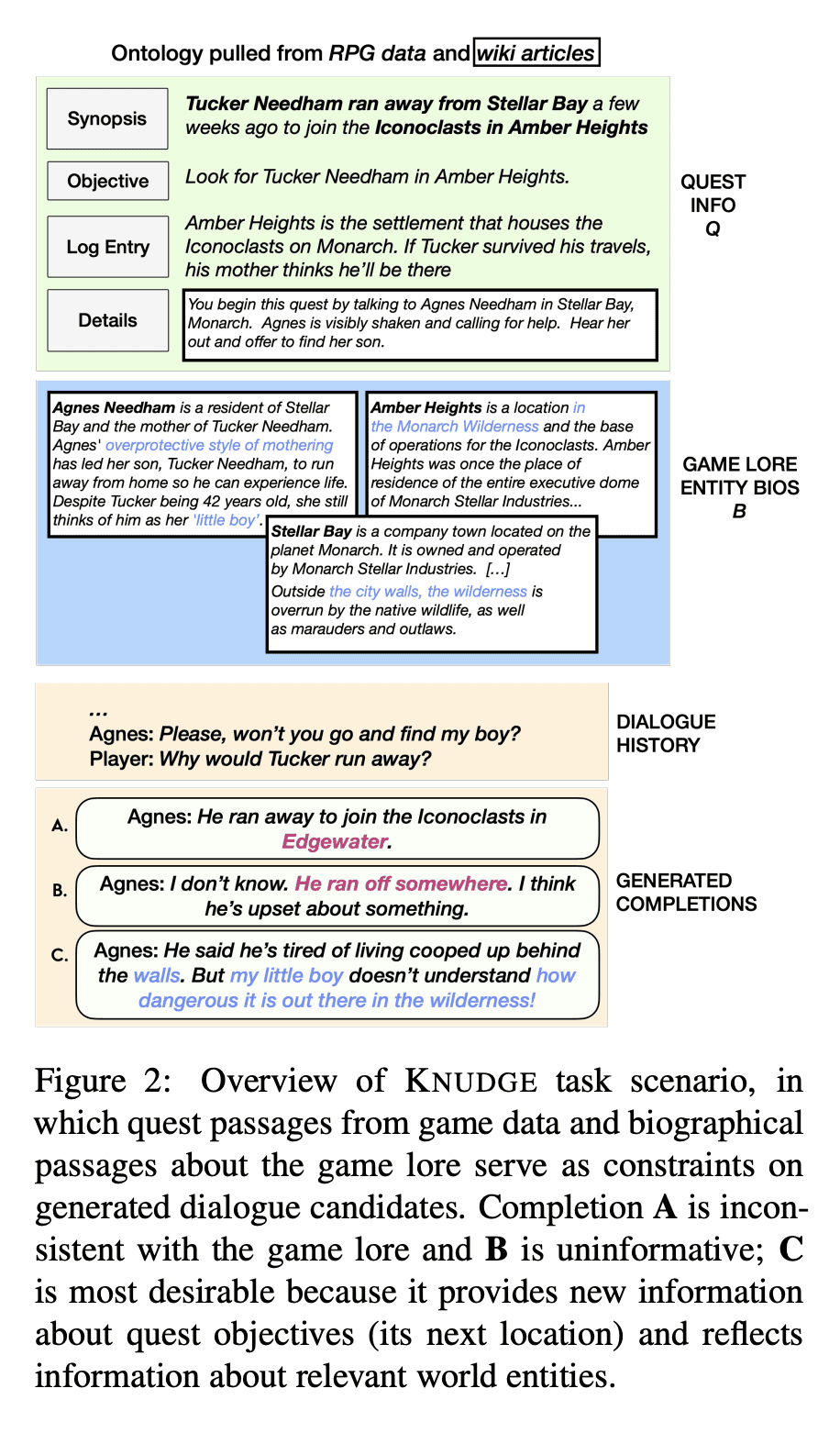
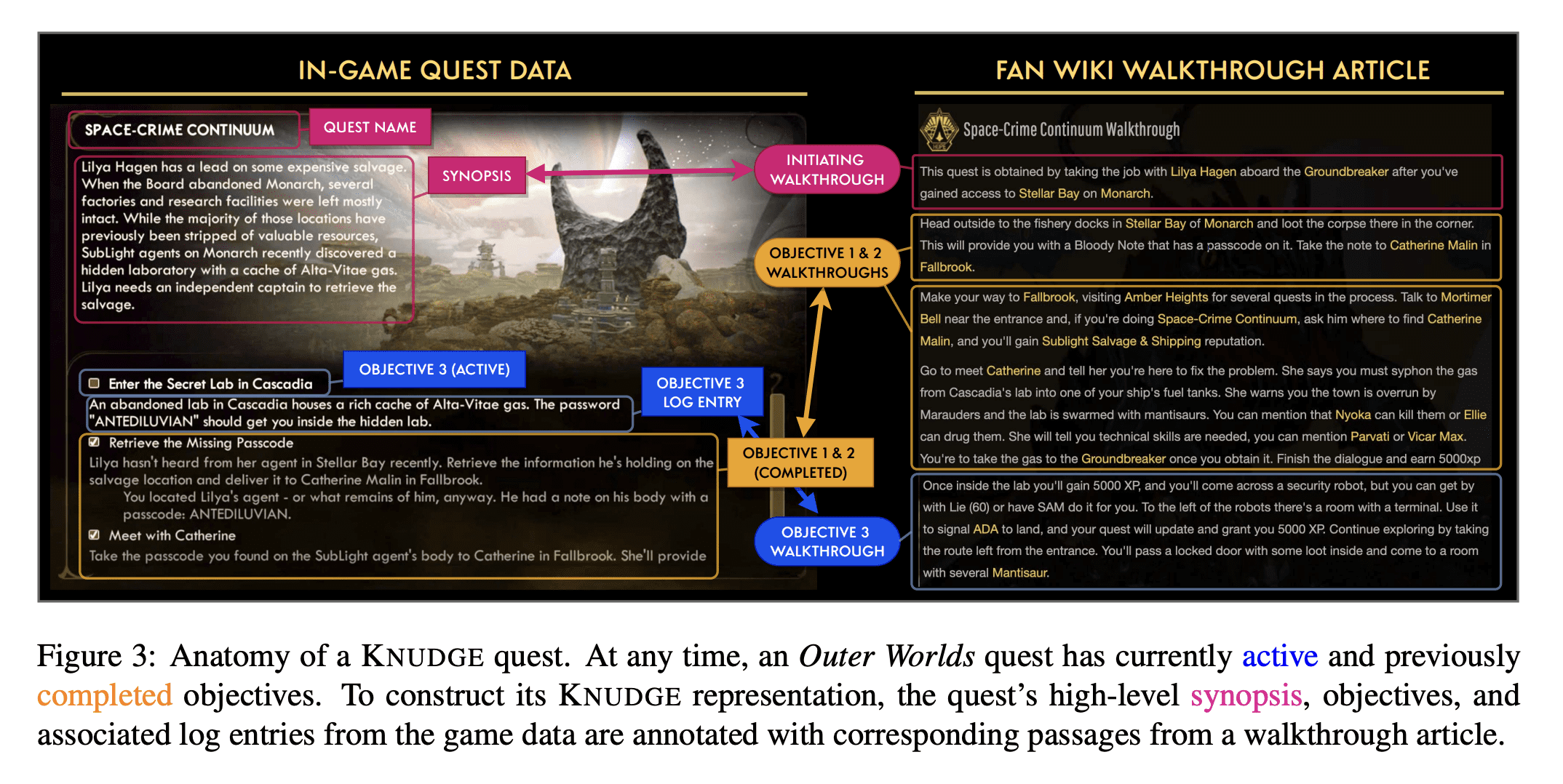
3、[CL] Ontologically Faithful Generation of Non-Player Character Dialogues
N Weir, R Thomas, R D'Amore, K Hill, B V Durme...
[Johns Hopkins University & Microsoft Semantic Machines & Microsoft Gaming]
非玩家人物本体忠实对话生成
要点:
- 提出KNUDGE(知识受限用户-NPC对话生成)任务,根据自然语言段落中提供的游戏知识和任务相关知识规范生成对话树;
- 构建KNUDGE数据集,由Obsidian Entertainment的《The Outer Worlds》游戏数据提供的45个副任务对话树组成,每个树最多可达到100个角色发言节点,包含复杂的分支和循环;
- 一系列基于神经语言模型的知识约束对话编写基线,表明约束信息可以合理地反映在真实生成的树中。
摘要:
本文提出一种基于流行电子游戏环境的语言生成任务。KNUDGE(知识受限用户-NPC对话生成)涉及生成以自然语言段落中捕获的本体为条件的对话树,提供任务和实体规范。KNUDGE是由直接从Obsidian Entertainment的《The Outer Worlds》的游戏数据中提取的支线任务对话构建的,带来了现实世界的复杂性:(1) 对话是分枝树,而不是线性话语链;(2) 话语必须忠实于游戏背景——角色人物、背景故事和实体关系;以及 (3) 对话必须向人类玩家准确揭示与任务相关的新细节。本文报告了监督和上下文学习技术的结果,发现未来在创建逼真的游戏质量对话方面有很大的空间。
We introduce a language generation task grounded in a popular video game environment. KNUDGE (KNowledge Constrained User-NPC Dialogue GEneration) involves generating dialogue trees conditioned on an ontology captured in natural language passages providing quest and entity specifications. KNUDGE is constructed from side quest dialogues drawn directly from game data of Obsidian Entertainment's The Outer Worlds, leading to real-world complexities in generation: (1) dialogues are branching trees as opposed to linear chains of utterances; (2) utterances must remain faithful to the game lore--character personas, backstories, and entity relationships; and (3) a dialogue must accurately reveal new quest-related details to the human player. We report results for supervised and in-context learning techniques, finding there is significant room for future work on creating realistic game-quality dialogues.
https://
arxiv.org/abs/2212.1061
8


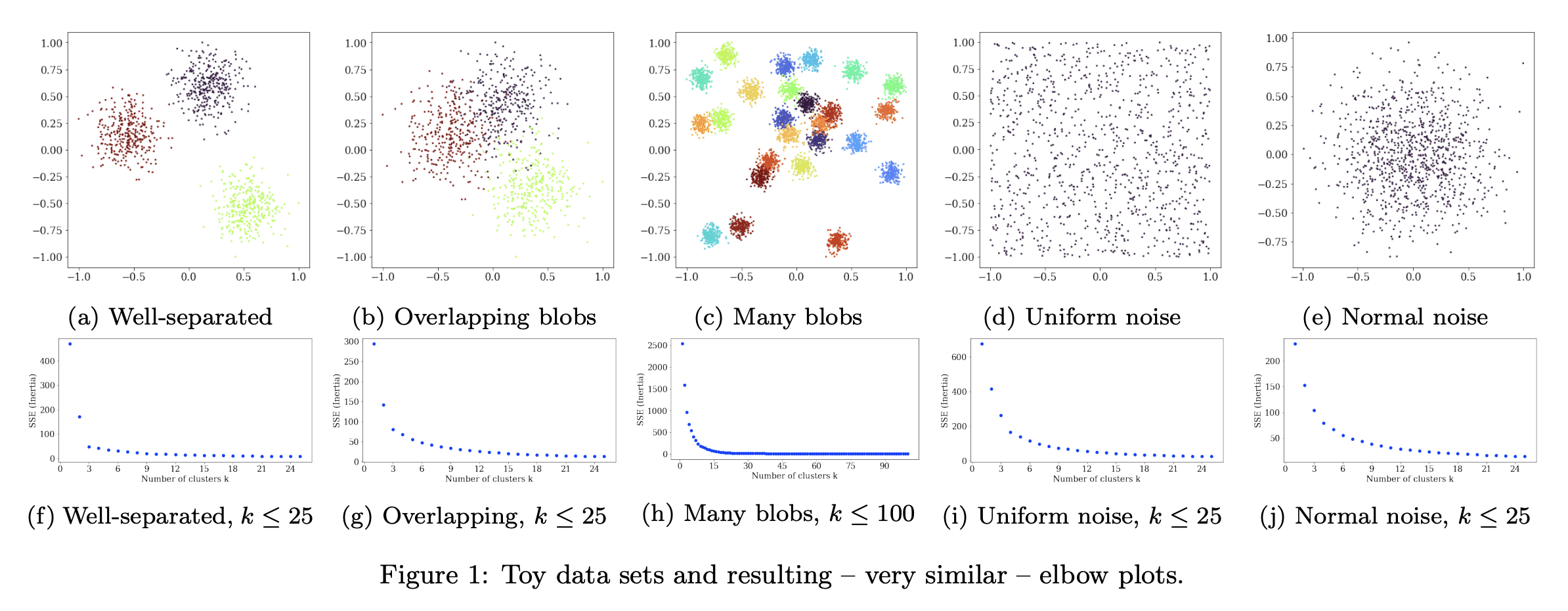
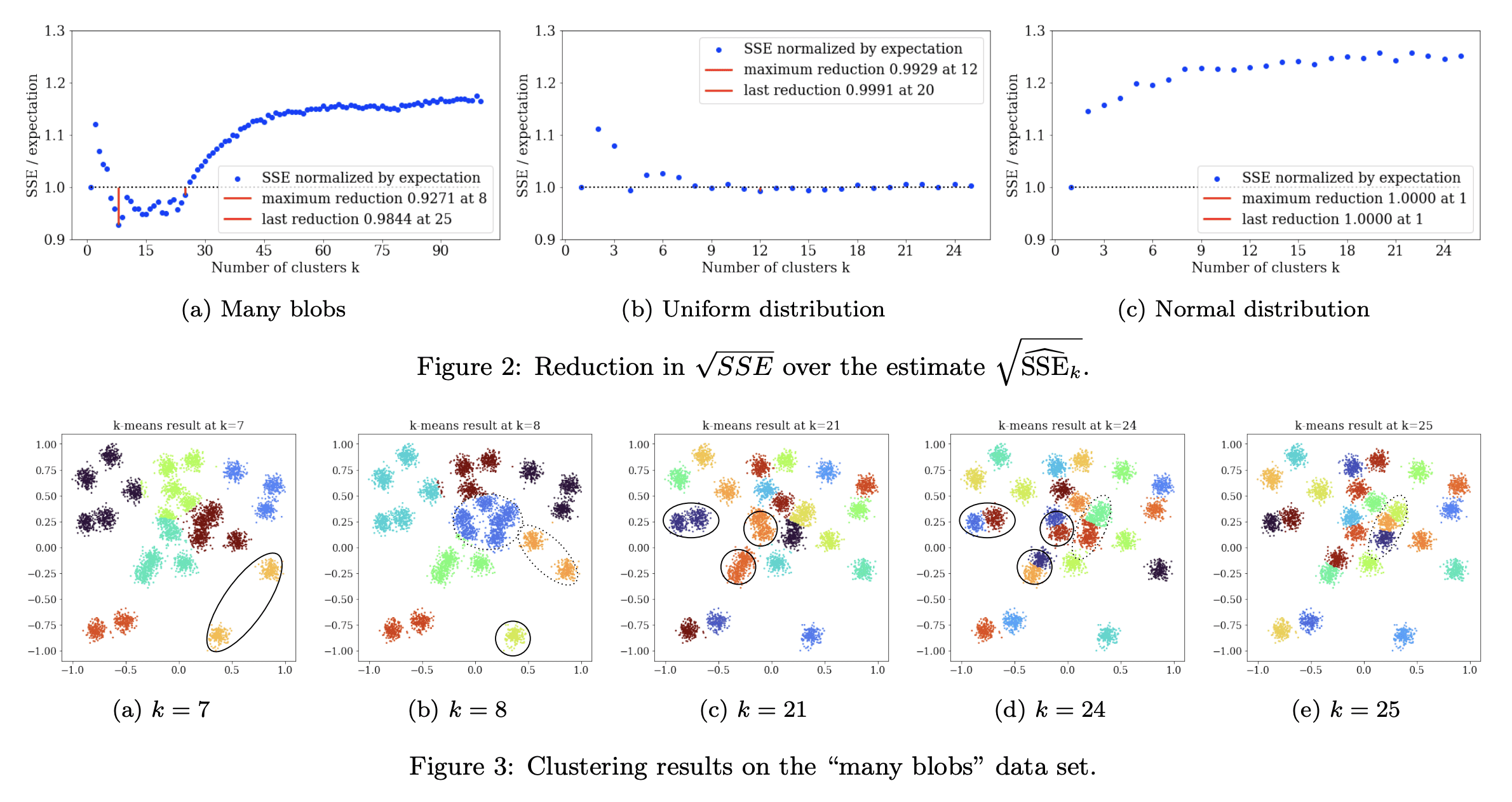
4、[LG] Stop using the elbow criterion for k-means and how to choose the number of clusters instead
E Schubert
[TU Dortmund University]
K-均值聚类应停止使用肘部准则以及替代的聚类数选择方法
要点:
- 对K-均值聚类来说,肘部法不可靠,严重缺乏理论支持,应该用更好的替代方法,如方差比率准则(VRC)、贝叶斯信息准则(BIC)或间隙统计;
- 教育工作者应该解释更好的替代方法,数据科学家不应依赖评估措施告诉他们什么是“最好的”;
- 科研论文的评审者应该拒绝使用肘部法选择“最佳”K值的结论。
摘要:
日常使用K均值聚类时的一个主要挑战是如何选择参数K,即聚类的数量。本文指出,很容易从常见的启发式“肘部法”中得出糟糕的结论。长期以来,文献中已经提出了更好的替代方法,本文想提请注意其中一些易于使用的选择,它们通常表现更好。本文呼吁完全停止使用肘部法,因为它严重缺乏理论支持,希望鼓励教育工作者讨论这种方法的问题——如果在课堂上介绍它的话——转而教授替代方案,而研究人员和评审人员应该拒绝从肘部法中得出的结论。
A major challenge when using k-means clustering often is how to choose the parameter k, the number of clusters. In this letter, we want to point out that it is very easy to draw poor conclusions from a common heuristic, the "elbow method". Better alternatives have been known in literature for a long time, and we want to draw attention to some of these easy to use options, that often perform better. This letter is a call to stop using the elbow method altogether, because it severely lacks theoretic support, and we want to encourage educators to discuss the problems of the method -- if introducing it in class at all -- and teach alternatives instead, while researchers and reviewers should reject conclusions drawn from the elbow method.
https://
arxiv.org/abs/2212.1218
9

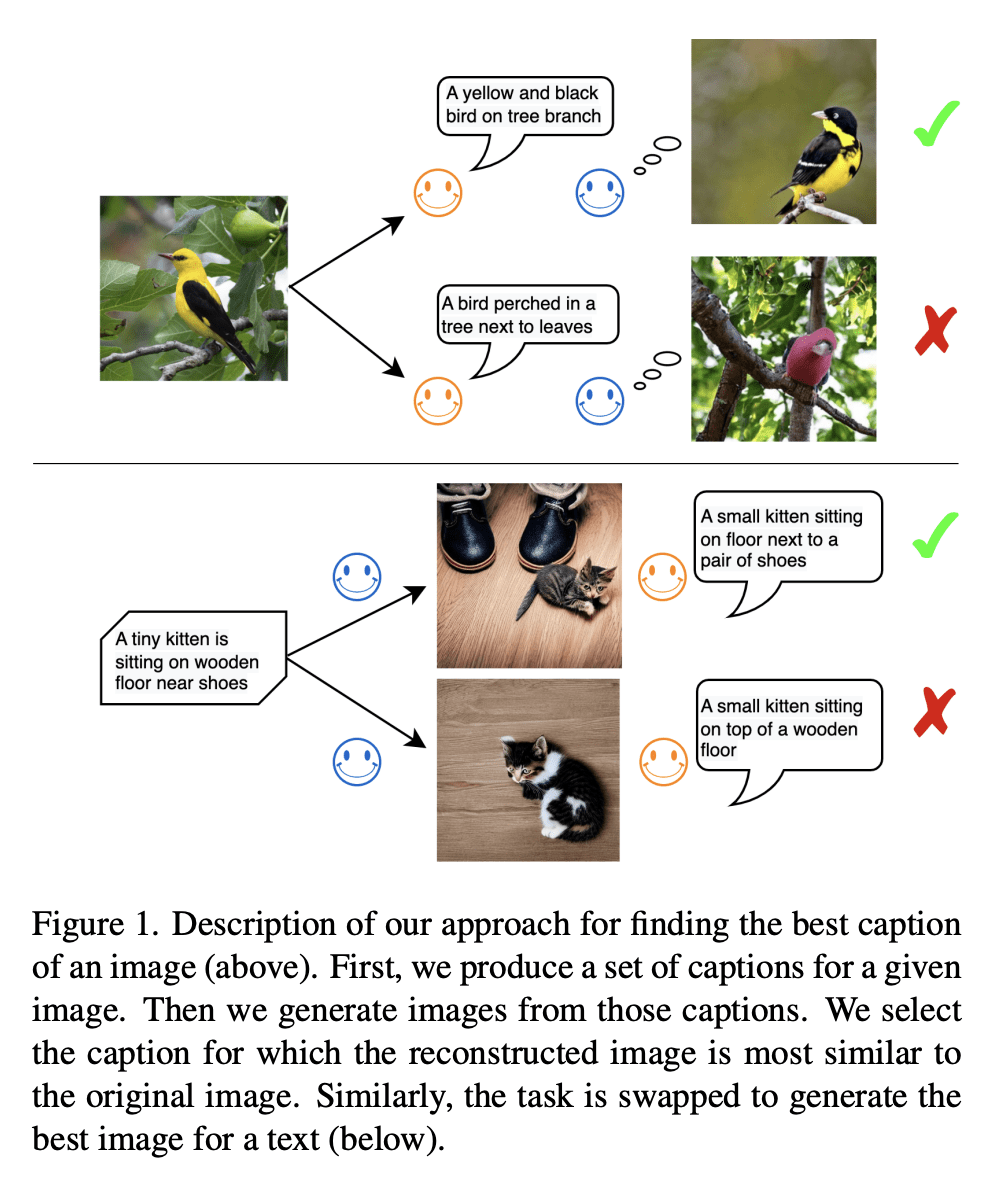
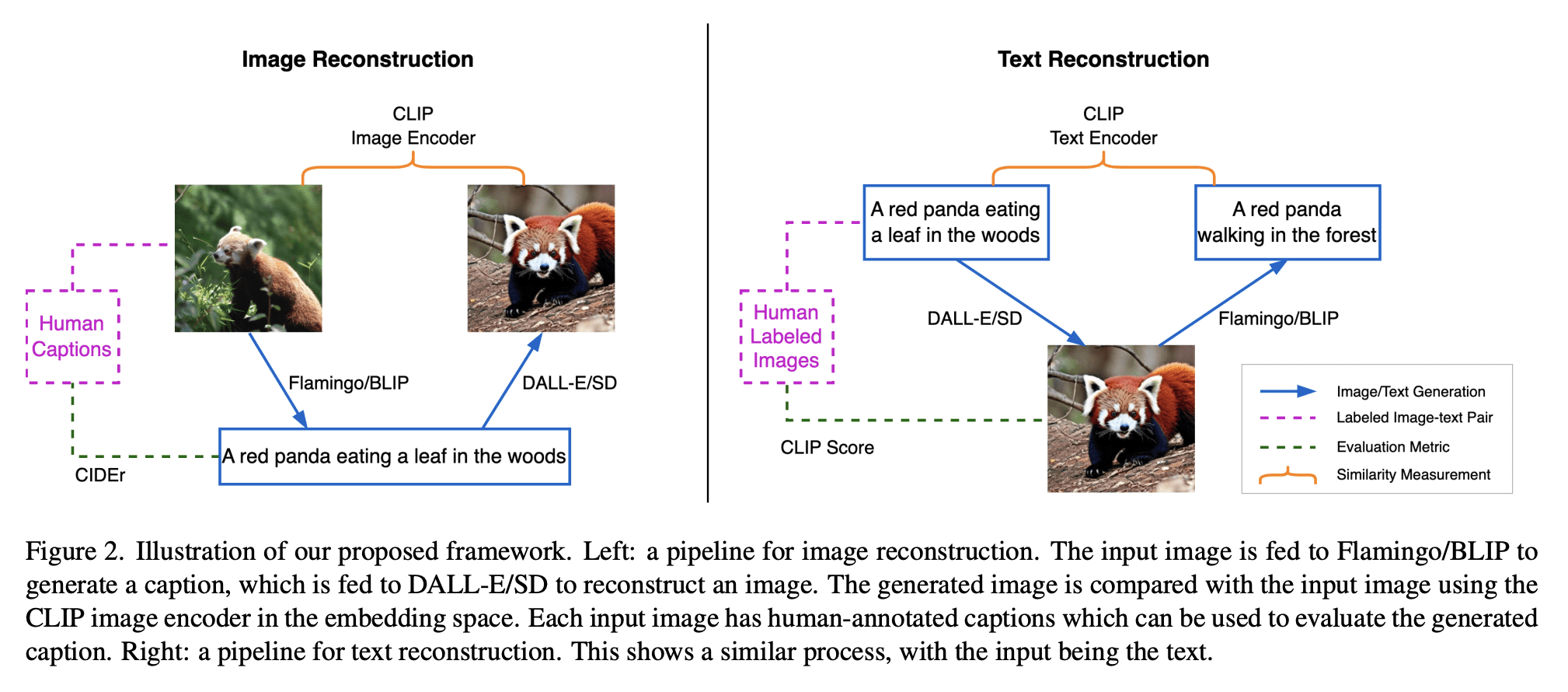
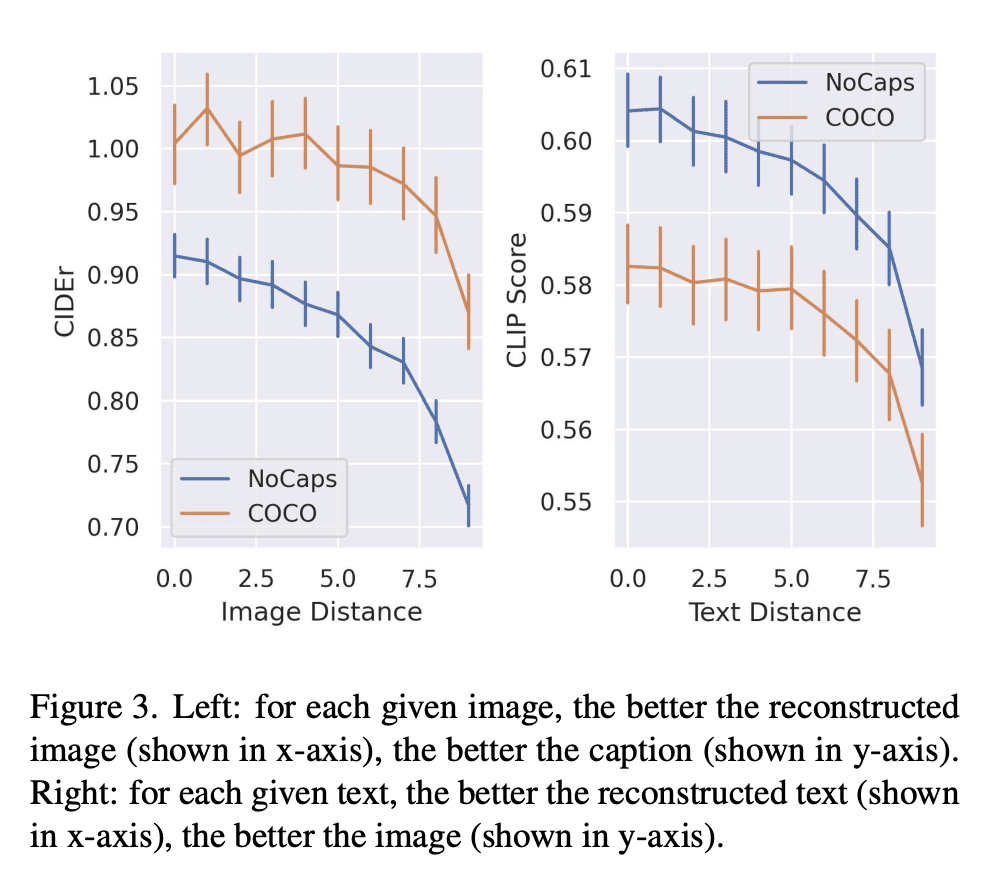
5、[CV] Do DALL-E and Flamingo Understand Each Other?
H Li, J Gu, R Koner, S Sharifzadeh, V Tresp
[LMU Munich & University of Oxford]
文本到图像和图像到文本的统一改进框架
要点:
- 最佳的图像描述是导致最佳重建原图像的描述;
- 最佳的图像是导致最佳重建原文本的图像;
- 提出一种有效的方法来改进基于文本到图像模型知识的核采样。
摘要: 多模态研究的一个主要目标是提高机器对图像和文本的理解。任务包括图像描述、文本到图像生成和视觉语言表示学习。到目前为止,研究的重点是图像和文本间的关系。例如,图像描述模型试图理解图像的语义,然后将其转换为文本。一个重要的问题是:哪种描述最能反映对图像内容的深刻理解?同样,给定一个文本,可以呈现文本语义的最佳图像是什么?本文认为给定图像的最佳文本或描述是能生成与该图像最相似的图像的文本。同样,给定文本的最佳图像是导致该文本重建的图像,生成文本最好与原始文本对齐。为此,本文提出了一个统一的框架,其中包括文本到图像生成模型和图像到文本生成模型。广泛的实验验证了该方法。
A major goal of multimodal research is to improve machine understanding of images and text. Tasks include image captioning, text-to-image generation, and vision-language representation learning. So far, research has focused on the relationships between images and text. For example, captioning models attempt to understand the semantics of images which are then transformed into text. An important question is: which annotation reflects best a deep understanding of image content? Similarly, given a text, what is the best image that can present the semantics of the text? In this work, we argue that the best text or caption for a given image is the text which would generate the image which is the most similar to that image. Likewise, the best image for a given text is the image that results in the caption which is best aligned with the original text. To this end, we propose a unified framework that includes both a text-to-image generative model and an image-to-text generative model. Extensive experiments validate our approach.
https://
arxiv.org/abs/2212.1224
9

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
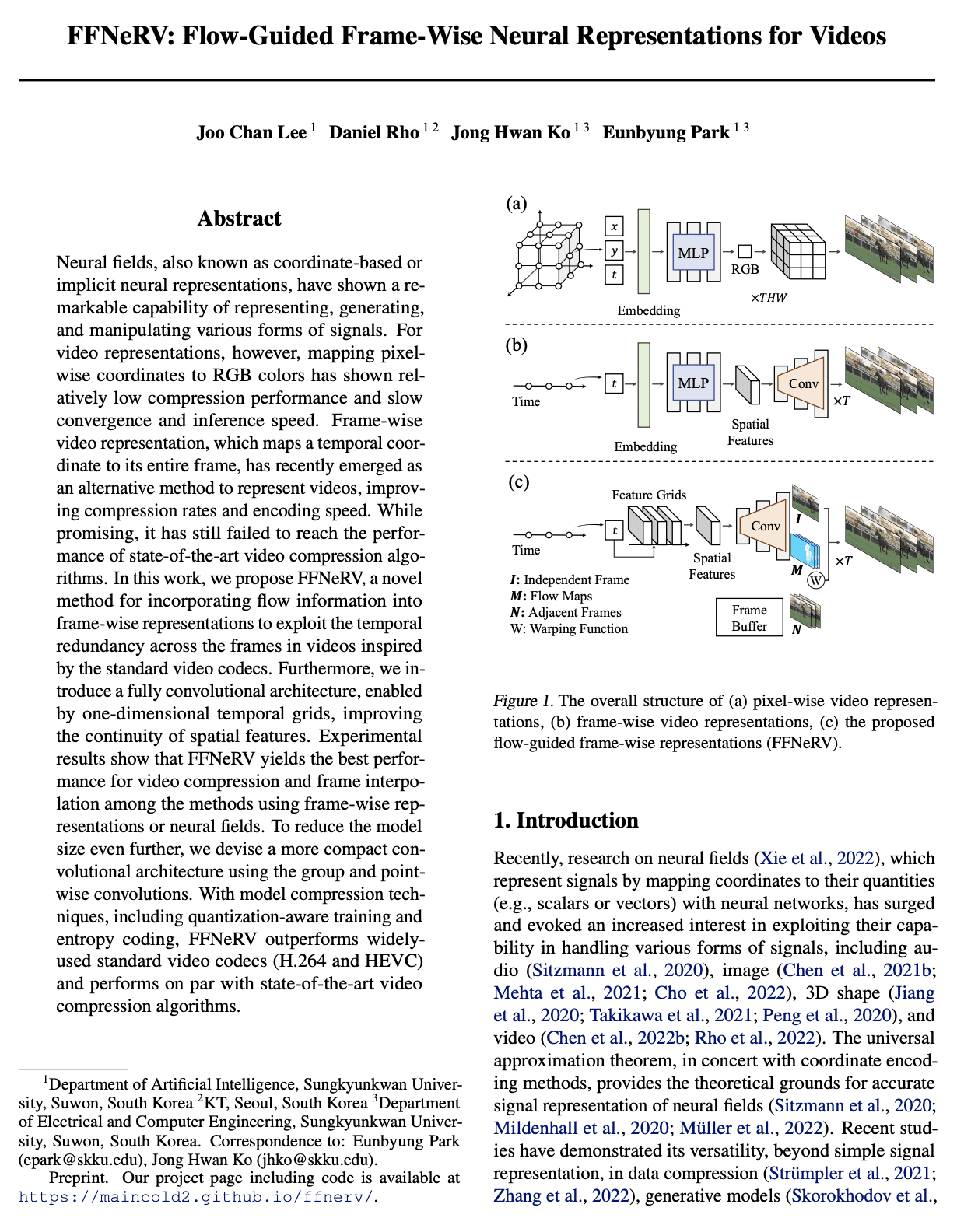
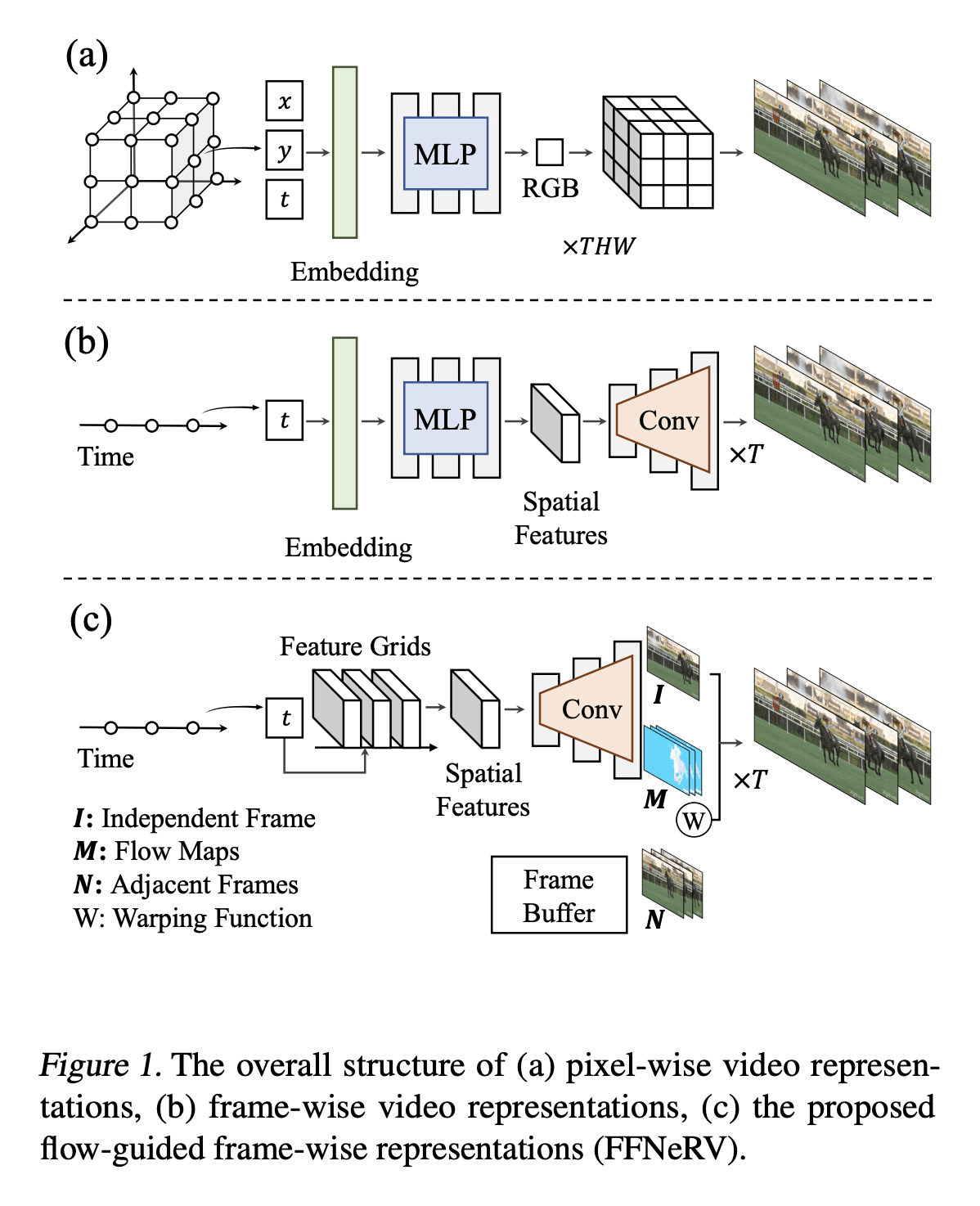
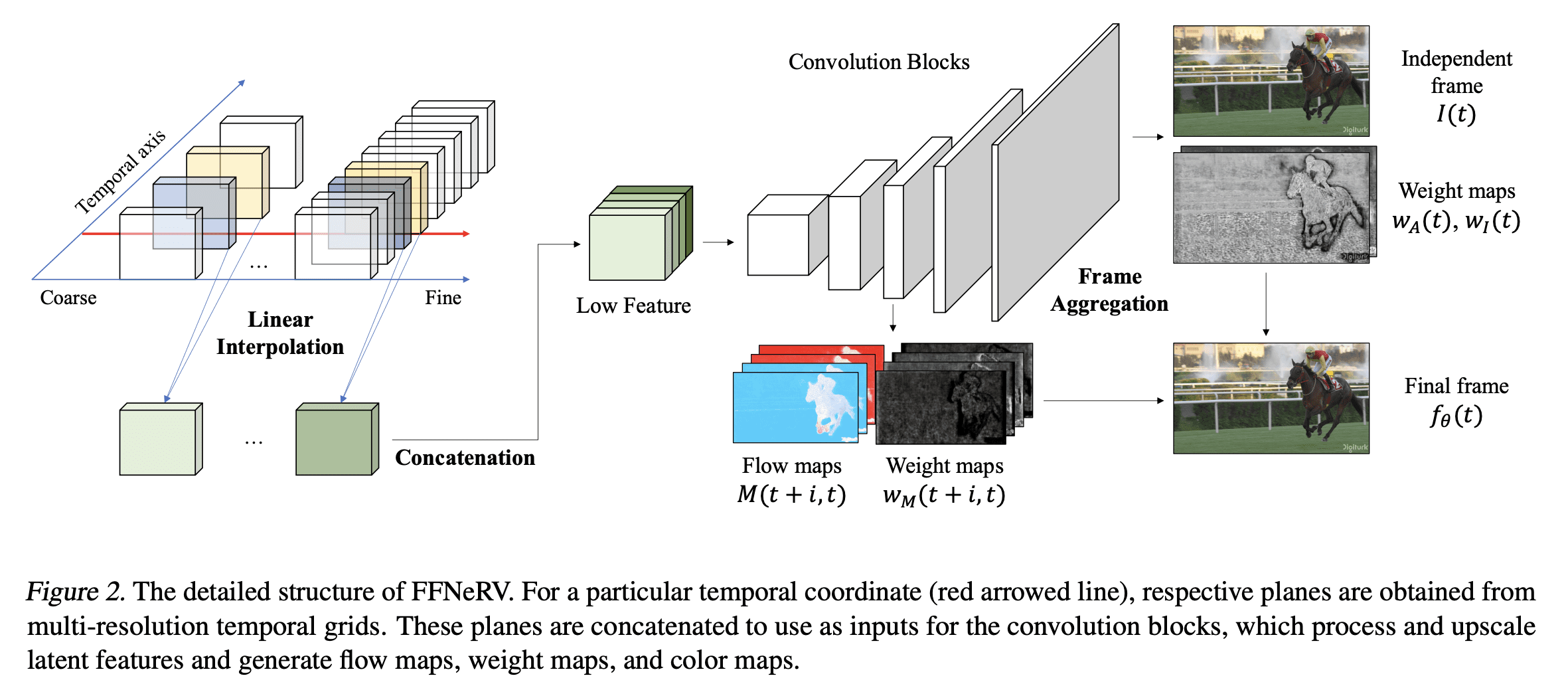
[CV] FFNeRV: Flow-Guided Frame-Wise Neural Representations for Videos
J C Lee, D Rho, J H Ko, E Park
[Sungkyunkwan University]
FFNeRV: 视频流引导框架感知神经表示
要点:
- 相对于像素坐标映射,帧级视频表示正显示出更高的压缩比和编码速度;
- FFNeRV是一种将流信息合并到帧级表示中以提高视频压缩性能的新方法;
- 通过模型压缩技术,FFNeRV与最先进的视频压缩算法表现相当。
https://
arxiv.org/abs/2212.1229
4
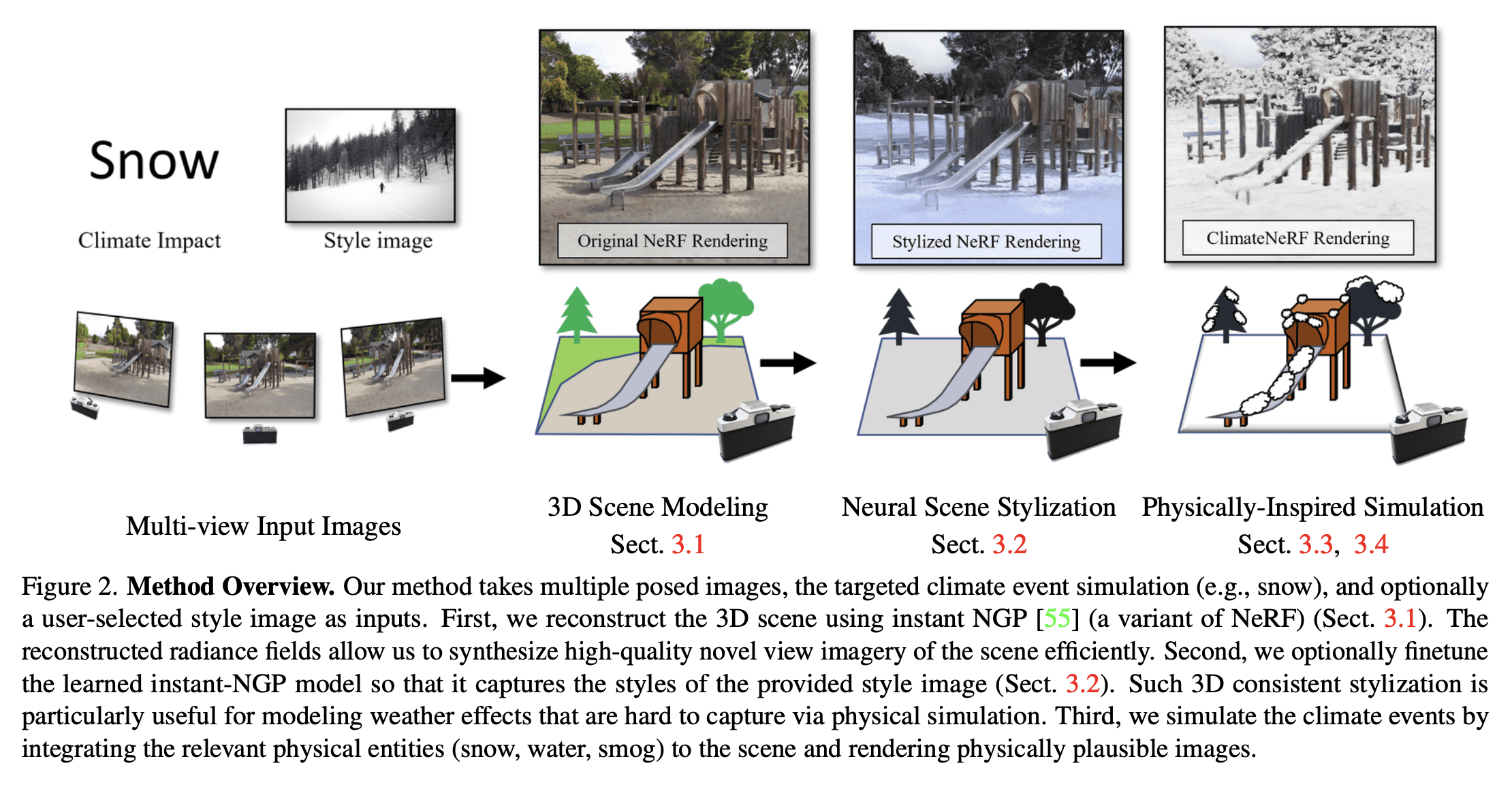
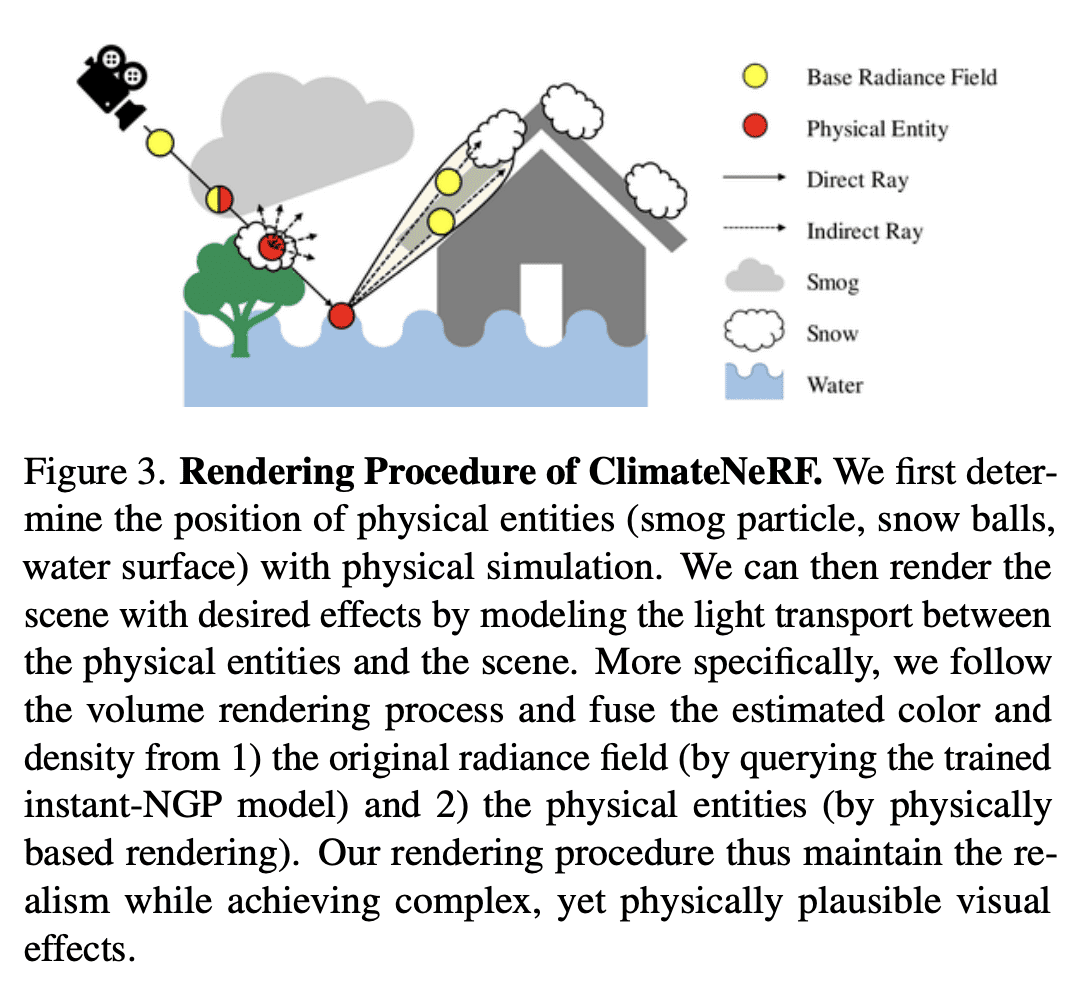
[CV] ClimateNeRF: Physically-based Neural Rendering for Extreme Climate Synthesis
Y Li, Z Lin, D Forsyth, J Huang, S Wang
[University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign & University of Maryland]
ClimateNeRF: 面向极端气候合成的基于物理神经渲染
要点:
- 物理模拟可以准确预测天气效应,而神经辐射场可以生成高质量的场景模型;
- 提出ClimateNeRF,一种新的NeRF编辑框架,可以将物理模拟与NeRF场景模型融合在一起,生成这些场景中气候变化的物理现象结果,包括烟雾、洪水和雪等。
- ClimateNeRF在帮助提高社区气候变化意识和提高对恶劣天气条件的无人驾驶鲁棒性方面具有潜力。
https://
arxiv.org/abs/2211.1322
6


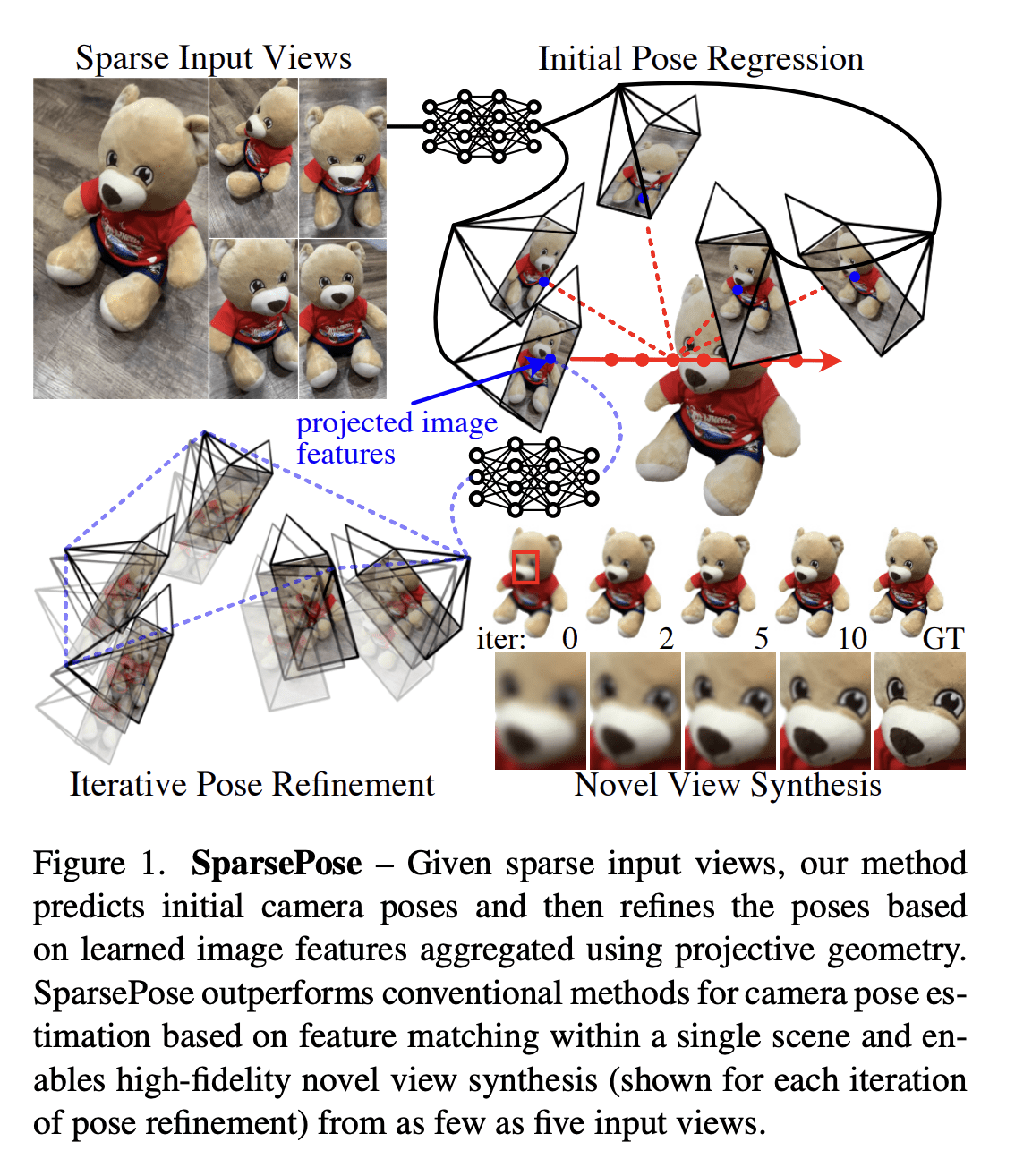
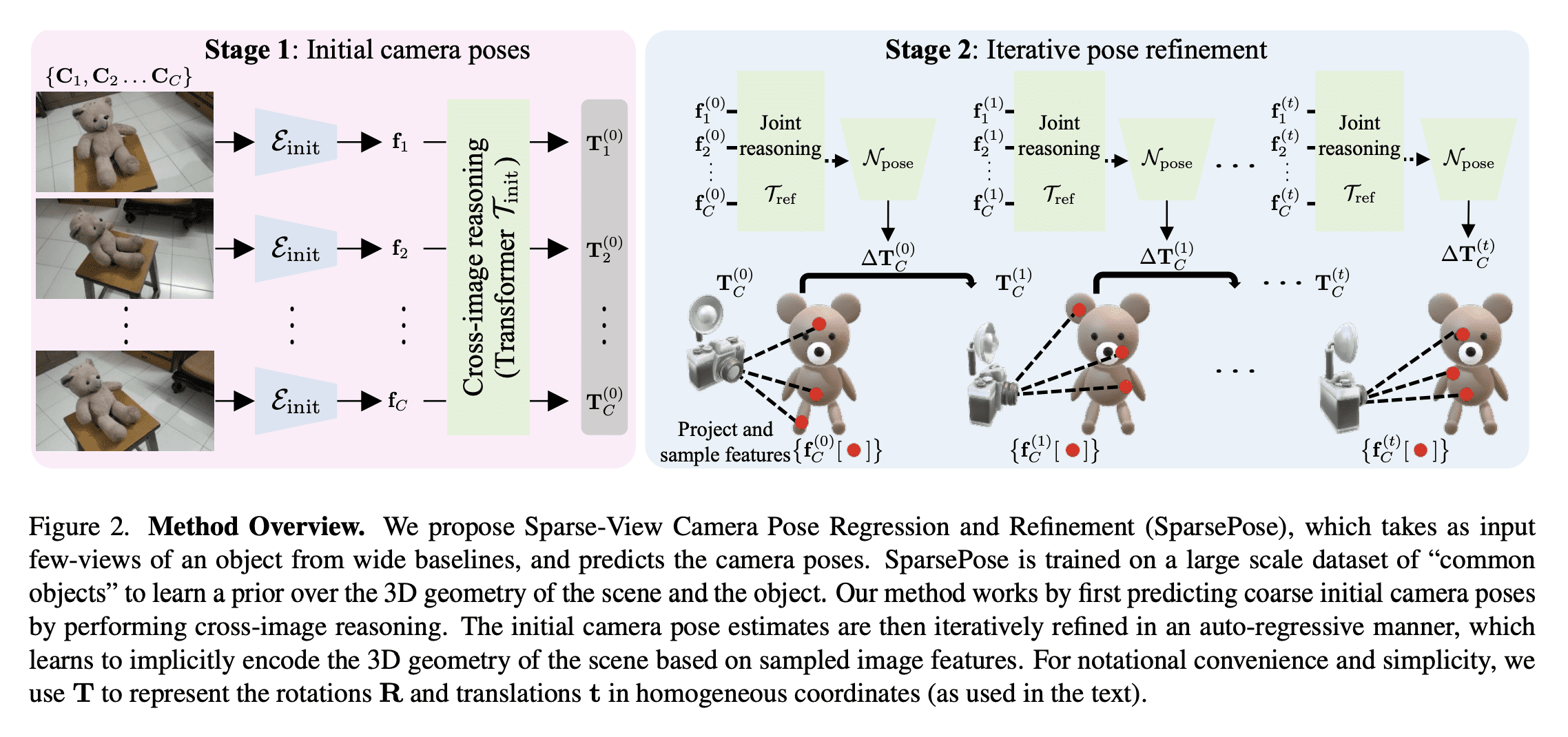
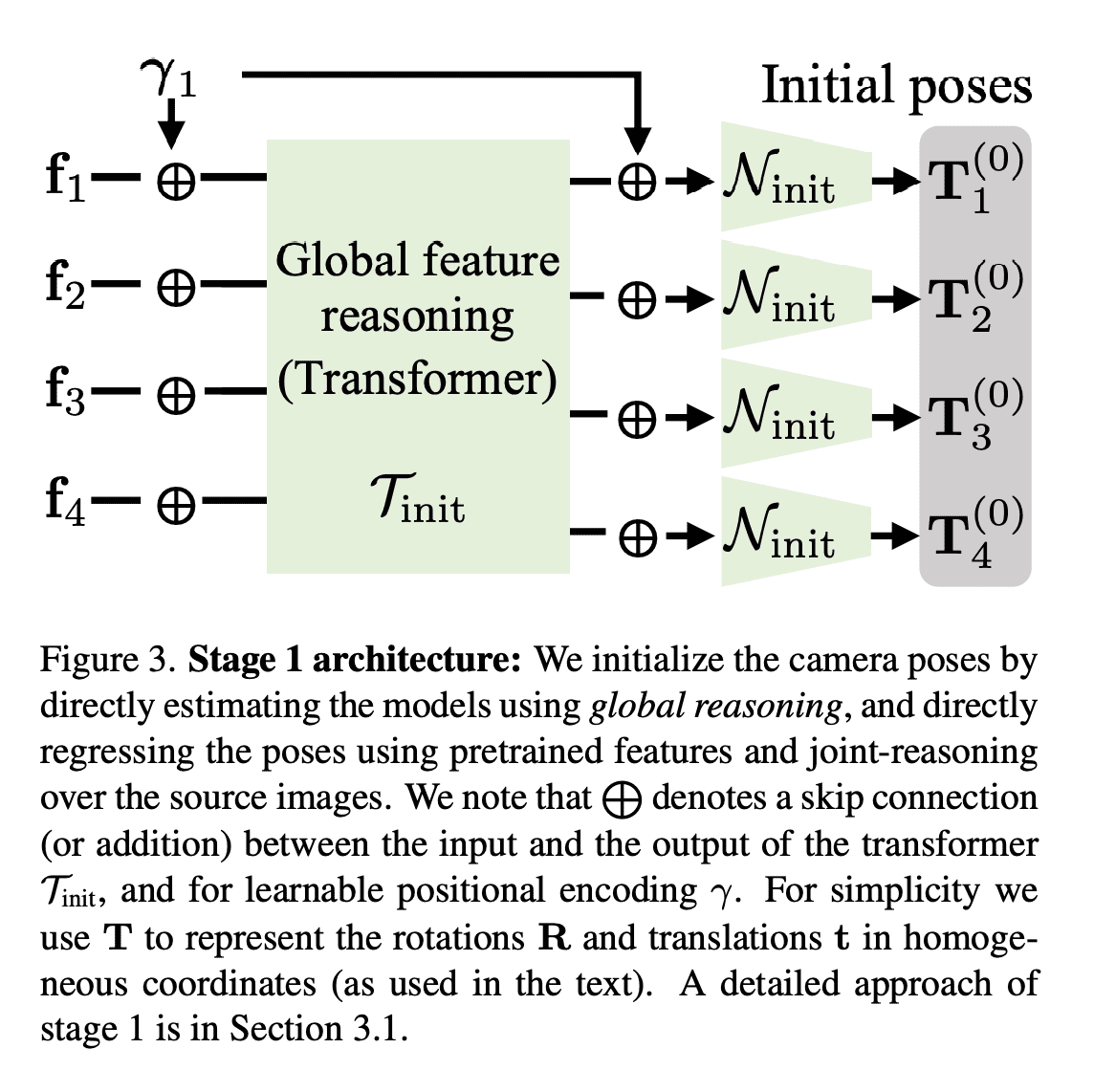
[CV] SparsePose: Sparse-View Camera Pose Regression and Refinement
S Sinha, J Y. Zhang, A Tagliasacchi, I Gilitschenski, D B. Lindell
[University of Toronto & CMU]
SparsePose: 稀疏视图相机姿态回归与细化
要点:
- 提出SparsePose,一种从稀疏输入图像预测相机姿态的方法;
- 实验证明该方法在稀疏场景下优于其他相机姿态估计技术;
- 评估了3D重建方法,相机估计可比竞争方法提供更高保真度的重建。
https://
arxiv.org/abs/2211.1699
1

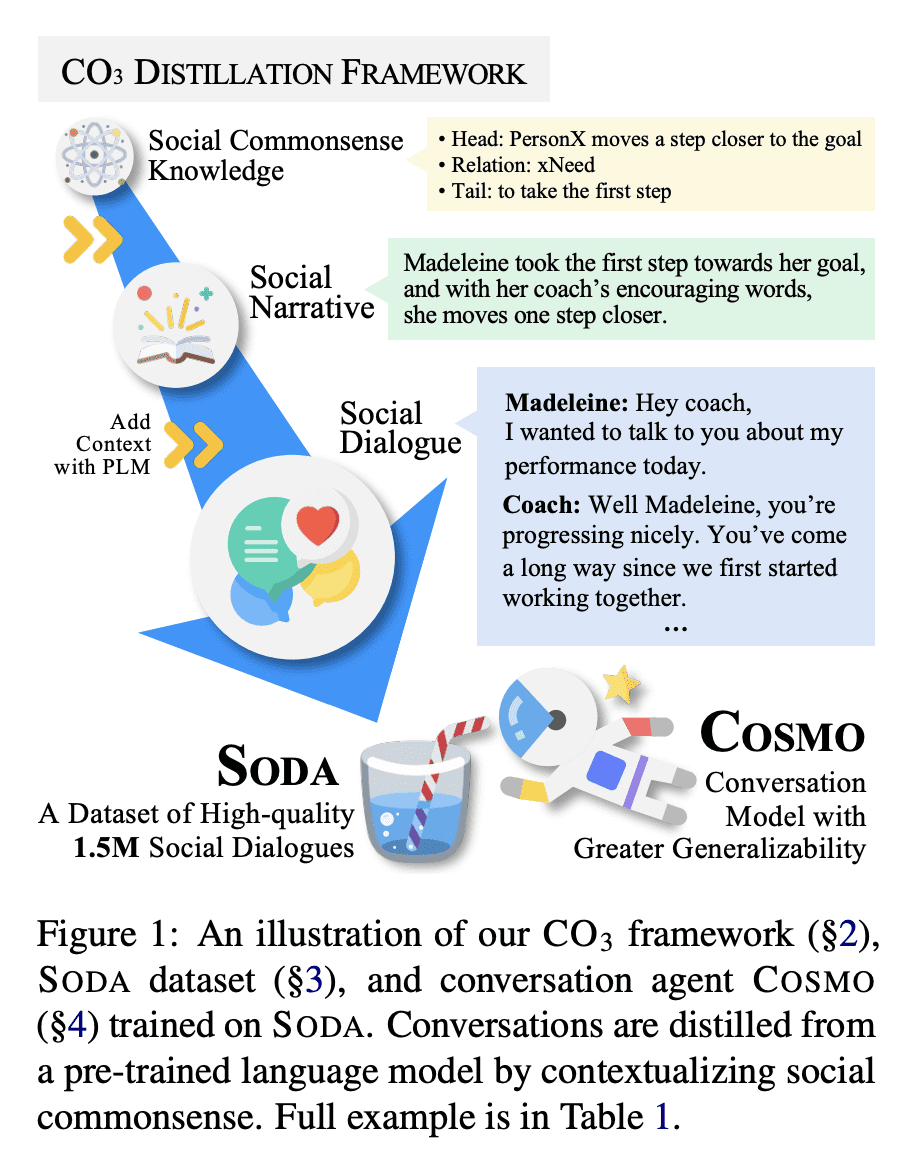
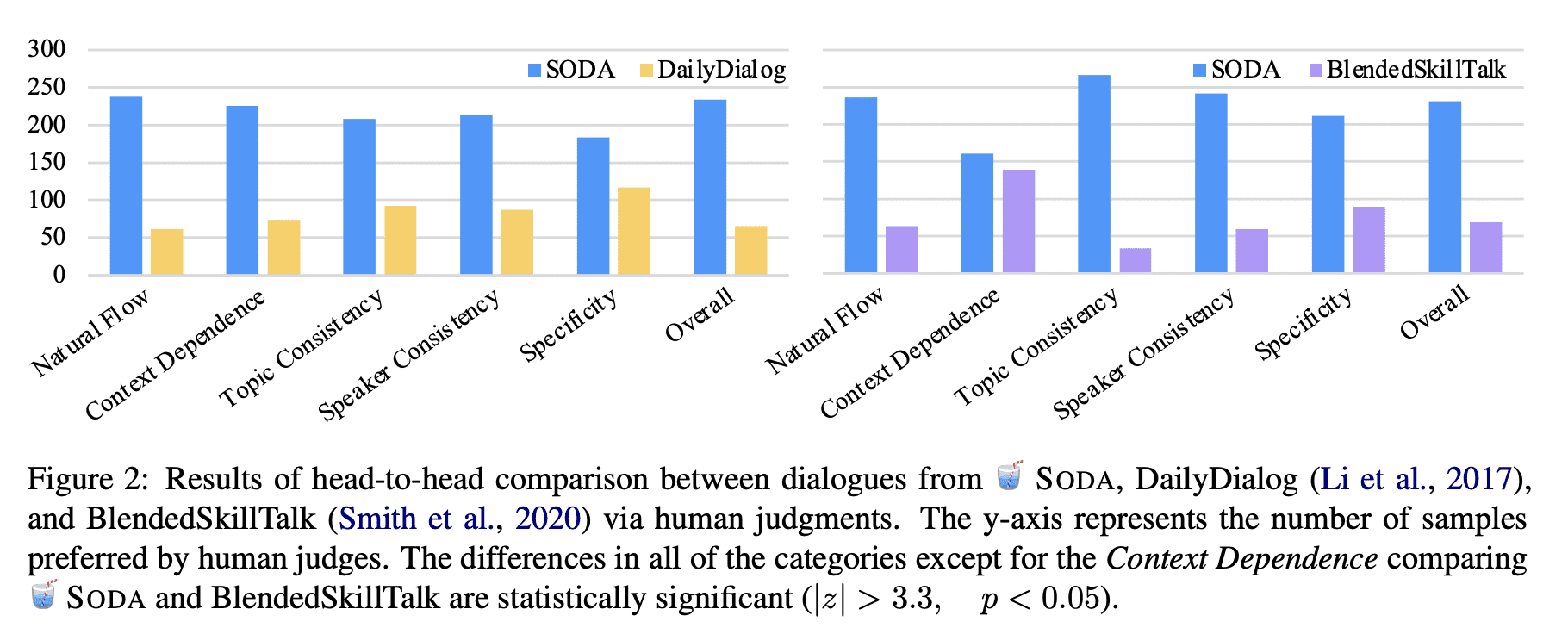
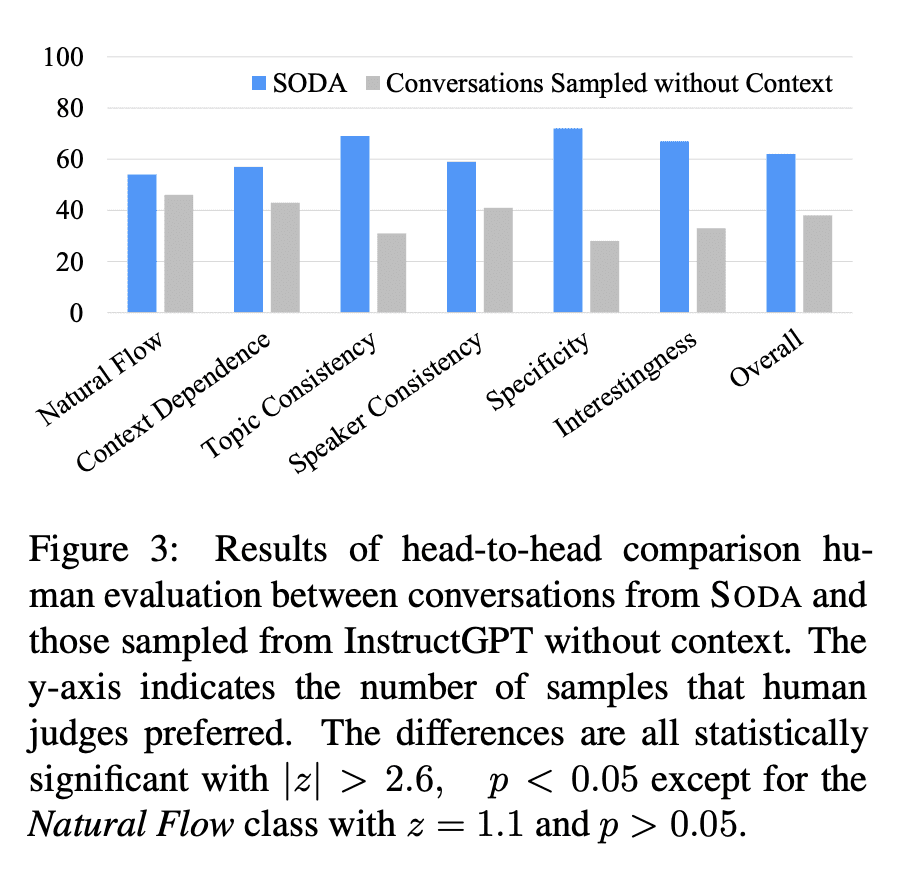
[CL] SODA: Million-scale Dialogue Distillation with Social Commonsense Contextualization
H Kim, J Hessel...
[Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence & University of Washington & University of Pittsburgh]
SODA: 基于社会常识背景化的百万级对话蒸馏
要点:
- 提出SODA:第一个公开可用的百万级高质量社交对话数据集;
- 人工评估表明,SODA中的对话比之前人工撰写的数据集更加一致,具体,令人惊讶地更自然;
- 训练了COSMO,一种可泛化的对话智能体,在域内和域外数据集中的表现都优于之前表现最好的智能体。广泛的评估表明,COSMO在未见数据集上比最佳对话模型更自然,更一致。
https://
arxiv.org/abs/2212.1046
5