redis做缓存
版本控制
将本地的代码上传到git仓库中的时候并不是所有的代码都需要上传到远程仓库,这时候就需要创建一个.gitignore文件来忽略他们
# Compiled class file
*.class
# Log file
*.log
# BlueJ files
*.ctxt
# Mobile Tools for Java (J2ME)
.mtj.tmp/
# Package Files #
*.jar
*.war
*.nar
*.ear
*.zip
*.tar.gz
*.rar
# virtual machine crash logs, see http://www.java.com/en/download/help/error_hotspot.xml
hs_err_pid*创建Gitee远程仓库
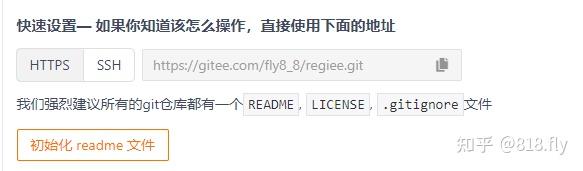
idea-创建本地仓库
在下列的操作中就会在本地的项目文件夹中产生了一个.git文件
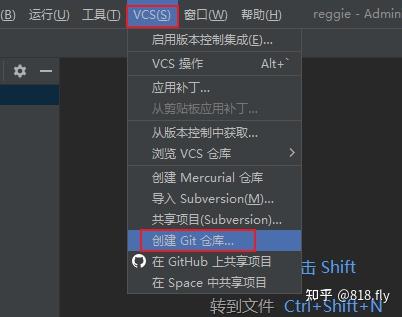
指定本项目工程
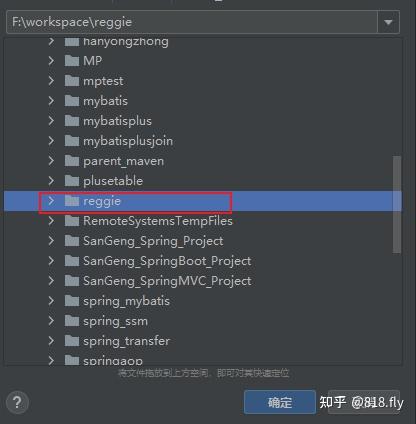
idea-提交并推送本地代码
1、 添加项目文件进暂存区
选中整个项目工程,右键
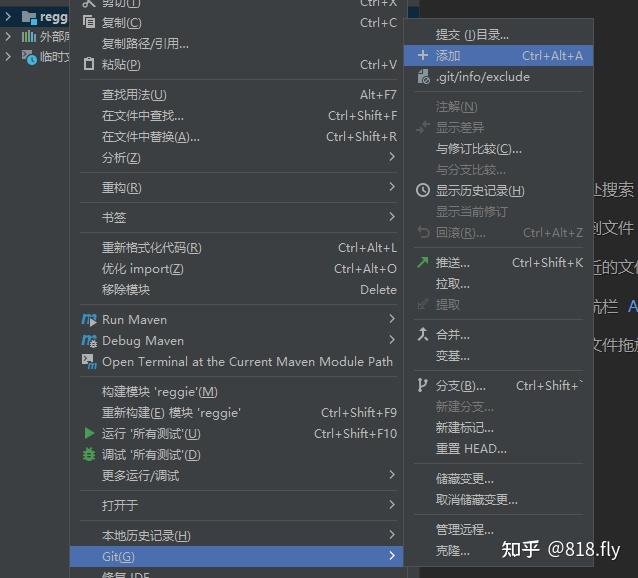
2、提交代码
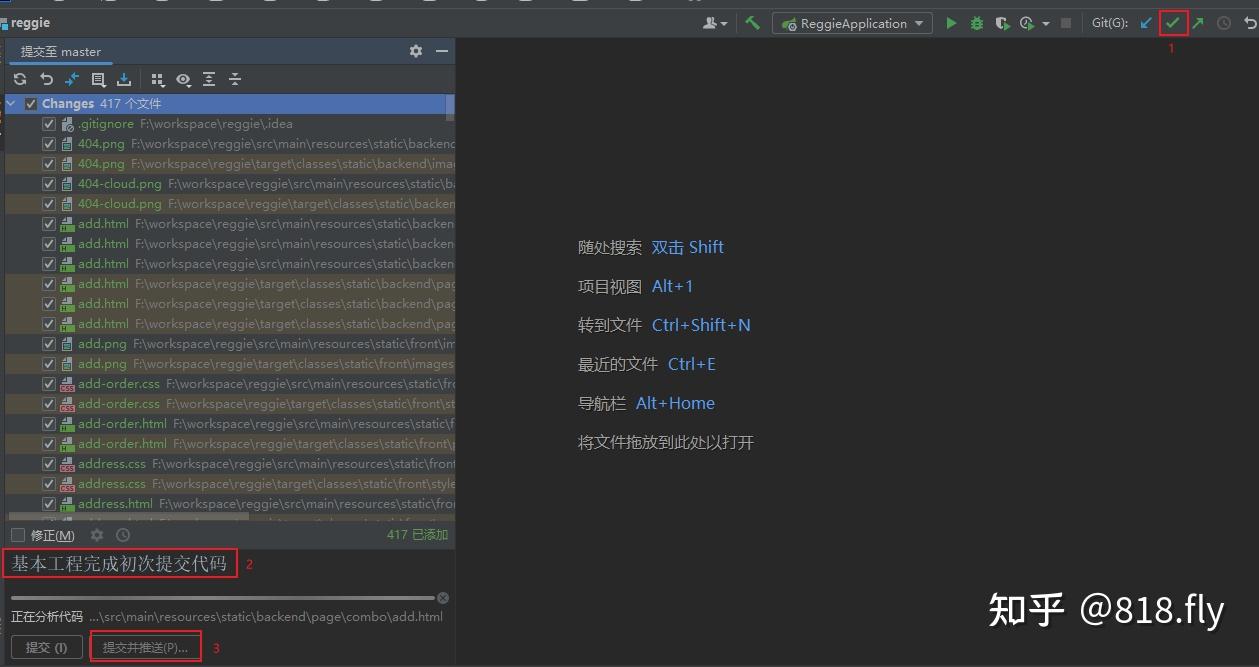
因为我们还没有定义远程提交的地址,所以点击推送并提交后会出现这样的情况,我们点击这个定义远程,把远程仓库地址放在这里就好了
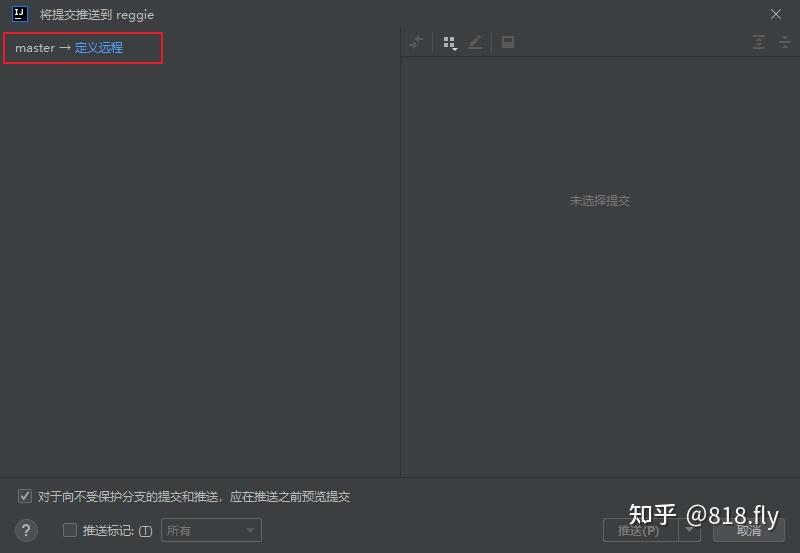
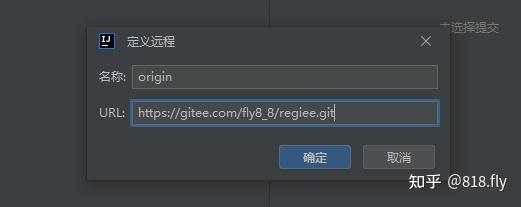
当你想给基本完成中的代码进行优化,你需要将优化的代码上传到另一个分支中
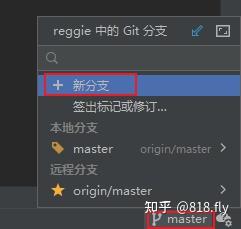
则现在显示的就是v1.0的分支了,现在将之前的基本功能完成的代码也推送到v1.0的分支中
推送之后在远程的仓库中也就产生了这个分支
maven坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>yml中加入redis相关配置
spring
redis:
host: 192.168.200.200
port: 6379
password: root@123456
database: 0编写Redis的配置类RedisConfig,定义RedisTemplate
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
//默认的Key序列化器为:JdkSerializationRedisSerializer
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
return redisTemplate;
}增加了这个配置类,最终我们在测试时通过redis的图形化界面查询就很方便,否则你查看key的时候编码是不方便看的,用了这个配置,我们存的什么key,查看到的就是这个字符串
缓存短信验证码
手机短信验证码是存放在redis数据库中的,因为手机短信验证码是有过期时间的,我们可以在redis中进行设置过期时间
在UserController中注入RedisTemplate对象,用于操作Redis;在UserController的sendMsg方法中,将生成的验证码保存到Redis
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
* 发送手机短信验证码
* @param user
* @return
@PostMapping("/sendMsg")
public R<String> sendMsg(@RequestBody User user){
//获取手机号
String phone = user.getPhone();
if(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(phone)){
//生成随机的4位验证码
String code = ValidateCodeUtils.generateValidateCode(4).toString();
log.info("code={}",code);
//调用阿里云提供的短信服务API完成发送短信
SMSUtils.sendMessage("","",phone,code);
//将生成的验证码放到redis中
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(phone,code,5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
return R.success("手机验证码短信发送成功");
}在UserController的login方法中,从Redis中获取生成的验证码,如果登录成功则删除Redis中缓存的验证码
@PostMapping("/login")
public R<User> login(@RequestBody Map map, HttpSession session){
log.info(map.toString());
//获取手机号
String phone = map.get("phone").toString();
//获取验证码
String code = map.get("code").toString();
//从Session中获取保存的验证码
// Object codeInSession = session.getAttribute(phone);
//从redis缓存中获取验证码
Object phoneCode = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(phone);
//进行验证码的比对(页面提交的验证码和Session中保存的验证码比对)
if(phoneCode != null && phoneCode.equals(code)){
//如果能够比对成功,说明登录成功
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(User::getPhone,phone);
User user = userService.getOne(queryWrapper);
if(user == null){
//判断当前手机号对应的用户是否为新用户,如果是新用户就自动完成注册
user = new User();
user.setPhone(phone);
user.setStatus(1);
userService.save(user);
session.setAttribute("user",user.getId());
//从Redis中删除缓存的验证码
redisTemplate.delete(phone);
return R.success(user);
return R.error("登录失败");
}SpringCache
基于注解的缓存功能,只需要简单地加一个注解,就能实现缓存功能,大大简化我们在业务中操作缓存的代码。
注解
@EnableCaching开启缓存注解功能
@Cacheable在方法执行前spring先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据;若没有数据,调用方法并将方法返回值放到缓存中
@CachePut将方法的返回值放到缓存中
@CacheEvict将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除
在spring boot项目中,使用缓存技术只需在项目中导入相关缓存技术的依赖包,并在启动类上使用@EnableCaching开启缓存支持即可。例如,使用Redis作为缓存技术,只需要导入Spring data Redis的maven坐标即可。
1、 main类上加@EnableCaching
在引导类上加该注解,就代表当前项目开启缓存注解功能。
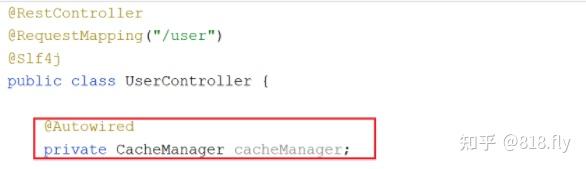
2、 注入CacheManager
我们可以在UserController注入一个CacheManager,在Debug时,我们可以通过CacheManager跟踪缓存中数据的变化。
3、pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>4、application.yml
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.200.200 #远程服务ip
port: 6379
password: root@123456
database: 0
cache:
redis:
time-to-live: 1800000 #设置缓存过期时间,毫秒单位,可选引入这个依赖后,我们在@Autowired private CacheManager cacheManager 这个的时候就有了redis作为的缓存技术
4、@Autowired private CacheManager cacheManager
在save方法上加注解@CachePut
当前UserController的save方法是用来保存用户信息的,我们希望在该用户信息保存到数据库的同时,也往缓存中缓存一份数据,我们可以在save方法上加上注解 @CachePut,用法如下:
@CachePut(value = "userCache", key = "#user.id") #这个user是参数中的user
@PostMapping
public User save(User user){
userService.save(user);
return user;
}作用: 将方法返回值,放入缓存。一般写在新增的方法上
value: 缓存的名称,表示这个是 某一类的缓存 , 每个缓存名称下面可以有很多key
key: 缓存的key ----------> 支持Spring的表达式语言SPEL语法
key的写法如下: 有四种写法
#user.id : #user指的是方法形参的名称, id指的是user的id属性 , 也就是使用user的id属性作为key ;
#user.name: #user指的是方法形参的名称, name指的是user的name属性 ,也就是使用user的name属性作为key ;
#result.id : #result代表方法返回值,该表达式 代表以返回对象的id属性作为key ;
#result.name : #result代表方法返回值,该表达式 代表以返回对象的name属性作为key ;
在delete方法上加注解@CacheEvict
当我们在 删除数据库user表的数据的时候,我们需要删除缓存中对应的数据,避免出现数据库数据与缓存数据不一致的情况 , 具体的使用方式如下:
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#p0") //#p0 代表第一个参数
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#root.args[0]") //#root.args[0] 代表第一个参数
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#id") //#id 代表变量名为id的参数
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public void delete(@PathVariable Long id){
userService.removeById(id);
}在update方法上加注解@CacheEvict
在更新数据之后,数据库的数据已经发生了变更,我们需要将缓存中对应的数据删除掉,避免出现数据库数据与缓存数据不一致的情况。 key的表达式有多种,最终都是拿到id属性
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#p0.id") //第一个参数的id属性
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#user.id") //参数名为user参数的id属性
//@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#root.args[0].id") //第一个参数的id属性
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",key = "#result.id") //返回值的id属性
@PutMapping
public User update(User user){
userService.updateById(user);
return user;
}@Cacheable注解
作用: 在方法执行前,spring先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据;若没有数据,调用方法并将方法返回值放到缓存中
value: 缓存的名称,每个缓存名称下面可以有多个key
key: 缓存的key ----------> 支持Spring的表达式语言SPEL语法
@Cacheable(value = "userCache",key = "#id")
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getById(@PathVariable Long id){
User user = userService.getById(id);
return user;
}缓存非null值
在@Cacheable注解中,提供了两个属性分别为: condition, unless
- condition : 表示满足什么条件, 再进行缓存 ;
- unless : 表示满足条件则不缓存 ; 与上述的condition是反向的 ,它可以使用#result的表达式
@Cacheable(value = "userCache",key = "#id", unless = "#result == null")
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getById(@PathVariable Long id){
User user = userService.getById(id);
return user;
}在list方法上加注解@Cacheable
在list方法中进行查询时, 有两个查询条件,如果传递了id,根据id查询; 如果传递了name, 根据name查询, 那么我们缓存的key在设计的时候,就需要既包含id,又包含name。 具体的代码实现如下:
@Cacheable(value = "userCache",key = "#user.id + '_' + #user.name")
@GetMapping("/list")
public List<User> list(User user){
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(user.getId() != null,User::getId,user.getId());
queryWrapper.eq(user.getName() != null,User::getName,user.getName());
List<User> list = userService.list(queryWrapper);
return list;
}注意:@Cacheable会将方法的返回值R缓存在Redis中,而在Redis中存储对象,该对象是需要被序列化的,而对象要想被成功的序列化,就必须得实现 Serializable 接口。而当前我们定义的R,并未实现 Serializable 接口。所以,要解决该异常,只需要让R实现 Serializable 接口即可。如下:

缓存套餐数据
在进行套餐数据查询时,我们需要根据分类ID和套餐的状态进行查询,所以我们在缓存数据时,可以将套餐分类ID和套餐状态组合起来作为key,如: 1627182182_1 (1627182182为分类ID,1为状态)。
@GetMapping("/list")
@Cacheable(value = "setmealCache",key = "#setmeal.categoryId + '_' + #setmeal.status")
public R<List<Setmeal>> list(Setmeal setmeal){
LambdaQueryWrapper<Setmeal> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(setmeal.getCategoryId() != null,Setmeal::getCategoryId,setmeal.getCategoryId());
queryWrapper.eq(setmeal.getStatus() != null,Setmeal::getStatus,setmeal.getStatus());
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Setmeal::getUpdateTime);
List<Setmeal> list = setmealService.list(queryWrapper);
return R.success(list);
}清理套餐数据
为了保证数据库中数据与缓存数据的一致性, 在我们添加套餐或者删除套餐数据之后,需要清空当前套餐缓存的全部数据 。那么@CacheEvict注解 如何清除某一份缓存下所有的数据呢 ,这里我们可以指定@CacheEvict中的一个属性 allEnties,将其设置为true即可。
@DeleteMapping
