Vue + TypeScript + Element 项目实战及踩坑记

前言
本文讲解如何在 Vue 项目中使用 TypeScript 来搭建并开发项目,并在此过程中踩过的坑 。
TypeScript 具有类型系统,且是 JavaScript 的超集,TypeScript 在 2018年 势头迅猛,可谓遍地开花。
Vue3.0 将使用 TS 重写,重写后的 Vue3.0 将更好的支持 TS。2019 年 TypeScript 将会更加普及,能够熟练掌握 TS,并使用 TS 开发过项目,将更加成为前端开发者的优势。
所以笔者就当然也要学这个必备技能,就以 边学边实践 的方式,做个博客项目来玩玩。
此项目是基于 Vue 全家桶 + TypeScript + Element-UI 的技术栈,且已经开源,github 地址 blog-vue-typescript 。
因为之前写了篇纯 Vue 项目搭建的相关文章 基于vue+mint-ui的mobile-h5的项目说明 ,有不少人加我微信,要源码来学习,但是这个是我司的项目,不能提供原码。
所以做一个不是我司的项目,且又是 vue 相关的项目来练手并开源吧。
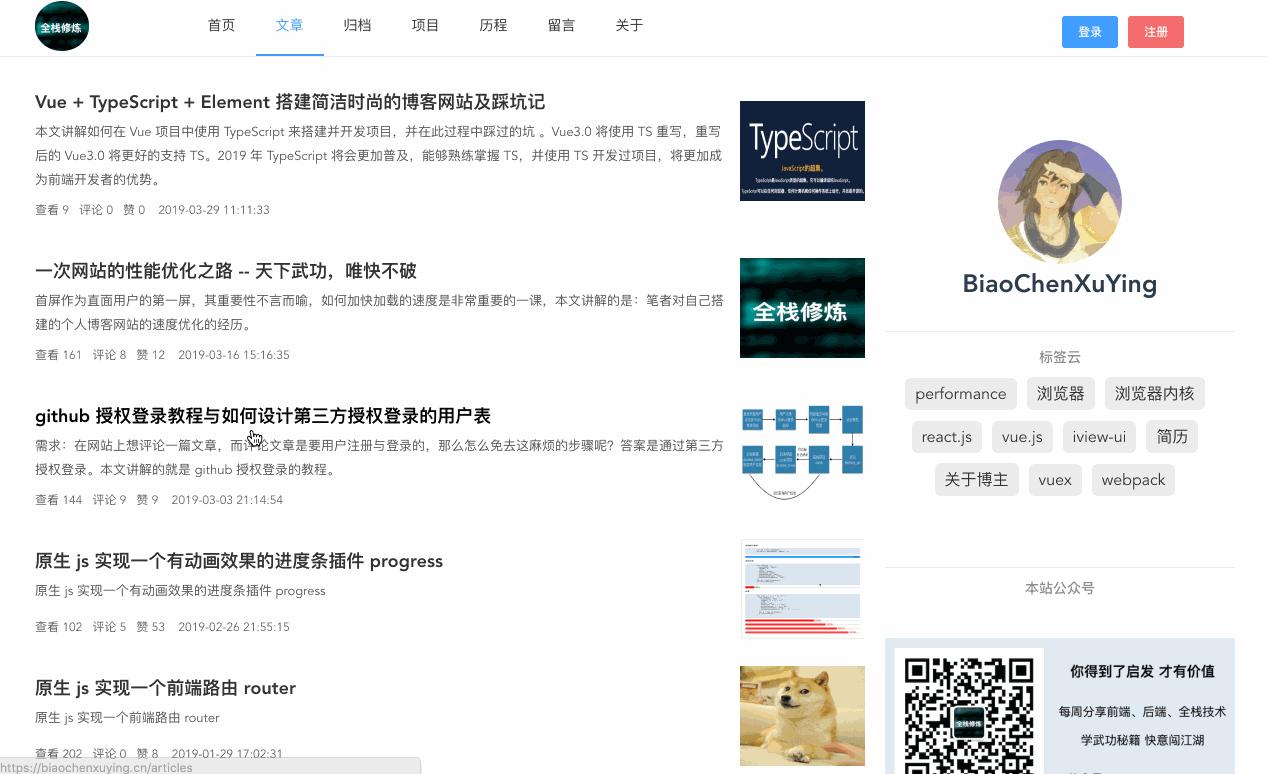
1. 效果
效果图:
- pc 端
- 移动端

完整效果请看: https://biaochenxuying.cn
2. 功能
已经完成功能
√ 登录
√ 注册
√ 文章列表
√ 文章归档
√ 标签
√ 关于
√ 点赞与评论
√ 留言
√ 历程
√ 文章详情(支持代码语法高亮)
√ 文章详情目录
√ 移动端适配
√ github 授权登录
待优化或者实现
x 使用 vuex-class
x 更多 TypeScript 的优化技巧
x 服务器渲染 SSR
3. 前端主要技术
所有技术都是当前最新的。
- vue: ^2.6.6
- typescript : ^3.2.1
- element-ui: 2.6.3
- vue-router : ^3.0.1
- webpack: 4.28.4
- vuex: ^3.0.1
- axios:0.18.0
- highlight.js: 9.15.6
- marked:0.6.1
4. 5 分钟上手 TypeScript
如果没有一点点基础,可能没学过 TypeScript 的读者会看不懂往下的内容,所以先学点基础。
TypeScript 的静态类型检查是个好东西,可以避免很多不必要的错误, 不用在调试或者项目上线的时候才发现问题 。
- 类型注解
TypeScript 里的类型注解是一种轻量级的为函数或变量添加约束的方式。变量定义时也要定义他的类型,比如常见的 :
// 布尔值
let isDone: boolean = false; // 相当于 js 的 let isDone = false;
// 变量定义之后不可以随便变更它的类型
isDone = true // 不报错
isDone = "我要变为字符串" // 报错
// 数字
let decLiteral: number = 6; // 相当于 js 的 let decLiteral = 6;
// 字符串
let name: string = "bob"; // 相当于 js 的 let name = "bob";
// 数组
// 第一种,可以在元素类型后面接上 [],表示由此类型元素组成的一个数组:
let list: number[] = [1, 2, 3]; // 相当于 js 的let list = [1, 2, 3];
// 第二种方式是使用数组泛型,Array<元素类型>:
let list: Array<number> = [1, 2, 3]; // 相当于 js 的let list = [1, 2, 3];
// 在 TypeScript 中,我们使用接口(Interfaces)来定义 对象 的类型。
interface Person {
name: string;
age: number;
let tom: Person = {
name: 'Tom',
age: 25
// 以上 对象 的代码相当于
let tom = {
name: 'Tom',
age: 25
// Any 可以随便变更类型 (当这个值可能来自于动态的内容,比如来自用户输入或第三方代码库)
let notSure: any = 4;
notSure = "我可以随便变更类型" // 不报错
notSure = false; // 不报错
// Void 当一个函数没有返回值时,你通常会见到其返回值类型是 void
function warnUser(): void {
console.log("This is my warning message");
// 方法的参数也要定义类型,不知道就定义为 any
function fetch(url: string, id : number, params: any): void {
console.log("fetch");
以上是最简单的一些知识点,更多知识请看 TypeScript 中文官网
5. 5 分钟上手 Vue +TypeScript
-
vue-class-component
vue-class-component 对Vue组件进行了一层封装,让Vue组件语法在结合了TypeScript语法之后更加扁平化:
<template>
<input v-model="msg">
<p>prop: {{propMessage}}</p>
<p>msg: {{msg}}</p>
<p>helloMsg: {{helloMsg}}</p>
<p>computed msg: {{computedMsg}}</p>
<button @click="greet">Greet</button>
</template>
<script>
import Vue from 'vue'
import Component from 'vue-class-component'
@Component({
props: {
propMessage: String
export default class App extends Vue {
// initial data
msg = 123
// use prop values for initial data
helloMsg = 'Hello, ' + this.propMessage
// lifecycle hook
mounted () {
this.greet()
// computed
get computedMsg () {
return 'computed ' + this.msg
// method
greet () {
alert('greeting: ' + this.msg)
</script>
上面的代码跟下面的代码作用是一样的:
<template>
<input v-model="msg">
<p>prop: {{propMessage}}</p>
<p>msg: {{msg}}</p>
<p>helloMsg: {{helloMsg}}</p>
<p>computed msg: {{computedMsg}}</p>
<button @click="greet">Greet</button>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// 属性
props: {
propMessage: {
type: String
data () {
return {
msg: 123,
helloMsg: 'Hello, ' + this.propMessage
// 声明周期钩子
mounted () {
this.greet()
// 计算属性
computed: {
computedMsg () {
return 'computed ' + this.msg
// 方法
methods: {
greet () {
alert('greeting: ' + this.msg)
</script>
vue-property-decorator 是在
vue-class-component
上增强了更多的结合
Vue
特性的装饰器,新增了这 7 个装饰器:
-
@Emit -
@Inject -
@Model -
@Prop -
@Provide -
@Watch -
@Component(从vue-class-component继承)
在这里列举几个常用的
@Prop/@Watch/@Component
, 更多信息,详见
官方文档
import { Component, Emit, Inject, Model, Prop, Provide, Vue, Watch } from 'vue-property-decorator'
@Component
export class MyComponent extends Vue {
@Prop()
propA: number = 1
@Prop({ default: 'default value' })
propB: string
@Prop([String, Boolean])
propC: string | boolean
@Prop({ type: null })
propD: any
@Watch('child')
onChildChanged(val: string, oldVal: string) { }
上面的代码相当于:
export default {
props: {
checked: Boolean,
propA: Number,
propB: {
type: String,
default: 'default value'
propC: [String, Boolean],
propD: { type: null }
methods: {
onChildChanged(val, oldVal) { }
watch: {
'child': {
handler: 'onChildChanged',
immediate: false,
deep: false
-
vuex-class
vuex-class :在vue-class-component写法中 绑定vuex。
import Vue from 'vue'
import Component from 'vue-class-component'
import {
State,
Getter,
Action,
Mutation,
namespace
} from 'vuex-class'
const someModule = namespace('path/to/module')
@Component
export class MyComp extends Vue {
@State('foo') stateFoo
@State(state => state.bar) stateBar
@Getter('foo') getterFoo
@Action('foo') actionFoo
@Mutation('foo') mutationFoo
@someModule.Getter('foo') moduleGetterFoo
// If the argument is omitted, use the property name
// for each state/getter/action/mutation type
@State foo
@Getter bar
@Action baz
@Mutation qux
created () {
this.stateFoo // -> store.state.foo
this.stateBar // -> store.state.bar
this.getterFoo // -> store.getters.foo
this.actionFoo({ value: true }) // -> store.dispatch('foo', { value: true })
this.mutationFoo({ value: true }) // -> store.commit('foo', { value: true })
this.moduleGetterFoo // -> store.getters['path/to/module/foo']
6. 用 vue-cli 搭建 项目
笔者使用最新的 vue-cli 3 搭建项目,详细的教程,请看我之前写的 vue-cli3.x 新特性及踩坑记 ,里面已经有详细讲解 ,但文章里面的配置和此项目不同的是,我加入了 TypeScript ,其他的配置都是 vue-cli 本来配好的了。详情请看 vue-cli 官网 。
6.1 安装及构建项目目录
安装的依赖:
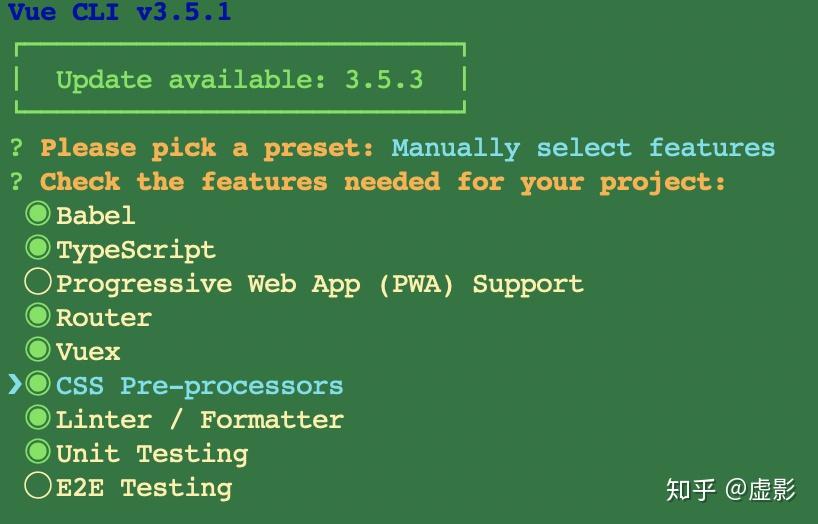
安装过程选择的一些配置:

搭建好之后,初始项目结构长这样:
├── public // 静态页面
├── src // 主目录
├── assets // 静态资源
├── components // 组件
├── views // 页面
├── App.vue // 页面主入口
├── main.ts // 脚本主入口
├── router.ts // 路由
├── shims-tsx.d.ts // 相关 tsx 模块注入
├── shims-vue.d.ts // Vue 模块注入
└── store.ts // vuex 配置
├── tests // 测试用例
├── .eslintrc.js // eslint 相关配置
├── .gitignore // git 忽略文件配置
├── babel.config.js // babel 配置
├── postcss.config.js // postcss 配置
├── package.json // 依赖
└── tsconfig.json // ts 配置
奔着 大型项目的结构 来改造项目结构,改造后 :
├── public // 静态页面
├── src // 主目录
├── assets // 静态资源
├── filters // 过滤
├── store // vuex 配置
├── less // 样式
├── utils // 工具方法(axios封装,全局方法等)
├── views // 页面
├── App.vue // 页面主入口
├── main.ts // 脚本主入口
├── router.ts // 路由
├── shime-global.d.ts // 相关 全局或者插件 模块注入
├── shims-tsx.d.ts // 相关 tsx 模块注入
├── shims-vue.d.ts // Vue 模块注入, 使 TypeScript 支持 *.vue 后缀的文件
├── tests // 测试用例
├── .eslintrc.js // eslint 相关配置
├── postcss.config.js // postcss 配置
├── .gitignore // git 忽略文件配置
├── babel.config.js // preset 记录
├── package.json // 依赖
├── README.md // 项目 readme
├── tsconfig.json // ts 配置
└── vue.config.js // webpack 配置
tsconfig.json 文件中指定了用来编译这个项目的根文件和编译选项。
本项目的 tsconfig.json 配置如下 :
{
// 编译选项
"compilerOptions": {
// 编译输出目标 ES 版本
"target": "esnext",
// 采用的模块系统
"module": "esnext",
// 以严格模式解析
"strict": true,
"jsx": "preserve",
// 从 tslib 导入外部帮助库: 比如__extends,__rest等
"importHelpers": true,
// 如何处理模块
"moduleResolution": "node",
// 启用装饰器
"experimentalDecorators": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
// 允许从没有设置默认导出的模块中默认导入
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true,
// 定义一个变量就必须给它一个初始值
"strictPropertyInitialization" : false,
// 允许编译javascript文件
"allowJs": true,
// 是否包含可以用于 debug 的 sourceMap
"sourceMap": true,
// 忽略 this 的类型检查, Raise error on this expressions with an implied any type.
"noImplicitThis": false,
// 解析非相对模块名的基准目录
"baseUrl": ".",
// 给错误和消息设置样式,使用颜色和上下文。
"pretty": true,
// 设置引入的定义文件
"types": ["webpack-env", "mocha", "chai"],
// 指定特殊模块的路径
"paths": {
"@/*": ["src/*"]
// 编译过程中需要引入的库文件的列表
"lib": ["esnext", "dom", "dom.iterable", "scripthost"]
// ts 管理的文件
"include": [
"src/**/*.ts",
"src/**/*.tsx",
"src/**/*.vue",
"tests/**/*.ts",
"tests/**/*.tsx"
// ts 排除的文件
"exclude": ["node_modules"]
更多配置请看官网的 tsconfig.json 的 编译选项
本项目的 vue.config.js:
const path = require("path");
const sourceMap = process.env.NODE_ENV === "development";
module.exports = {
// 基本路径
publicPath: "./",
// 输出文件目录
outputDir: "dist",
// eslint-loader 是否在保存的时候检查
lintOnSave: false,
// webpack配置
// see https://github.com/vuejs/vue-cli/blob/dev/docs/webpack.md
chainWebpack: () => {},
configureWebpack: config => {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === "production") {
// 为生产环境修改配置...
config.mode = "production";
} else {
// 为开发环境修改配置...
config.mode = "development";
Object.assign(config, {
// 开发生产共同配置
resolve: {
extensions: [".js", ".vue", ".json", ".ts", ".tsx"],
alias: {
vue$: "vue/dist/vue.js",
"@": path.resolve(__dirname, "./src")
// 生产环境是否生成 sourceMap 文件
productionSourceMap: sourceMap,
// css相关配置
css: {
// 是否使用css分离插件 ExtractTextPlugin
extract: true,
// 开启 CSS source maps?
sourceMap: false,
// css预设器配置项
loaderOptions: {},
// 启用 CSS modules for all css / pre-processor files.
modules: false
// use thread-loader for babel & TS in production build
// enabled by default if the machine has more than 1 cores
parallel: require("os").cpus().length > 1,
// PWA 插件相关配置
// see https://github.com/vuejs/vue-cli/tree/dev/packages/%40vue/cli-plugin-pwa
pwa: {},
// webpack-dev-server 相关配置
devServer: {
open: process.platform === "darwin",
host: "localhost",
port: 3001, //8080,
https: false,
hotOnly: false,
proxy: {
// 设置代理
// proxy all requests starting with /api to jsonplaceholder
"/api": {
// target: "https://emm.cmccbigdata.com:8443/",
target: "http://localhost:3000/",
// target: "http://47.106.136.114/",
changeOrigin: true,
ws: true,
pathRewrite: {
"^/api": ""
before: app => {}
// 第三方插件配置
pluginOptions: {
// ...
6.2 安装 element-ui
本来想搭配 iview-ui 来用的,但后续还想把这个项目搞成 ssr 的,而 vue + typescript + iview + Nuxt.js 的服务端渲染还有不少坑, 而 vue + typescript + element + Nuxt.js 对 ssr 的支持已经不错了,所以选择了 element-ui 。
安装:
npm i element-ui -S
按需引入, 借助 babel-plugin-component ,我们可以只引入需要的组件,以达到减小项目体积的目的。
npm install babel-plugin-component -D
然后,将 babel.config.js 修改为:
module.exports = {
presets: ["@vue/app"],
plugins: [
"component",
libraryName: "element-ui",
styleLibraryName: "theme-chalk"
接下来,如果你只希望引入部分组件,比如 Button 和 Select,那么需要在 main.js 中写入以下内容:
import Vue from 'vue';
import { Button, Select } from 'element-ui';
import App from './App.vue';
Vue.component(Button.name, Button);
Vue.component(Select.name, Select);
/* 或写为
* Vue.use(Button)
* Vue.use(Select)
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
6.3 完善项目目录与文件
route
使用路由懒加载功能。
export default new Router({
mode: "history",
routes: [
path: "/",
name: "home",
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "home" */ "./views/home.vue")
path: "/articles",
name: "articles",
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (articles.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () =>
import(/* webpackChunkName: "articles" */ "./views/articles.vue")
utils
- utils/utils.ts 常用函数的封装, 比如 事件的节流(throttle)与防抖(debounce)方法:
// fn是我们需要包装的事件回调, delay是时间间隔的阈值
export function throttle(fn: Function, delay: number) {
// last为上一次触发回调的时间, timer是定时器
let last = 0,
timer: any = null;
// 将throttle处理结果当作函数返回
return function() {
// 保留调用时的this上下文
let context = this;
// 保留调用时传入的参数
let args = arguments;
// 记录本次触发回调的时间
let now = +new Date();
// 判断上次触发的时间和本次触发的时间差是否小于时间间隔的阈值
if (now - last < delay) {
// 如果时间间隔小于我们设定的时间间隔阈值,则为本次触发操作设立一个新的定时器
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(function() {
last = now;
fn.apply(context, args);
}, delay);
} else {
// 如果时间间隔超出了我们设定的时间间隔阈值,那就不等了,无论如何要反馈给用户一次响应
last = now;
fn.apply(context, args);
- utils/config.ts 配置文件,比如 github 授权登录的回调地址、client_id、client_secret 等。
const config = {
'oauth_uri': 'https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize',
'redirect_uri': 'https://biaochenxuying.cn/login',
'client_id': 'XXXXXXXXXX',
'client_secret': 'XXXXXXXXXX',
// 本地开发环境下
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {
config.redirect_uri = "http://localhost:3001/login"
config.client_id = "502176cec65773057a9e"
config.client_secret = "65d444de381a026301a2c7cffb6952b9a86ac235"
export default config;
如果你的生产环境也要 github 登录授权的话,请在 github 上申请一个 Oauth App ,把你的 redirect_uri,client_id,client_secret 的信息填在 config 里面即可。具体详情请看我写的这篇文章 github 授权登录教程与如何设计第三方授权登录的用户表
- utils/urls.ts 请求接口地址,统一管理。
// url的链接
export const urls: object = {
login: "login",
register: "register",
getArticleList: "getArticleList",
export default urls;
- utils/https.ts axios 请求的封装。
import axios from "axios";
// 创建axios实例
let service: any = {};
service = axios.create({
baseURL: "/api", // api的base_url
timeout: 50000 // 请求超时时间
// request拦截器 axios的一些配置
service.interceptors.request.use(
(config: any) => {
return config;
(error: any) => {
// Do something with request error
console.error("error:", error); // for debug
Promise.reject(error);
// respone拦截器 axios的一些配置
service.interceptors.response.use(
(response: any) => {
return response;
(error: any) => {
console.error("error:" + error); // for debug
return Promise.reject(error);
export default service;
把 urls 和 https 挂载到 main.ts 里面的 Vue 的 prototype 上面。
import service from "./utils/https";
import urls from "./utils/urls";
Vue.prototype.$https = service; // 其他页面在使用 axios 的时候直接 this.$http 就可以了
Vue.prototype.$urls = urls; // 其他页面在使用 urls 的时候直接 this.$urls 就可以了
然后就可以统一管理接口,而且调用起来也很方便啦。比如下面 文章列表的请求。
async handleSearch() {
this.isLoading = true;
const res: any = await this.$https.get(this.$urls.getArticleList, {
params: this.params
this.isLoading = false;
if (res.status === 200) {
if (res.data.code === 0) {
const data: any = res.data.data;
this.articlesList = [...this.articlesList, ...data.list];
this.total = data.count;
this.params.pageNum++;
if (this.total === this.articlesList.length) {
this.isLoadEnd = true;
} else {
this.$message({
message: res.data.message,
type: "error"
} else {
this.$message({
message: "网络错误!",
type: "error"
store ( Vuex )
一般大型的项目都有很多模块的,比如本项目中有公共信息(比如 token )、 用户模块、文章模块。
├── modules // 模块
├── user.ts // 用户模块
├── article.ts // 文章模块
├── types.ts // 类型
└── index.ts // vuex 主入口
- store/index.ts 存放公共的信息,并导入其他模块
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
import * as types from "./types";
import user from "./modules/user";
import article from "./modules/article";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const initPageState = () => {
return {
token: ""
const store = new Vuex.Store({
strict: process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production",
// 具体模块
modules: {
user,
article
state: initPageState(),
mutations: {
[types.SAVE_TOKEN](state: any, pageState: any) {
for (const prop in pageState) {
state[prop] = pageState[prop];
actions: {}
export default store;
- types.ts
// 公共 token
export const SAVE_TOKEN = "SAVE_TOKEN";
// 用户
export const SAVE_USER = "SAVE_USER";
- user.ts
import * as types from "../types";
const initPageState = () => {
return {
userInfo: {
_id: "",
name: "",
avator: ""
const user = {
state: initPageState(),
mutations: {
[types.SAVE_USER](state: any, pageState: any) {
for (const prop in pageState) {
state[prop] = pageState[prop];
actions: {}
export default user;
7. markdown 渲染
markdown 渲染效果图:

markdown 渲染 采用了开源的 marked, 代码高亮用了 highlight.js 。
用法:
第一步:npm i marked highlight.js --save
npm i marked highlight.js --save
第二步: 导入封装成 markdown.js,将文章详情由字符串转成 html, 并抽离出文章目录。
marked 的封装 得感谢这位老哥。
const highlight = require("highlight.js");
const marked = require("marked");
const tocObj = {
add: function(text, level) {
var anchor = `#toc${level}${++this.index}`;
this.toc.push({ anchor: anchor, level: level, text: text });
return anchor;
// 使用堆栈的方式处理嵌套的ul,li,level即ul的嵌套层次,1是最外层
// <ul>
// <li></li>
// <ul>
// <li></li>
// </ul>
// <li></li>
// </ul>
toHTML: function() {
let levelStack = [];
let result = "";
const addStartUL = () => {
result += '<ul class="anchor-ul" id="anchor-fix">';
const addEndUL = () => {
result += "</ul>\n";
const addLI = (anchor, text) => {
result +=
'<li><a class="toc-link" href="#' + anchor + '">' + text + "<a></li>\n";
this.toc.forEach(function(item) {
let levelIndex = levelStack.indexOf(item.level);
// 没有找到相应level的ul标签,则将li放入新增的ul中
if (levelIndex === -1) {
levelStack.unshift(item.level);
addStartUL();
addLI(item.anchor, item.text);
} // 找到了相应level的ul标签,并且在栈顶的位置则直接将li放在此ul下
else if (levelIndex === 0) {
addLI(item.anchor, item.text);
} // 找到了相应level的ul标签,但是不在栈顶位置,需要将之前的所有level出栈并且打上闭合标签,最后新增li
else {
while (levelIndex--) {
levelStack.shift();
addEndUL();
addLI(item.anchor, item.text);
// 如果栈中还有level,全部出栈打上闭合标签
while (levelStack.length) {
levelStack.shift();
addEndUL();
// 清理先前数据供下次使用
this.toc = [];
this.index = 0;
return result;
toc: [],
index: 0
class MarkUtils {
constructor() {
this.rendererMD = new marked.Renderer();
this.rendererMD.heading = function(text, level, raw) {
var anchor = tocObj.add(text, level);
return `<h${level} id=${anchor}>${text}</h${level}>\n`;
highlight.configure({ useBR: true });
marked.setOptions({
renderer: this.rendererMD,
headerIds: false,
gfm: true,
tables: true,
breaks: false,
pedantic: false,
sanitize: false,
smartLists: true,
smartypants: false,
highlight: function(code) {
return highlight.highlightAuto(code).value;
async marked(data) {
if (data) {
let content = await marked(data); // 文章内容
let toc = tocObj.toHTML(); // 文章目录
return { content: content, toc: toc };
} else {
return null;
const markdown = new MarkUtils();
export default markdown;
第三步: 使用
import markdown from "@/utils/markdown";
// 获取文章详情
async handleSearch() {
const res: any = await this.$https.post(
this.$urls.getArticleDetail,
this.params
if (res.status === 200) {
if (res.data.code === 0) {
this.articleDetail = res.data.data;
// 使用 marked 转换
const article = markdown.marked(res.data.data.content);
article.then((response: any) => {
this.articleDetail.content = response.content;
this.articleDetail.toc = response.toc;
} else {
// ...
} else {
// ...
// 渲染
<div id="content"
class="article-detail"
v-html="articleDetail.content">
第四步:引入 monokai_sublime 的 css 样式
<link href="http://cdn.bootcss.com/highlight.js/8.0/styles/monokai_sublime.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
第五步:对 markdown 样式的补充
如果不补充样式,是没有黑色背景的,字体大小等也会比较小,图片也不会居中显示
/*对 markdown 样式的补充*/
pre {
display: block;
padding: 10px;
margin: 0 0 10px;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 1.42857143;
color: #abb2bf;
background: #282c34;
word-break: break-all;
word-wrap: break-word;
overflow: auto;
h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6{
margin-top: 1em;
/* margin-bottom: 1em; */
strong {
font-weight: bold;
p > code:not([class]) {
padding: 2px 4px;
font-size: 90%;
color: #c7254e;
background-color: #f9f2f4;
border-radius: 4px;
p img{
/* 图片居中 */
margin: 0 auto;
display: flex;
#content {
font-family: "Microsoft YaHei", 'sans-serif';
font-size: 16px;
line-height: 30px;
#content .desc ul,#content .desc ol {
color: #333333;
margin: 1.5em 0 0 25px;
#content .desc h1, #content .desc h2 {
border-bottom: 1px solid #eee;
padding-bottom: 10px;
#content .desc a {
color: #009a61;
8. 注意点
- 关于 页面
对于 关于 的页面,其实是一篇文章来的,根据文章类型 type 来决定的,数据库里面 type 为 3
的文章,只能有一篇就是 博主介绍 ;达到了想什么时候修改内容都可以。
所以当 当前路由 === '/about' 时就是请求类型为 博主介绍 的文章。
type: 3, // 文章类型: 1:普通文章;2:是博主简历;3 :是博主简介;
-
移动端适配
移动端使用 rem 单位适配。
// 屏幕适配( window.screen.width / 移动端设计稿宽 * 100)也即是 (window.screen.width / 750 * 100) ——*100 为了方便计算。即 font-size 值是手机 deviceWidth 与设计稿比值的 100 倍
document.getElementsByTagName('html')[0].style.fontSize = window.screen.width / 7.5 + 'px';
如上:通过查询屏幕宽度,动态的设置 html 的 font-size 值,移动端的设计稿大多以宽为 750 px 来设置的。
比如在设计图上一个 150 * 250 的盒子(单位 px):
原本在 css 中的写法:
width: 150px;
heigth: 250px;
通过上述换算后,在 css 中对应的 rem 值只需要写:
width: 1.5rem; // 150 / 100 rem
heigth: 2.5rem; // 250 / 100 rem
如果你的移动端的设计稿是以宽为 1080 px 来设置的话,就用 window.screen.width / 10.8 吧。
9. 踩坑记
- 1. 让 vue 识别全局方法/变量
- 我们经常在 main.ts 中给 vue.prototype 挂载实例或者内容,以方便在组件里面使用。
import service from "./utils/https";
import urls from "./utils/urls";
Vue.prototype.$https = service; // 其他页面在使用 axios 的时候直接 this.$http 就可以了
Vue.prototype.$urls = urls; // 其他页面在使用 urls 的时候直接 this.$urls 就可以了
然而当你在组件中直接 this. http 或者 this .urls 时会报错的,那是因为 http 和urls 属性,并没有在 vue 实例中声明。
- 再比如使用 Element-uI 的 meesage。
import { Message } from "element-ui";
Vue.prototype.$message = Message;
之前用法如下图:
this.$message({
message: '恭喜你,这是一条成功消息',
type: 'success'
然而还是会报错的。
再比如 监听路由的变化:
import { Vue, Watch } from "vue-property-decorator";
import Component from "vue-class-component";
import { Route } from "vue-router";
@Component
export default class App extends Vue {
@Watch("$route")
routeChange(val: Route, oldVal: Route) {
// do something
只是这样写的话,监听 $route 还是会报错的。
想要以上三种做法都正常执行,就还要补充如下内容:
在 src 下的 shims-vue.d.ts 中加入要挂载的内容。 表示 vue 里面的 this 下有这些东西。
import VueRouter, { Route } from "vue-router";
declare module "vue/types/vue" {
interface Vue {
$router: VueRouter; // 这表示this下有这个东西
$route: Route;
$https: any; // 不知道类型就定为 any 吧(偷懒)
$urls: any;
$Message: any;
- 2. 引入的模块要声明
比如 在组件里面使用 window.document 或者 document.querySelector 的时候会报错的,npm run build 不给通过。
再比如:按需引用 element 的组件与动画组件:
import { Button } from "element-ui";
import CollapseTransition from "element-ui/lib/transitions/collapse-transition";
npm run serve 时可以执行,但是在 npm run build 的时候,会直接报错的,因为没有声明。
正确做法:
我在 src 下新建一个文件 shime-global.d.ts ,加入内容如下:
// 声明全局的 window ,不然使用 window.XX 时会报错
declare var window: Window;
declare var document: Document;
declare module "element-ui/lib/transitions/collapse-transition";
declare module "element-ui";
当然,这个文件你加在其他地方也可以,起其他名字都 OK。
但是即使配置了以上方法之后,有些地方使用 http:// document.XXX ,比如 document.title 的时候,npm run build 还是通过不了,所以只能这样了:
<script lang="ts">
// 在用到 document.XXX 的文件中声明一下即可
declare var document: any;
// 此处省略 XXXX 多的代码
</script>
- 3. this 的类型检查
比如之前的 事件的节流(throttle)与防抖(debounce)方法:
export function throttle(fn: Function, delay: number) {
return function() {
// 保留调用时的 this 上下文
let context = this;
function 里面的 this 在 npm run serve 时会报错的,因为 tyescript 检测到它不是在类(class)里面。
正确做法:
在根目录的 tsconfig.json 里面加上 "noImplicitThis": false ,忽略 this 的类型检查。
// 忽略 this 的类型检查, Raise error on this expressions with an implied any type.
"noImplicitThis": false,
- 4. import 的 .vue 文件
import .vue 的文件的时候,要补全 .vue 的后缀,不然 npm run build 会报错的。
比如:
import Nav from "@/components/nav"; // @ is an alias to /src
import Footer from "@/components/footer"; // @ is an alias to /src
要修改为:
import Nav from "@/components/nav.vue"; // @ is an alias to /src
import Footer from "@/components/footer.vue"; // @ is an alias to /src
- 5. 装饰器 @Component
报错。
<script lang="ts">
import { Vue, Component } from "vue-property-decorator";
export default class LoadingCustom extends Vue {}
</script>
以下才是正确,因为这里的 Vue 是从 vue-property-decorator import 来的。
<script lang="ts">
import { Vue, Component } from "vue-property-decorator";
@Component
export default class LoadingCustom extends Vue {}
</script>
- 6. 路由的组件导航守卫失效
vue-class-component 官网里面的路由的导航钩子的用法是没有效果的 Adding Custom Hooks
路由的导航钩子不属于 Vue 本身,这会导致 class 组件转义到配置对象时导航钩子无效,因此如果要使用导航钩子需要在 router 的配置里声明(网上别人说的,还没实践,不确定是否可行)。
- 7. tsconfig.json 的 strictPropertyInitialization 设为 false,不然你定义一个变量就必须给它一个初始值。
- position: sticky;
本项目中的文章详情的目录就是用了 sticky。
.anchor {
position: sticky;
top: 213px;
margin-top: 213px;
position:sticky 是 css 定位新增属性;可以说是相对定位 relative 和固定定位 fixed 的结合;它主要用在对 scroll 事件的监听上;简单来说,在滑动过程中,某个元素距离其父元素的距离达到 sticky 粘性定位的要求时(比如 top:100px );position:sticky 这时的效果相当于 fixed 定位,固定到适当位置。
用法像上面那样用即可,但是有使用条件:
1、父元素不能 overflow:hidden 或者 overflow:auto 属性。
2、必须指定 top、bottom、left、right 4 个值之一,否则只会处于相对定位
3、父元素的高度不能低于 sticky 元素的高度
4、sticky 元素仅在其父元素内生效
- 8. eslint 报找不到文件和装饰器的错
App.vue 中只是写了引用文件而已,而且 webpack 和 tsconfig.josn 里面已经配置了别名了的。
import Nav from "@/components/nav.vue"; // @ is an alias to /src
import Slider from "@/components/slider.vue"; // @ is an alias to /src
import Footer from "@/components/footer.vue"; // @ is an alias to /src
import ArrowUp from "@/components/arrowUp.vue"; // @ is an alias to /src
import { isMobileOrPc } from "@/utils/utils";
但是,还是会报如下的错:

只是代码不影响文件的打包,而且本地与生产环境的代码也正常,没报错而已。
这个 eslint 的检测目前还没找到相关的配置可以把这些错误去掉。
- 9. 路由模式修改为 history
因为文章详情页面有目录,点击目录时定位定相应的内容,但是这个目录定位内容是根据锚点来做的,如果路由模式为 hash 模式的话,本来文章详情页面的路由就是 #articleDetail 了,再点击目录的话(比如 #title2 ),会在 #articleDetail 后面再加上 #title2,一刷新会找不到这个页面的。
10. Build Setup
// git clone
git clone https://github.com/biaochenxuying/blog-vue-typescript.git
// cd
cd blog-vue-typescript
// install dependencies
npm install
