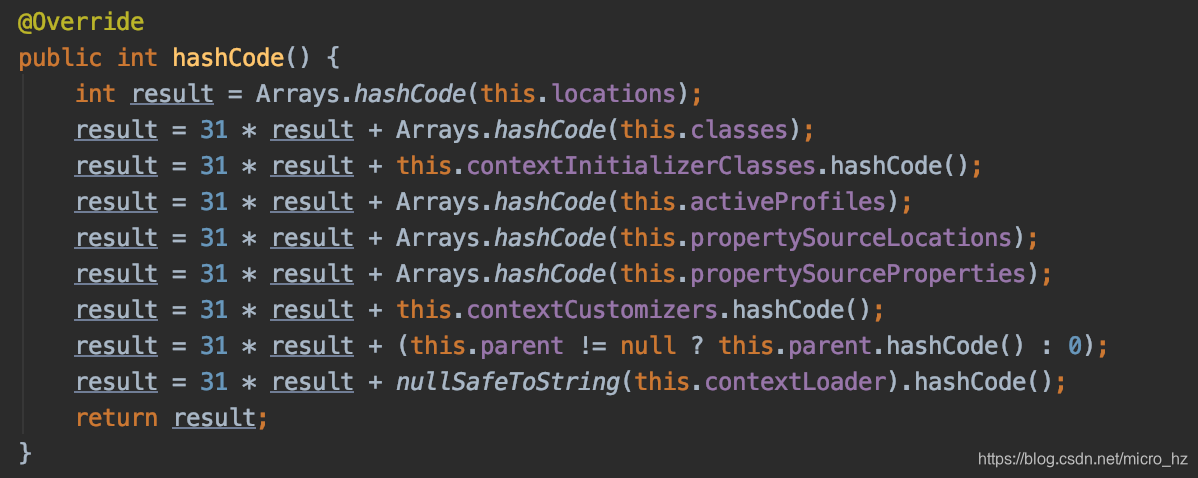
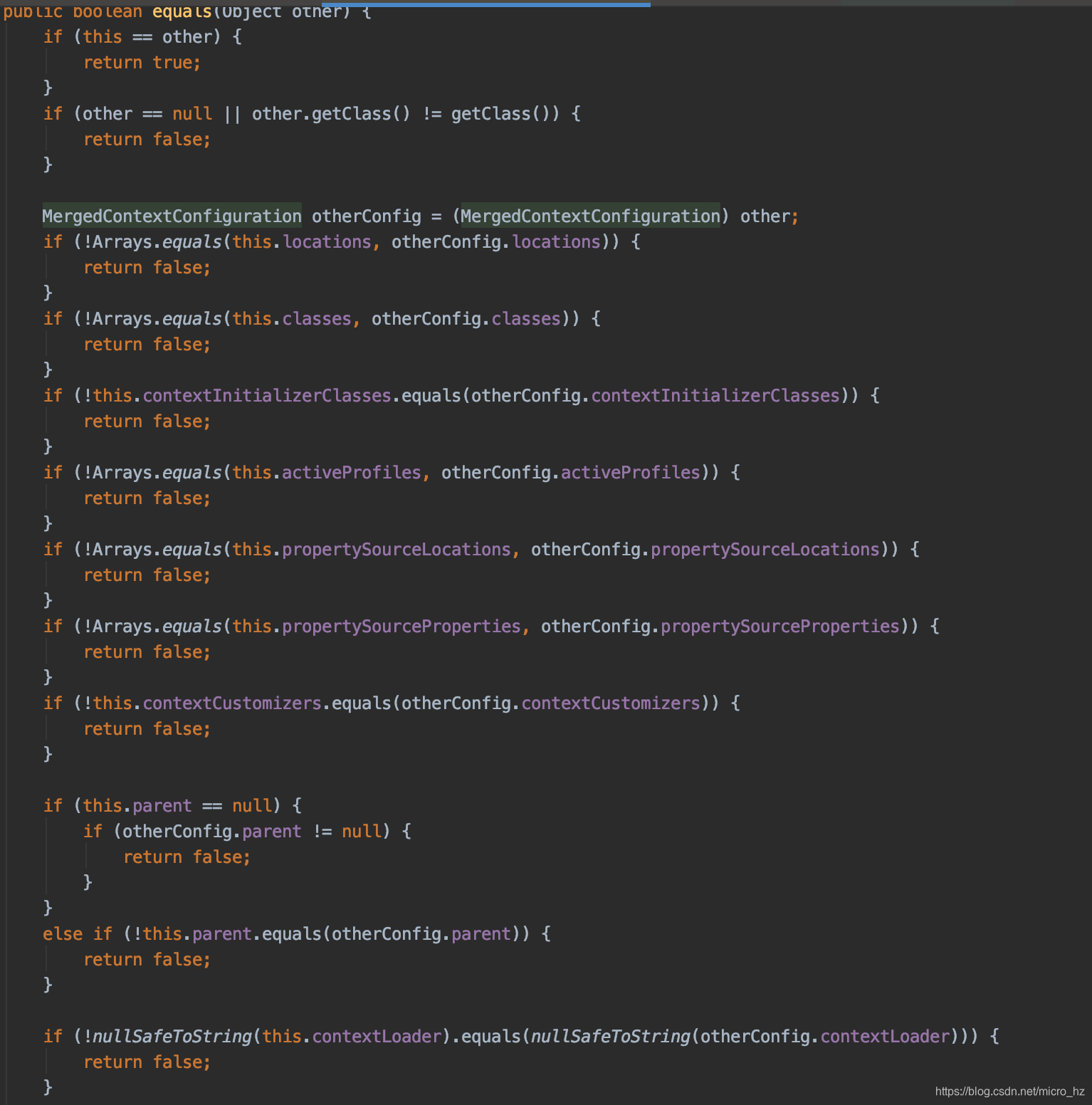
* @param testClass the test class for which the configuration was merged
* @param locations the merged context resource locations
* @param classes the merged annotated classes
* @param contextInitializerClasses the merged context initializer classes
* @param activeProfiles the merged active bean definition profiles
* @param propertySourceLocations the merged {@code PropertySource} locations
* @param propertySourceProperties the merged {@code PropertySource} properties
* @param contextCustomizers the context customizers
* @param contextLoader the resolved {@code ContextLoader}
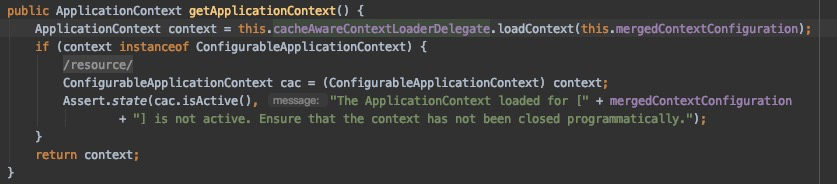
* @param cacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate a cache-aware context loader
* delegate with which to retrieve the parent context
* @param parent the parent configuration or {@code null} if there is no parent
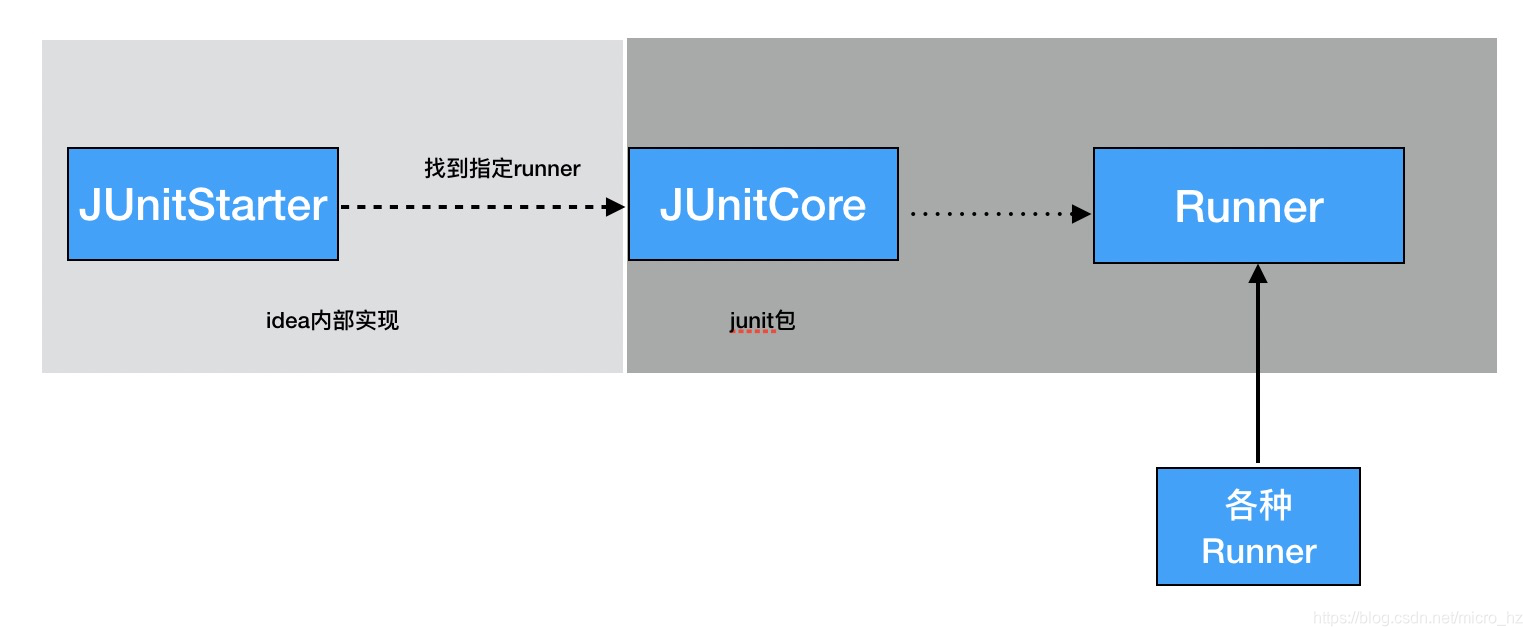
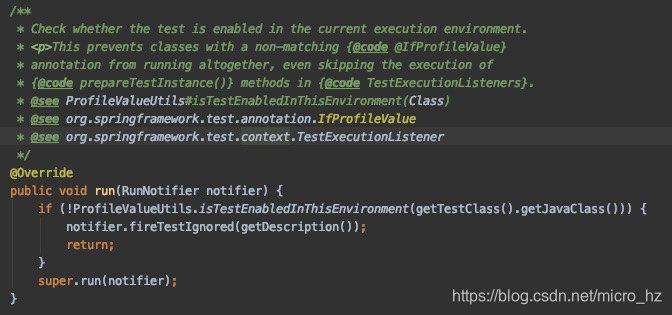
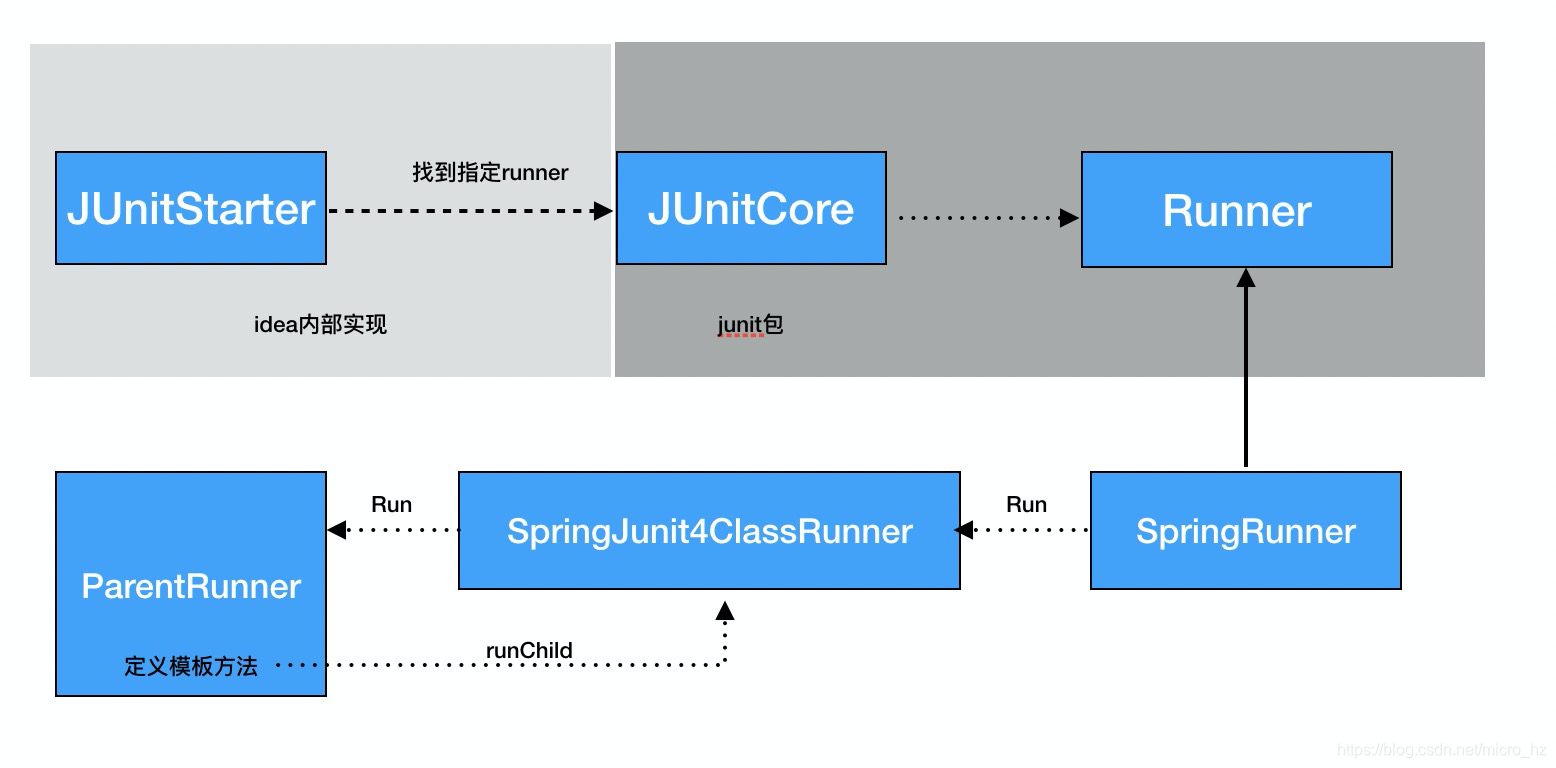
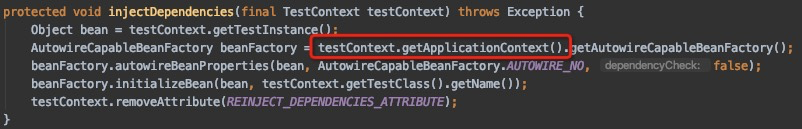
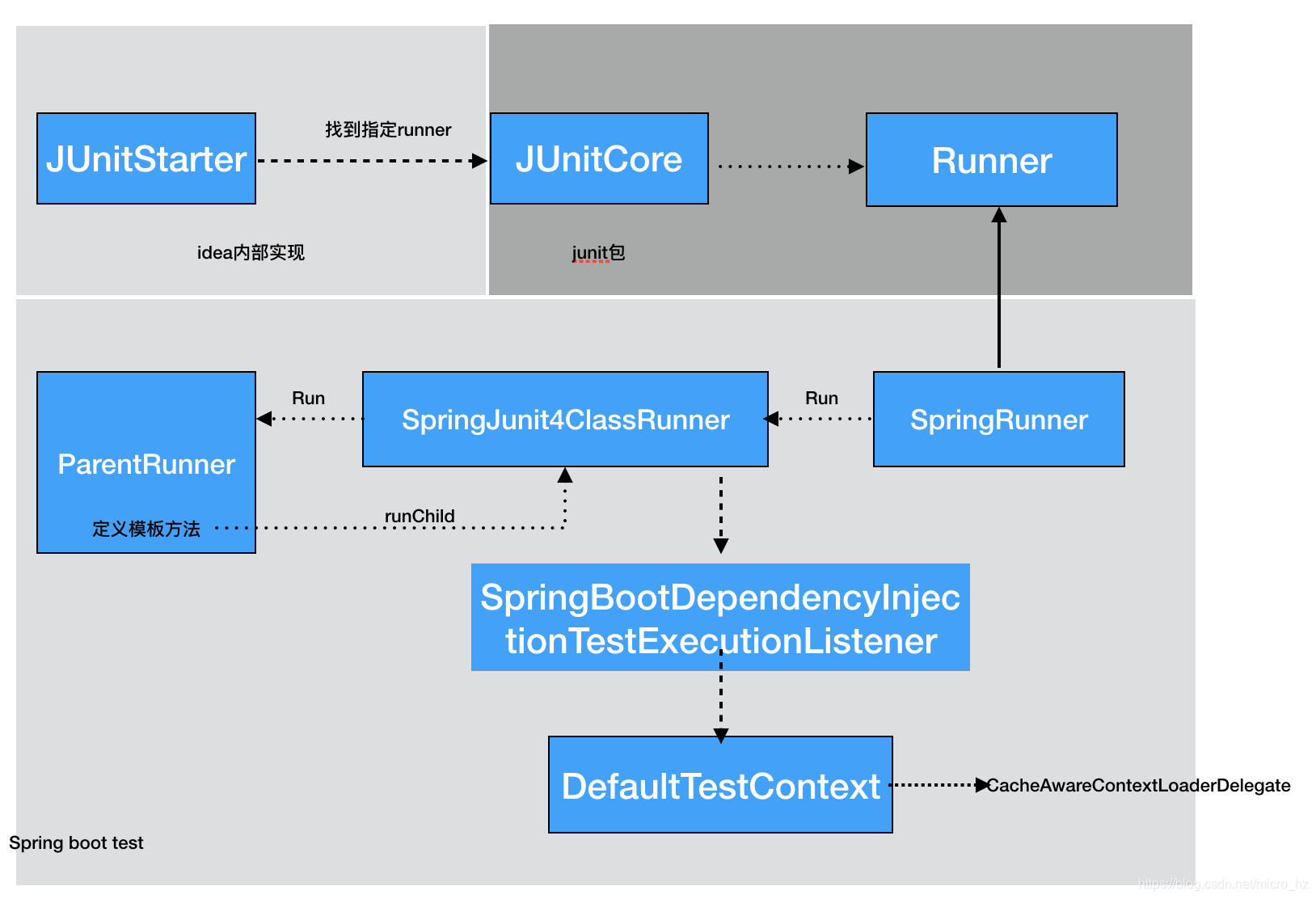
这些参数确定了能否共享SpringApplication,那两个测试类一个@Autowired,另一个使用@MockBean,肯定是改变这里面某个值,我们可以回溯这个MergedContextConfiguration是在什么时候被初始化的。这个还要追溯到idea的启动类,找到Runner的时候,SpringJUnit4ClassRunner的初始化的过程。
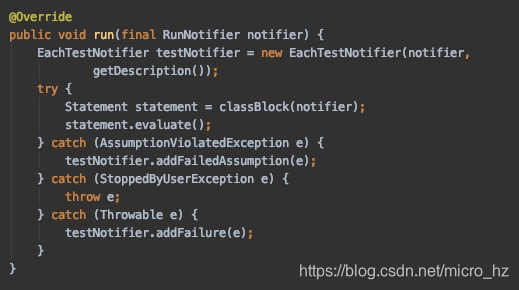
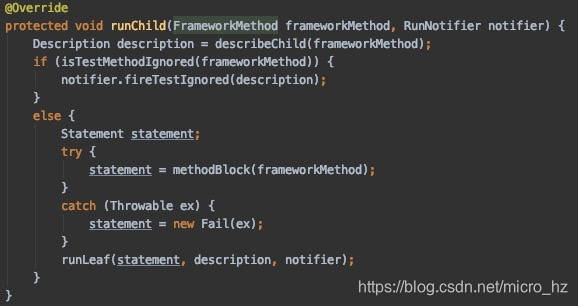
在每个测试类的运行都会唤起SpringJUnit4ClassRunner初始化,调用构造函数的时候会去加载测试类的上下文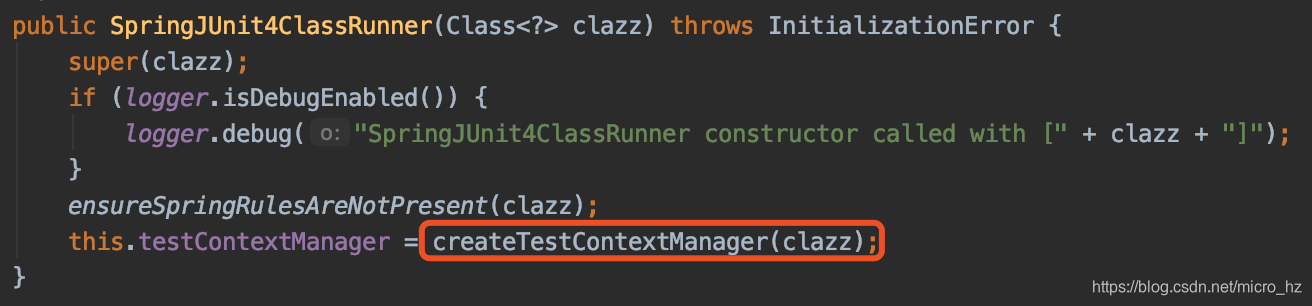
去创建这个TextContextManager
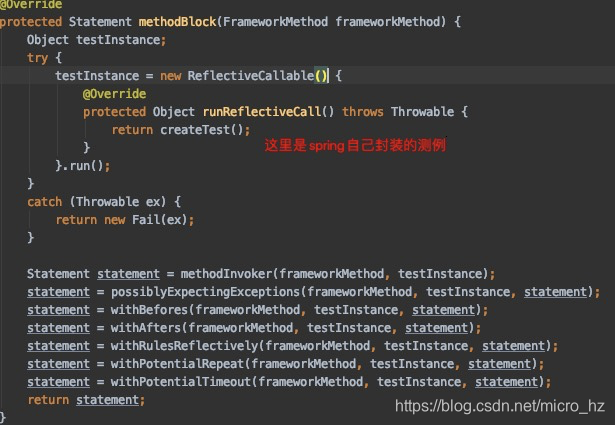
这里首先会根据被测试类的继承关系和注解的递归去找到固定包下面被注解@BootstrapWith修饰的类,因为是Spring boot test这里会根据@SpringBootTest 注解找到SpringBootTestContextBootstrapper类,找到这个引导类之后就会去初始化MergedContextConfiguration了。
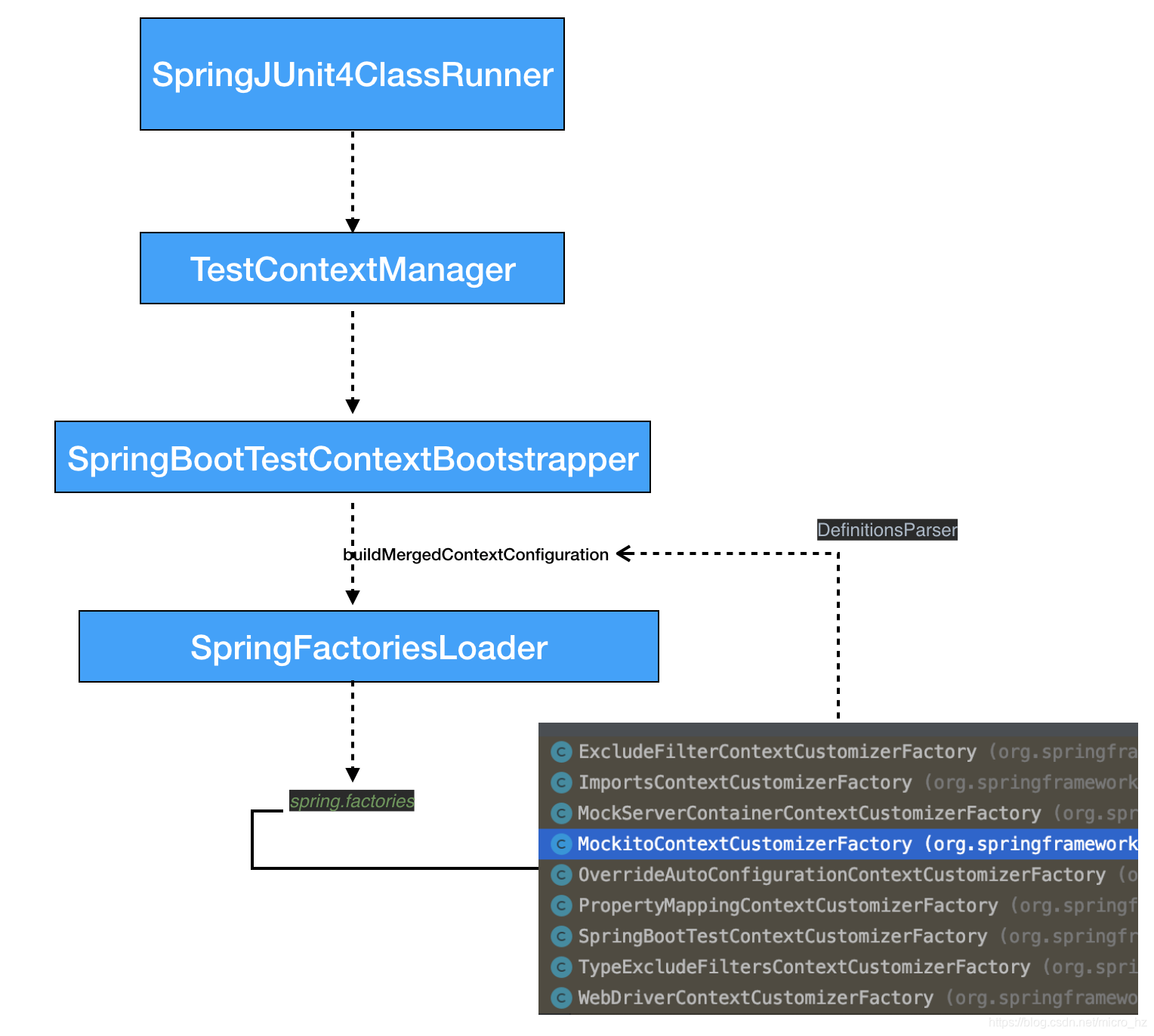
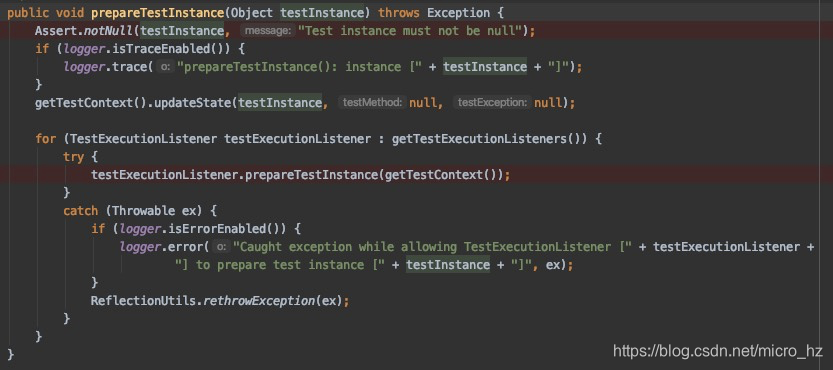
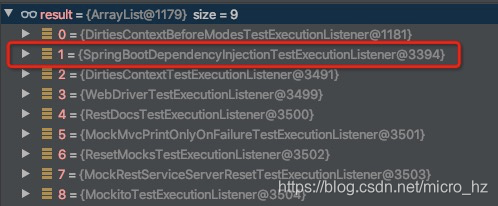
引导类通过SPI机制加载到所有的Customizer,并根据需要DefinitionsParser,进行转换,保存在MergedContextConfiguration的一个字段,mock的一个属性会在转换的时候记录到,而非mock的contextCustomizers则不会记录。
注意这里提到的
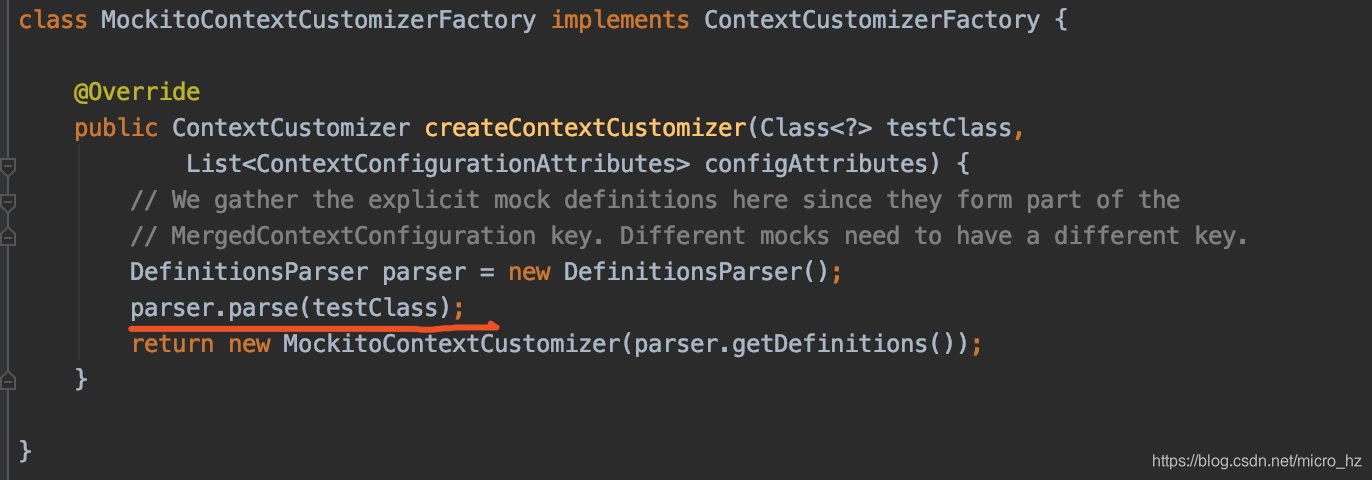
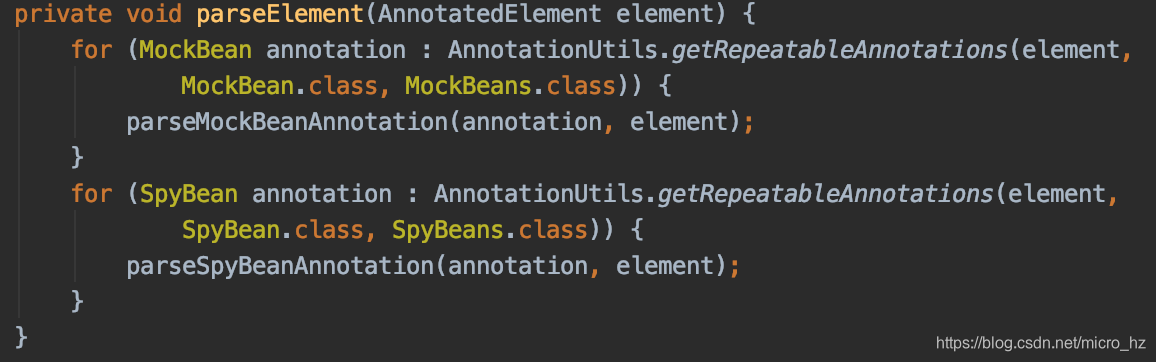
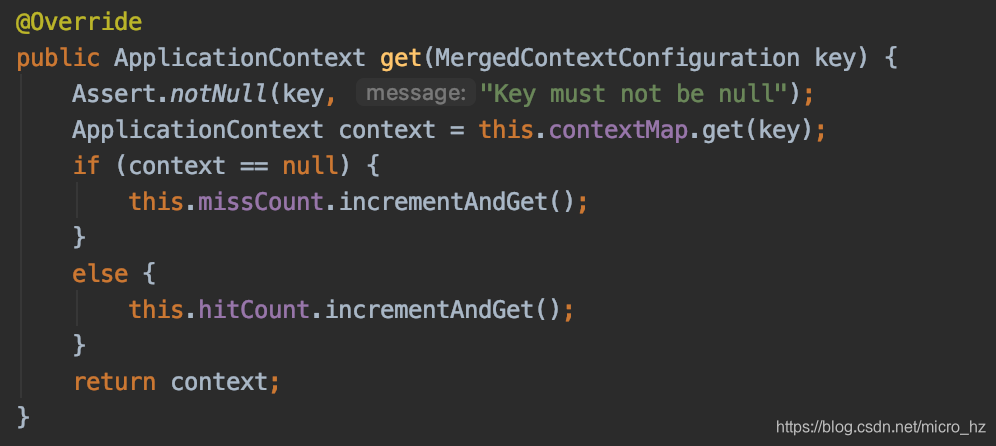
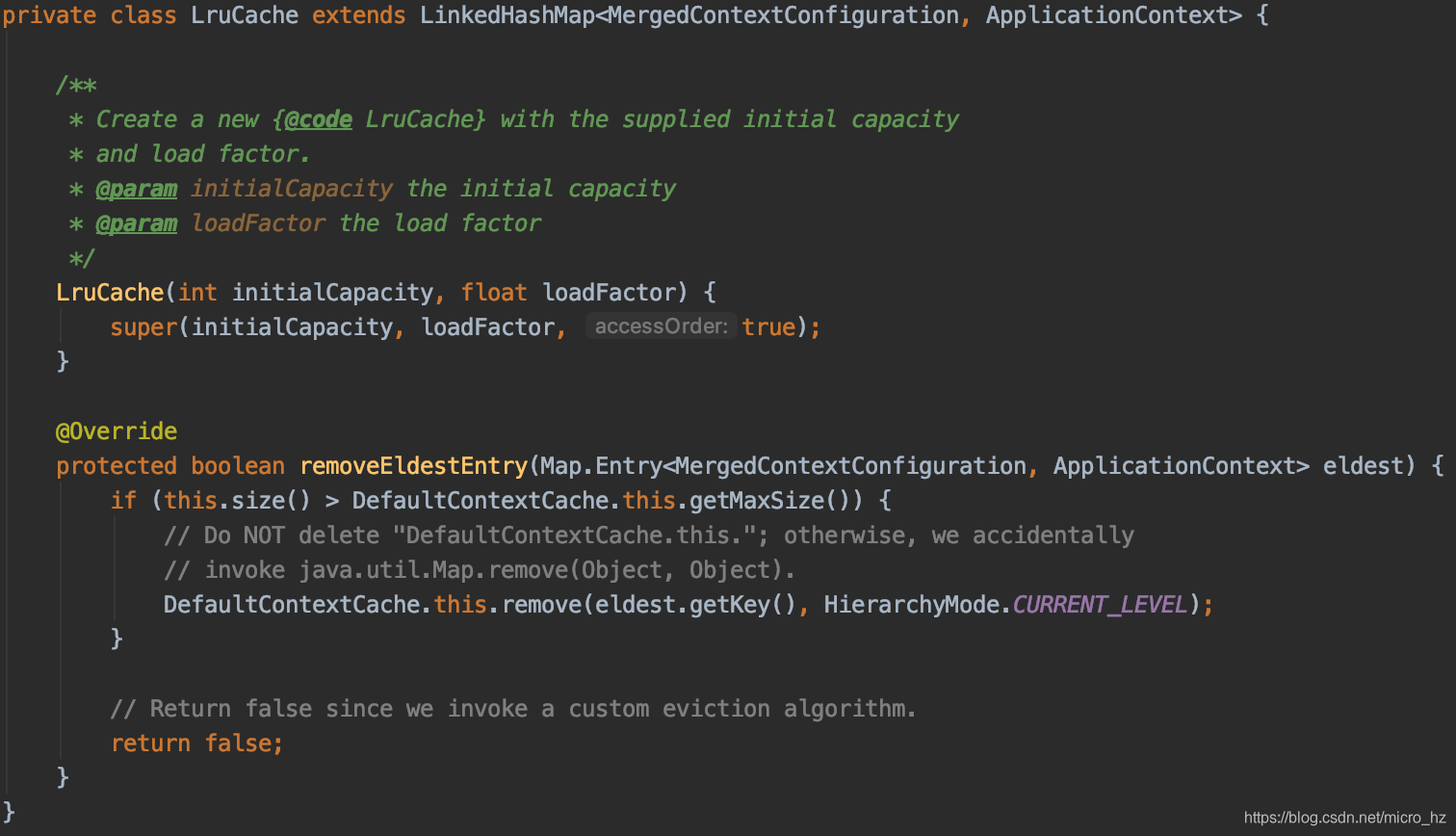
两个类一个用mock的字段,一个用非mock的字段,两个MockitoContextCustomizer的definitions就不一样,因此无法共享上下文,因此需要重新启动一个Spring容器,并存放到CacheAwareContextLoaderDelegate,以便后面共享。
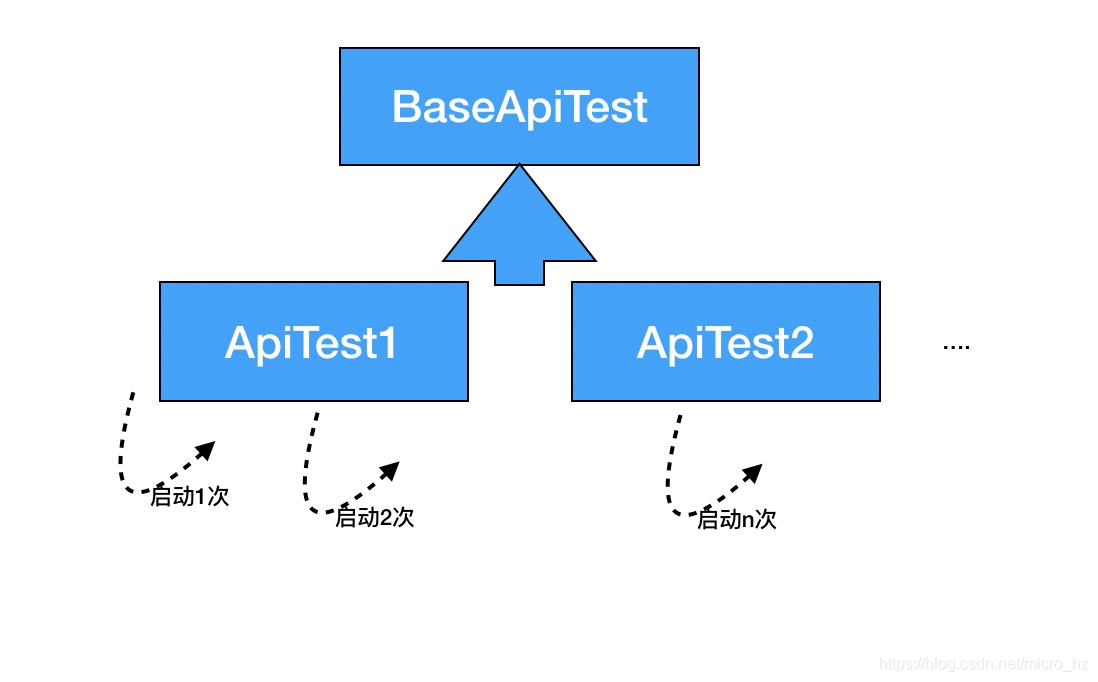
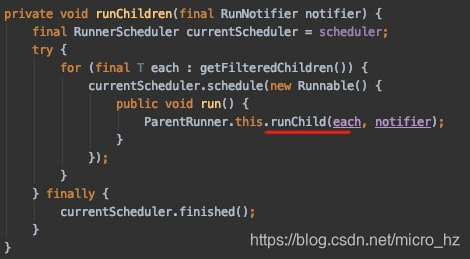
分析源码的设计,发现应用了很多SPI与可扩展的设计,idea与junit的解耦,junit的抽象与模板定义与各个测试框架的扩展。针对容器重启的角度,对于一个类来说,一定是共享一个spring上下文,但是不同的类可能由于注入的bean的方式不同导致无法共享spring上下文,所以导致重启会浪费掉一些时间,因此建议确定好mock的边界,对尽量多的测例共享一个容器视角可以提高单测效率,基于此可以设计多继承关系的单测结构,并把注入的bean向上共享,避免各个测试子类自己去注入出现不一致的情况。
背景spring boot test的项目中常用的测试框架, 最近在写集成测试的时候发现一个比较奇怪的问题,当我在运行多个测试用例的时候会偶尔重新启动整个容器上下文,由于后期业务逐渐复杂,大量的测试用例需要运行,这个问题直接导致回归测试的效率降低。举个例子:几个类:@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTest(classes = TestApplication.class)public class BaseApiTest { @Test