最详细的python爬虫指南(二):获取网页内容
得到正确的网页编码之后呢,就要把我们需要的网页内容提取出来,比如电影信息,职位信息,图片等等。
下面给大家带来获取网页内容的几种方法,在这之前先简单介绍下基本的网页(HTML)知识
HTML是超文本标记语言,被web浏览器进行解析查看。它的文档制作简单,功能强大 ,支持很多其他格式文件的嵌入。”超文本“文档主要由头部(head)和主体(body )两部分组成。
文档主体部分可包含的标签元素有很多,各个标签元素的功能也不同,例如: <div id=‘id’ class=‘class’ attr=‘’>content</div>
div是标签名
id是为该标签设置的唯一标识
class是该标签的样式类
attr是设置的其他属性
content是的标签的文本内容
先来看一段简单的网页编码,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
h1{color:red;}
#header1{font-family:隶书;}
.header1{font-size:60px;}
</style>
</head>
hello world
# 超链接
<a href="http:www.baidu.com">百度</a>
<img src="http://pic.netbian.com/uploads/allimg/180906/180605-1536228365101e.jpg" alt="">
<h1 id="header1">1号一级标题</h1>
<h1 class="header1">2号一级标题</h1>
<h2>二级标题</h2>
<h6>六级标题</h6>
<p>段落文字</p>
# 列表标签
<li>子标签</li>,<li></li>,<li></li>,<li></li>
<div>容器</div>
<span>文字类</span>
文本框:<input type="text">
单选框:<input type="radio">男
<input type="radio">女
多选框:<input type="checkbox">语文
<input type="checkbox">数学
密码框:<input type="password">
按钮:<input type="button" value="我是按钮">
<select>
<option value="">0001</option>
<option value="">0002</option>
<option value="">0003</option>
<option value="">0004</option>
<option value="">0005</option>
<option value="">0006</option>
</select>
</body>
</html>常用标签:
a 超链接 ,img 图片 ,h1 h2 ... h6 标题
p, ul+li 容器 , div 容器, span 文本
input 输入 设置标签属性
选择器: 标签选择器 id选择器 类选择器
id选择器:#id_name,选择id=id_name的所有元素
类选择器:.cls_name,选择class=cls_name的所有元素
标签选择:lable,选择标签名为lable的所有元素,用逗号隔开可选择多个标签
全部选择:*,选择所有的元素
交集选择器:h1.head1{} 连起来写
并集选择器:a,span{} 逗号隔开
后台选择器:
div p{} 会选取到内的
div>p {} 第一代
好的,简单的网页基础之后就来看看怎样获取正确的网页内容吧
(1)正则表达式获取网页内容
正则表达式是一个特殊的字符序列,它能帮助你方便的检查 一个字符串是否与某种模式匹配。Python 自带了re模块,它提供了对正则表达式的支持。
规则的创建:例如:reg =re.compile('提取规则',第二个参数)
第二个参数:
re.S 改变 . 的模式,可以匹配 空行
re.I 忽略大小写
正则表达式通常通过特殊的语法来表示。方法如下:
(1)^表示字符串的开始,$表示字符串的末尾
(2)字母和数字表示他们自身。一个正则表达式模式中的字母和数字 匹配同样的字符串。
(3)其它模式特殊符号描述
正则表达式非常强大,在这里我们只说一下如何获取我们需要的网页内容,简单来说只有两点:
1.需要留下的 用(.*?)注意前后一定要有一个原来存在的内容
2. 删除的用.*?
以51job职位信息为例,打开网站右击检查就可以看到网页编码
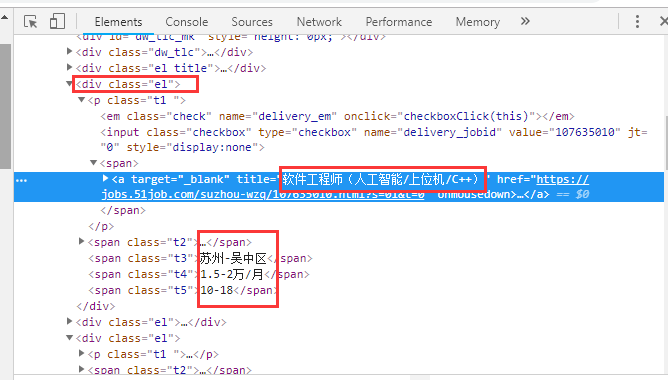
我们需要的是职位名称以及地区、薪资、发布时间等职位信息,创建规则如下:
reg = re.compile('<div class="el">.*?<a target="_blank" title="(.*?)".*?<a target="_blank" title="(.*?)".*?<span class="t3">(.*?)</span>.*?<span class="t4">(.*?)</span>.*?<span class="t5">(.*?)</span>.*?</div>',re.S)
data = re.findall(reg,html)这样就可以将这一页所有的职位信息提取出来。
(2)beautifulsoup获取网页内容
#导入 bs4 库
import bs4
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
#准备一串heml代码信息用来练习获取内容
html = """
<head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<h1><b>123456</b></h1>
<p class="title" name="dromouse">
<b>The Dormouse's story</b>
aaaaa
<p class="title" name="dromouse" title='new'><b>The Dormouse's story</b>a</p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="siterr" id="link4">Tillie</a>;
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="siterr" id="link5">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
<p class="story">...</p>
<ul id="ulone">
<li>01</li>
<li>02</li>
<li>03</li>
<li>04</li>
<li>05</li>
<div class='div11'>
<ul id="ultwo">
<li>0001</li>
<li>0002</li>
<li>0003</li>
<li>0004</li>
<li>0005</li>
</body>
</html>
#1.得到beautifulsoup对象
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'html.parser')
#2.获取内容
#获取标题对象
print(soup.title)
#获取文本内容
print(soup.title.get_text())
print(soup.title.string)
print(soup.title.text)
#通过上下级关系获取
print(soup.title.parent)
print(soup.title.child)#没有下级返回None
#获取第一个P标签
print(soup.p)
#获取P的孩子们
print(soup.p.children)
for i,each in enumerate(soup.p.children):
print(i,each)
print(list(soup.p.children)[2])
#获取标签的属性
print(soup.a)
print(soup.a.id)#获取不到
print(soup.a.href)#获取不到
print(soup.a.name)
#应该这样写
print(soup.a.attrs['id'])
print(soup.a.attrs['href'])
print(soup.a.attrs['class'])#class得到一个list
#获取多个
print(soup.find('p'))#获取一个P
print(soup.find_all('p'))#获取SOUP内的P,要看是谁的find_all()
#多层查询
print(soup.find_all('ul')[0].find_all('li'))
print(soup.find('ul').find_all('li'))
#通过指定的 属性获取对象
print(soup.find(id='ulone'))#单个对象
print(soup.find('ul',id='ulone'))#单个对象
print(soup.find_all('ul',id='ulone'))#这个是列表,实际使用要加下表的
#calss这么写class_
print(soup.find_all('p',class_='title'))
#更通用的方式
print(soup.find_all('p',attrs={'class':'title'}))
print(soup.find_all('p',attrs={'class':'title','title':'new'}))
#使用函数 作为参数获取元素
def judgeTitle(t):
if t == 'div11':
return True
print(soup.find_all(class_=judgeTitle))
import re
reg = re.compile('sis')
def judgeLen(t):
#f返回长度为6,且包含’sis‘的参数
return len(str(t))==6 and bool(re.search(reg,t))
print(soup.find_all(class_=judgeLen))
#limit参数:限制访问个数
print(soup.find_all('a',limit=2))
#recursive参数:recursive = Ture 寻找子孙。false只寻找子
print(soup.find_all('body')[0].find_all('ul',recursive='false'))注意 :beautifulsoup获取网页内容必须先将网页内容转化为beautifulsoup对象
(3)xpath获取网页内容
/ 从根节点选取。
// 从匹配选择的当前节点选择文档中的节点,而不考虑它们的位置。
. 选取当前节点。
.. 选取当前节点的父节点。
@ 选取属性。
#导入模块
from scrapy.selector import Selector
#练习用的网页编码
html = '''<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<bookstore>
<title lang="eng1">Harry Potter</title>
<price>29.99</price>
<book>123456</book>
</book>
<title lang="eng2">Learning XML</title>
<price>39.95</price>
</book>
22222222
</book>
3333333
</book>
</bookstore>'''
selector = Selector(text=html)
#//book 选取所有Book标签
#单独获取第二个boook
#方法一:列表下标
#print(selector.xpath('//book')[1])
#方法二:xpath方法,xpath字符串内,下标从一开始.选取某某内的第一个
#推荐下面的写法,先确定父元素
# print(selector.xpath('//div')[0].xpath('book[1]'))
# # print(selector.xpath('//div')[0].xpath('book')[0])
# # #@表示的是某标签的属性,<p class='p1'></p> //
# # print(selector.xpath('//@lang'))
# # #zhidingshuxing
# # print(selector.xpath('//title[@lang="eng1"]'))\
# / 一般用来层层寻找,不能跳层
bookstore = selector.xpath('//bookstore')[0]
#print(bookstore.xpath('./book/div/book'))
#last的用法:提取父元素下倒数的子元素,计数从0开始
print(bookstore.xpath('./book[last()-1]'))
#position的用法:提取父元素下正数的子元素,计数从1开始
print(bookstore.xpath('./book[position()>=3]'))
print(bookstore.xpath('//title | //price'))
(4)css获取网页内容
CSS选择器用于选择你想要的元素的样式的模式。
下面以网易云音乐排行榜举例说明:
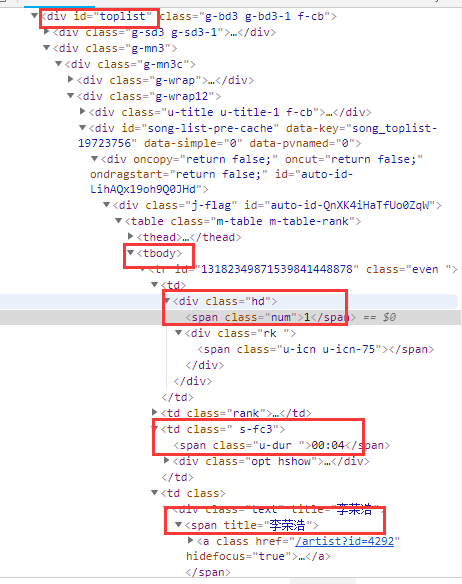
假设我们现在要获取排行榜的排名、歌手、歌曲:
#寻找大容器(相当于父节点)
toplist = browser.find_element_by_id('toplist')
#寻找tbody
tbody = toplist.find_elements_by_tag_name('tbody')[0]
#寻找所有tr
trs = tbody.find_elements_by_tag_name('tr')
#创建一个列表来接受获取的内容
datalist = []
#for循环遍历每一个tr,找到我们需要的元素
for each in trs:
#获取排名
rank = each.find_elements_by_tag_name('td')[0].find_element_by_class_name('num').text
#获取歌曲名称
