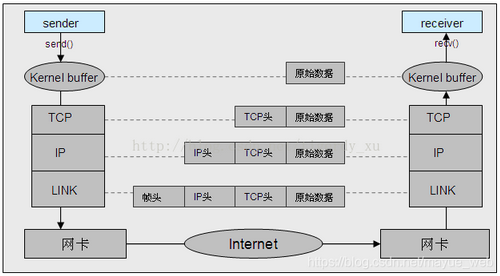
unix下流式套接字tcp与数据报套接字udp的区别
1)TCP面向流,数据分包、连包,UDP面向消息,不分包。
2)TCP必须连接后才能收发数据,UDP直接发送。
3)TCP不必记录客户端地址,直接收发数据,而UDP必须记录客户端地址后向具体地址发送数据。
4)通信流程不同,tcp需要保证可靠连接需要connect,accept,listen,udp不需要
5)收发数据接口不一样,tcp使用send,recv(),udp使用recvfrom(),sendto()
注意:
1)在sock()函数中
int socket(int domain _, int type J int protocol);
// domain 套接字中使用的协议族( Protocol Famjly )信息。
// type 套接字数据传输类型信息
// protocol 计算机间通信中使用的协议信息
协议族确定了通信规则,套接字类型确定了数据传输方式。,决定了协议族并不能同时决定数据传输方 式,换言之, socket 函数第1个参数PF INET协议族中也存在多种数据传输方式。
2)使用sendto、recvfrom 时的缓冲区大小设置
UDP仅提供数据报作为IP数据包的数据部分,IP数据包具有16位长度的字段,因此数据大小限制为2 ^ 16字节(65536),超过该大小时,需要分包发送。接收端接收时不能保证数据包的顺序与完整性。
3)在bind前,通过unlink移除已存在的文件连接
int unlink(const char *__name); //Remove the link NAME.
首先你要明确一个概念,一个文件是否存在取决于它的inode是否存在,你在目录里看到的是目录项里一条指向该inode的链接,
而不是文件的本身.当你调用unlink的时候他直接把目录项里的该条链接删除了,但是inode并没有动,该文件还是存在的,
这时候你会发现,目录里找不到该文件,但是已经打开这个文件的进程可以正常读写.只有当打开这个inode的所有文件描述符
被关闭,指向该inode的链接数为0的情况下,这个文件的inode才会被真正的删除.
从unlink的名字上就应该能判断出来,unlink含义为取消链接,remove才是删除的意思
3. 代码示例
AF_UNIX,SOCK_DGRAM, 面向消息的数据报套接字
#ifndef _COMM_H
#define _COMM_H
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "spdlog/spdlog.h"
#endif
comm.h
int main() {
int fd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
char* path = "/tmp/test.data";
struct sockaddr_un endPoint;
endPoint.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(endPoint.sun_path, path);
std::vector<char> buf(1, '0');
while (true) {
sleep(1);
auto ret = sendto(fd, buf.data(), buf.size(), MSG_DONTWAIT,
(const sockaddr*)&endPoint, sizeof(endPoint));
if (ret < 0) {
spdlog::error("send error with {}", strerror(errno));
continue;
spdlog::info("send size {}", ret);
buf.push_back('0');
close(fd);
return 0;
client.cc
int main() {
// AF_UNIX: 本地通信的UNIX协议族
// SOCK_DGRAM: 面向消息的数据报套接字类型
// 前两个参数就可确定协议类型时,默认为0
int fd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if (fd <= 0) {
spdlog::error("get socket fd failed!");
return fd;
char* path = "/tmp/test.data";
struct sockaddr_un endPoint;
endPoint.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(endPoint.sun_path, path);
//删除该文件对应的inode链接,防止重复创建
unlink(endPoint.sun_path);
if (bind(fd, (const sockaddr*)&endPoint, sizeof(sockaddr_un)) < 0) {
spdlog::error("bind error with {}!", strerror(errno));
close(fd);
return -1;
std::vector<char> buf(1024 * 100);
socklen_t sockLen = sizeof(sockaddr_un);
while (true) {
sleep(1);
auto ret = recvfrom(fd, buf.data(), buf.size(), MSG_DONTWAIT,
(sockaddr*)&endPoint, &sockLen);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("recvfrom error with %s\n", strerror(errno));
continue;
spdlog::info("recvform size={}", ret);
return 0;
server.cc
面向连接的流式套接字模型可见:示例
4、参考资料
嵌入式linux网络编程,UNIX域套接字,进程间通信机制
AF_UNIX 本地通信
关于PF_INET和AF_INET的区别
细说linux IPC系列
细说linux IPC(二):基于socket的进程间通信(下)