In the above command code the view model object is passed via the constructor. So the view model class needs to create a command object and expose this command object using “ICommand” interface. This “ICommand” interface will be consumed and call in the WPF XAML. Some important points regarding the “CustomerViewModel” class with respect to consuming the command class :-
-
The command class is a private member level object of the “CustomerViewModel” class.
-
In the view model class constructor the current object instance is passed to the command class. When we explained the command class code in the previous section we said the command class constructor takes the view model class instance. So in this section we are passing the current instance to the command class.
-
The command object is exposed as “ICommand” interface instance so that it can be consumed in XAML.
using System.ComponentModel;
public class CustomerViewModel
private ButtonCommand objCommand; // Point 1
public CustomerViewModel()
objCommand = new ButtonCommand(this); // Point 2
public ICommand btnClick // Point 3
return objCommand;
}
Add a button to your UI so that you can connect the button action to the “ICommand” method exposed. Now go to the properties of the button, scroll to the command property, right click on it and click create data binding.
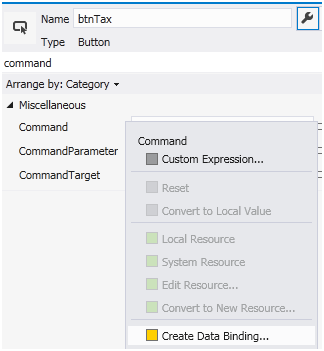
Then select static resource and attach the “ButtonCommand” with the button.
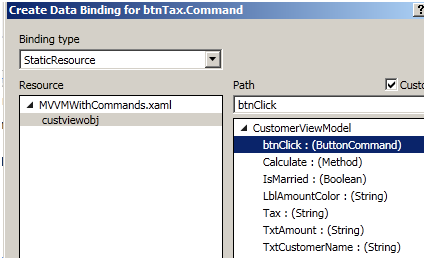
When you click on calculate tax button it executes “CalculateTax” method and stores the tax value in the “_tax” variable. For “CalculateTax” method code read previous section “Level 3:- Adding actions and INotifyPropertyChanged interface”.
In other words the UI will not be automatically notified about the tax calculation. So we need to send some kind of notification from the object to the UI saying that tax values have changed and the UI has reload the binding values.
So in the view model class we need to send anINotify event to the view.
上面的 command 代码中,ViewModel 对象是通过构造函数传递进来。所以 ViewModel 类需要创建一个 command 对象来暴露这个对象的“ICommand”接口。这个“ICommand”接口将被 WPF XAML 使用并调用。下面是一些关于“CustomerViewModel”类使用 command 类的要点:
在你的 UI 中添加一个按钮,这样就可以把按钮的执行动作连接到暴露的“ICommand”接口。现在打开 button 的属性栏,选择 command 属性,右击创建一个数据绑定。
当你点击了 Calculate Tax 按钮,它就执行了“CalculateTax”方法。并将税值结果存在“_tax”变量中。关于“CalculateTax”方法代码,可以阅读前面的小节“第三步:添加执行动作和“INotifyPropertyChanged”接口”。
To enable notification in your view model class we need to do three things. All three things are pointed in the below code with comments like point 1 , point 2 and point 3.
Point 1 :- Implement “INotifyPropertyChanged” interface as shown in the below code. Once you implement the interface it creates an object of “PropertyChangedEventHandler” event.
Point 2 and 3 :- In the “Calculate” method raise event using “PropertyChanged” object and in that provide for which property is the notification. For instance in this case it’s for “Tax” property. To be on the safe side we will also check if the “PropertyChanged” object is not null.
public class CustomerViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged // Point 1
public void Calculate()
obj.CalculateTax();
if (PropertyChanged != null) // Point 2
PropertyChanged(this,new PropertyChangedEventArgs("Tax"));
// Point 3
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
}
If you run the application you should be able to see how on the button click “Tax” value gets updated.
Level 4:- Decoupling actions from view model
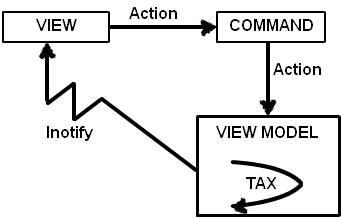
So till now we have created a simple screen with MVVM which has both properties and command implemented. We have a view whose UI input elements i.e. textbox is connected to view model using bindings and any kind of actions like button clicks are connected using commands. View model talks with model internally.

But in the above architecture there is one problem the command class is having aHEAVY COUPLING with the view model.If you remember the command class code ( i have pasted the same again below) in the constructor we are passing the view model object , which means that this command class cannot be reused with other view model class.
public class ButtonCommand : ICommand
private CustomerViewModel obj; // Point 1
public ButtonCommand(CustomerViewModel _obj) // Point 2
obj = _obj;
......
......
......
为了让你的 ViewModel 类能够实现通知,我们必须做三件事情。这三件事情都在下面的代码注释中指出,例如 Point1, Point2 和 Point3。
Point1: 如下面代码那样实现“INotifyPropertyChanged”接口。一旦你实现了该接口,它就创建了对象的“PropertyChangedEventHandler”事件。
Point2 和 3: 在“Calculate”方法中用“PropertyChanged”对象去触发事件,并在其中指定了某个属性的通知。在这里是“Tax”属性。安全起见,我们同样也要检查“PropertyChanged”是否不为空。
public class CustomerViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged // Point 1
public void Calculate()
obj.CalculateTax();
if (PropertyChanged != null) // Point 2
PropertyChanged(this,new PropertyChangedEventArgs("Tax"));
// Point 3
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
}如果你运行程序,你应该可以看见当点击按钮后“Tax”值被更新了。
第四步:在 ViewModel 中解耦执行动作
到目前为止,我们用 MVVM 框架创建了一个简单的界面。这个界面同时包含了属性和命令实现。我们拥有了一个视图,它的 UI 输入元素(例如 textbox)通过绑定和 ViewModel 连接起来,它的任何执行动作(例如按钮点击)通过命令和 ViewModel 连接起来。ViewModel 和内部的 Model 通讯。
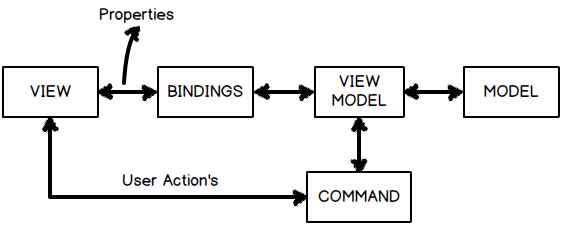
但是在上面的结构中还有一个问题:command 类和 ViewModel 类存在着过度耦合的情况。如果你还记得 command 类代码(我在下面贴出来了)中的构造函数是传递了 ViewModel 对象,这意味着这个 command 类无法被其它的 ViewModel 类所复用。
public class ButtonCommand : ICommand
private CustomerViewModel obj; // Point 1
public ButtonCommand(CustomerViewModel _obj) // Point 2
obj = _obj;
......
......
......
But now let’s thing logically “What’s anaction?” at the end of the day. It’s an event which comes from the end user like mouse clicks (right or left) , button clicks , menu clicks , function key press etc. So there should be a way to generalize these actions and attach it in a more general way to the view models.
If you think logically actions are logics which are wrapped in to methods and functions. So what’s the generalized way of point to “methods” and “functions” … think , think , think ….. “DELEGATES” , “DELEGATES” and “DELEGATES”.
We would need two delegates one for “CanExecute” and the other for “Execute”. The “CanExecute” returns a Boolean so used for validation and depending on the validations it enables and disables the user interface. The “Execute” will execute when the “CanExecute” is true.
public class ButtonCommand : ICommand
public bool CanExecute(object parameter) // Validations
public void Execute(object parameter) // Executions
}
So in other words we need two delegates one a function which returns Boolean value and the other an action which returns void. So how about creating a “Func” and an “Action”. Both of these guys “Func” and “Action” are ready made delegates.
In case you are new to action and func you can see this video for the same
但是在考虑了所有情况之后,让我们逻辑地思考下“什么是一个动作?”。它是一个事件,可以由用户从鼠标点击(左键或右键),按钮点击,菜单点击,功能键按下等。所以应该有一种方式通用化这些动作,并且让各种 ViewModel 有一种更通用的方法去绑定它。
逻辑上讲,如果你认为任务动作是一些方法和函数的封装逻辑。那有什么是“方法”和“函数”的通用表达方式呢?......努力想想.......再想想.......“委托”,“委托”,没错,还是“委托”。
我们需要两个委托,一个给“CanExecute”,另一个给“Execute”。“CanExecute”返回一个布尔值用来验证以及根据验证来使能(Enable)或者禁用(Disable)用户界面。“Execute”委托则将在“CanExecute”委托返回 true 时执行。
public class ButtonCommand : ICommand
public bool CanExecute(object parameter) // Validations
public void Execute(object parameter) // Executions
}
因此,换句话说,我们需要两个委托,一个返回布尔值,另一个执行动作并返回空。所以,创建一个“Func”和一个“Action”如何?“Func”和“Action”都可以用来创建委托。
如果你还不熟悉 Func 和 Action,可以看下下面这个视频。(译注:作者在这里提供了一个 YouTube 的视频链接,大概说的就是 C# 中 Func<> 和 Action<> 这两个委托的区别,前者 Func<> 模版参数包含返回值类型,而 Action<> 表示无返回值的泛型委托,参见这里)

So by using the delegate architecture let’s try to create a generalized command class. We have made three changes to the command class ( below is the code for the same) and I have marked them as Point 1, 2 and 3:-
Point 1 :- We have removed the view model object from the constructor and we are accepting two delegates one is “Func” and other is “Action”.“Func” for the validation i.e. when the action will execute and the “Action” what to execute. Both these delegate values are passed via the constructor and set to private respective delegate variables internally.
Point 2 and 3 :-The Fun delegate ( WhentoExecute ) is called “CanExecute” and in execute the action “Whattoexecute” is called.
public class ButtonCommand : ICommand
private Action WhattoExecute;
private Func<bool> WhentoExecute;
public ButtonCommand(Action What , Func<bool> When) // Point 1
WhattoExecute = What;
WhentoExecute = When;
public bool CanExecute(object parameter)
return WhentoExecute(); // Point 2
public void Execute(object parameter)
WhattoExecute(); // Point 3
}
In the model we already knew what to execute i.e. “CalculateTax” , we have also a put a simple function and named it “IsValid” which will validate if the “Customer” class is valid or not.
public class Customer
public void CalculateTax()
if (_Amount > 2000)
_Tax = 20;
else if (_Amount > 1000)
_Tax = 10;
_Tax = 5;
public bool IsValid()
if (_Amount == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
From the view model class we are passing both methods and function in the command constructor one for the “Func” and one for the “Action”.
public class CustomerViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
private Customer obj = new Customer();
privateButtonCommandobjCommand;
publicCustomerViewModel()
objCommand = new ButtonCommand(obj.CalculateTax,
obj.IsValid);
}
This makes the architecture much better and decoupled as this command class can be attached with any view model in a generic way.Below is the improvised architecture, do notice how the view model is talking with the command class via delegate ( func and action).
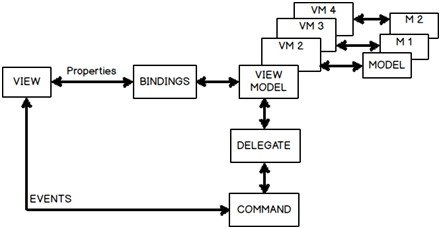
通过使用委托的方法,我们试着创建一个通用的 command 类。我们对 command 类做了三个修改(代码参见下面),同时我也标注了三点 Point 1,2 和 3。
Point1: 我们在构造函数中移除了 ViewModel 对象,改为接受两个委托,一个是“Func”,另一个是“Action”。“Func”委托用作验证(例如验证何时动作将被执行),而“Action”委托用来执行动作。两个委托都是通过构造函数参数传递进来,并赋值给类内部的对应私有成员变量。
Point2 和 3: Func<> 委托(WhentoExecute)被“CanExecute”调用,执行动作的委托 Whattoexecute 则是在“Execute”中被调用。
public class ButtonCommand : ICommand
private Action WhattoExecute;
private Func<bool> WhentoExecute;
public ButtonCommand(Action What , Func<bool> When) // Point 1
WhattoExecute = What;
WhentoExecute = When;
public bool CanExecute(object parameter)
return WhentoExecute(); // Point 2
public void Execute(object parameter)
WhattoExecute(); // Point 3
}
在 Model 类中我们已经知道要执行什么了(例如“CalculateTax”),我们也创建一个简单的函数“IsValid”来验证“Customer”类是否有效。
public class Customer
public void CalculateTax()
if (_Amount > 2000)
_Tax = 20;
else if (_Amount > 1000)
_Tax = 10;
_Tax = 5;
public bool IsValid()
if (_Amount == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
在 ViewModel 类中我们同时传递函数和方法给 command 类的构造函数,一个给“Func”,一个给“Action”。
public class CustomerViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
private Customer obj = new Customer();
privateButtonCommandobjCommand;
publicCustomerViewModel()
objCommand = new ButtonCommand(obj.CalculateTax,
obj.IsValid);
}
这样使得框架更好,更解耦, 使得这个 command 类可以以一个通用的方式被其它 ViewModel 引用。下面是改善后的架构, 需要注意 ViewModel 如何通过委托(Func和Action)和 command 类交互。

Level 5:- Leveraging PRISM
Finally a framework would be great if it can bring down some work in our MVVM code.PRISM is one of those frameworks which comes to rescue. The main use of PRISM is for modular development but it has a nice “DelegateCommand” class which can be used rather than creating our own command class.
So the first thing is download PRISM from http://www.microsoft.com/en-in/download/details.aspx?id=42537, compile the solution and reference two DLL’s “Microsoft.Practices.Prism.Mvvm.dll” and “Microsoft.Practices.Prism.SharedInterfaces.dll”.
You can now get rid of your custom command class and import “Microsoft.Practices.Prism.Commands” namespace and use the delegate command as shown in the below code.
public class CustomerViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
private Customer obj = new Customer();
private DelegateCommand objCommand;
public CustomerViewModel()
objCommand = new DelegateCommand(obj.CalculateTax,
obj.IsValid);
}
Demonstration of WPF MVVM in video format
I have also demonstrated from scratch how to implement MVVM with WPF in the below youtube video.
public class CustomerViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
private Customer obj = new Customer();
private DelegateCommand objCommand;
public CustomerViewModel()
objCommand = new DelegateCommand(obj.CalculateTax,
obj.IsValid);
WPF MVVM 的视频演示
我同时也在下面的视频中从头演示了如何实现 WPF MVVM(译注:一个 YouTube 链接...)。








