CUDA入门到精通(5)vs2019+cuda11.4创建空项目手动配置CUDA工程项目
编译前面提到了:
简单倒是简答,但是有个问题就是这个项目是vs2019和CUDA11.4心照不宣的缺省配置出来的。虽然能够用,但是一些中间环节依然不够清楚。
这里从常规c++空项目开始,建立能够运行的CUDA项目。

创建有:

生成:
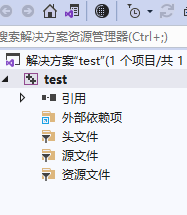
添加文件:

有:
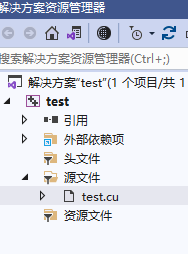
test.cu的内容和前面文章一样:
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
cudaError_t addWithCuda(int* c, const int* a, const int* b, unsigned int size);
__global__ void addKernel(int* c, const int* a, const int* b)
int i = threadIdx.x;
c[i] = a[i] + b[i];
int main()
const int arraySize = 5;
const int a[arraySize] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
const int b[arraySize] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
int c[arraySize] = { 0 };
// Add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t cudaStatus = addWithCuda(c, a, b, arraySize);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addWithCuda failed!");
return 1;
printf("{1,2,3,4,5} + {10,20,30,40,50} = {%d,%d,%d,%d,%d}\n",
c[0], c[1], c[2], c[3], c[4]);
// cudaDeviceReset must be called before exiting in order for profiling and
// tracing tools such as Nsight and Visual Profiler to show complete traces.
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceReset();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceReset failed!");
return 1;
return 0;
// Helper function for using CUDA to add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t addWithCuda(int* c, const int* a, const int* b, unsigned int size)
int* dev_a = 0;
int* dev_b = 0;
int* dev_c = 0;
cudaError_t cudaStatus;
// Choose which GPU to run on, change this on a multi-GPU system.
cudaStatus = cudaSetDevice(0);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaSetDevice failed! Do you have a CUDA-capable GPU installed?");
goto Error;
// Allocate GPU buffers for three vectors (two input, one output) .
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_c, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_a, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_b, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
// Copy input vectors from host memory to GPU buffers.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_a, a, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_b, b, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
// Launch a kernel on the GPU with one thread for each element.
addKernel << <1, size >> > (dev_c, dev_a, dev_b);
// Check for any errors launching the kernel
cudaStatus = cudaGetLastError();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addKernel launch failed: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus));
goto Error;
// cudaDeviceSynchronize waits for the kernel to finish, and returns
// any errors encountered during the launch.
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceSynchronize();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceSynchronize returned error code %d after launching addKernel!\n", cudaStatus);
goto Error;
// Copy output vector from GPU buffer to host memory.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
Error:
cudaFree(dev_c);
cudaFree(dev_a);
cudaFree(dev_b);
return cudaStatus;
}编译运行有:
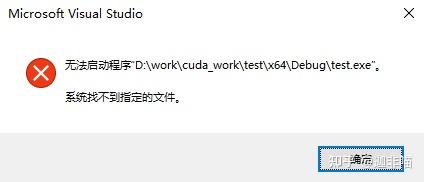
说明从空项目建立的工程,编译器没有识别test.cu。
此时右键点击test工程项目:
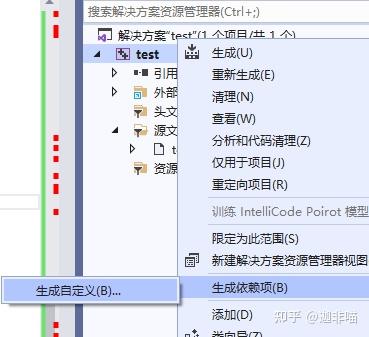
点击生成依赖项和生成自定义有:
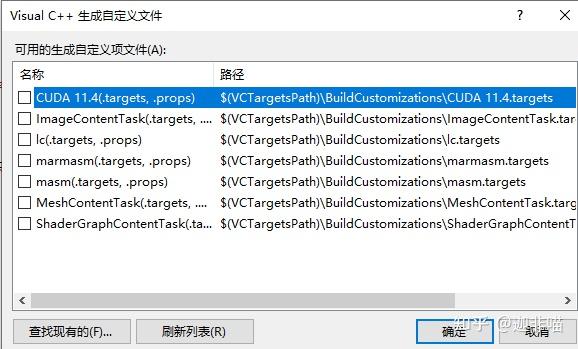
选择CUDA:

确定。
此时右键点击test.cu:
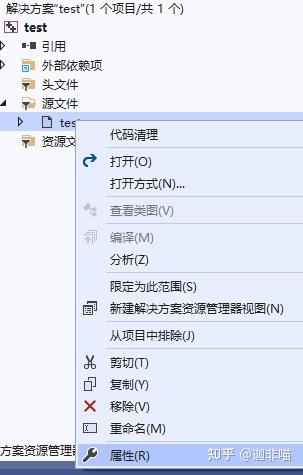
选择属性有:

将项类型改为:
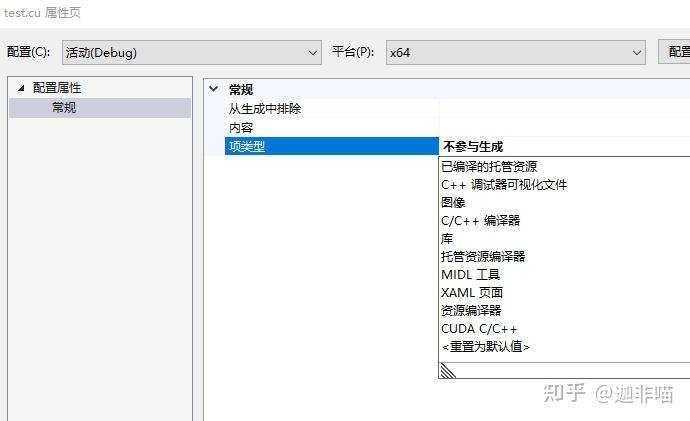
选择CUDA C/C++有:

编译,有:
已启动生成…
1>------ 已启动生成: 项目: test, 配置: Debug x64 ------
1>Compiling CUDA source file test.cu...
