当您需要将自建Elasticsearch中的全量或增量数据迁移至阿里云Elasticsearch时,可通过在ECS中自建Logstash,并通过Logstash的管道配置功能实现。本文为您介绍具体的实现方法。
背景信息
本文中数据迁移的流程如下。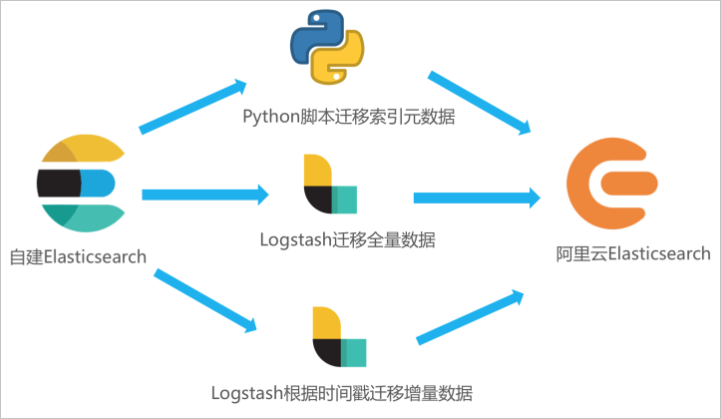
- 在ECS服务器部署自建Elasticsearch并准备待迁移的数据。
- 开通阿里云Elasticsearch服务。
- 在ECS服务器运行Python脚本迁移索引元数据。
- 部署Logstash,并通过Logstash管道配置功能,将自建Elasticsearch中的全量或增量数据迁移至阿里云Elasticsearch中。
注意事项
- 本文在阿里云ECS上部署自建Logstash,该Logstash所在的ECS需要与阿里云Elasticsearch集群在同一专有网络下,同时该Logstash需要能够同时访问源Elasticsearch集群(自建)和目标Elasticsearch集群(阿里云)。
- 数据迁移可以全量迁移或增量迁移。如果业务侧时刻存在写入更新,首次迁移时,需先全量迁移,再通过时间标识字段(或其他可标识增量的字段)进行增量迁移,否则迁移后新数据极易被旧数据覆盖。如果已有全量数据,可以只通过标识字段实现增量数据迁移。
操作流程
步骤一:准备环境与实例
-
创建阿里云Elasticsearch实例。
具体操作请参见 创建阿里云Elasticsearch实例 。本文使用的测试环境如下。
环境项 环境信息 地域 华东1(杭州)。 版本 通用商业版7.10.0。 实例规格配置 3个可用区、3个数据节点、单节点4核CPU、16 GB内存、100 GB ESSD云盘。 -
创建ECS实例,用于部署自建Elasticsearch、自建Kibana和自建Logstash。
具体操作请参见 自定义购买实例 。本文使用的测试环境如下。
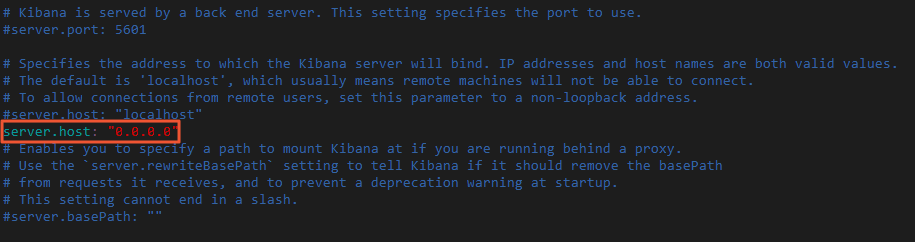
环境项 环境信息 地域 华东1(杭州)。 实例规格 4 vCPU 16 GiB内存。 镜像 公共镜像、CentOS、7.9 64位。 存储 系统盘、ESSD云盘、100 GiB。 网络 与阿里云Elasticsearch相同的专有网络,选中 分配公网IPv4地址 ,并按使用流量计费,带宽峰值为100 Mbps。 安全组 入方向添加5601端口(即Kibana端口),在授权对象中添加您客户端的IP地址。 重要- 如果您的客户端处在家庭网络或公司局域网中,您需要在授权对象中添加局域网的公网出口IP地址,而非客户端机器的IP地址。建议您通过浏览器访问 https://myip.ipip.net 查询。
- 您也可以在授权对象中添加0.0.0.0/0,表示允许所有IPv4地址访问ECS实例。此配置会导致ECS实例完全暴露在公网中,增加安全风险,生产环境尽量避免。
-
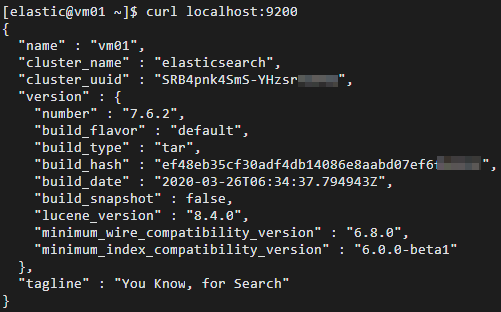
部署自建Elasticsearch。
本文使用的自建Elasticsearch版本为7.6.2,1个数据节点,具体操作步骤如下:
-
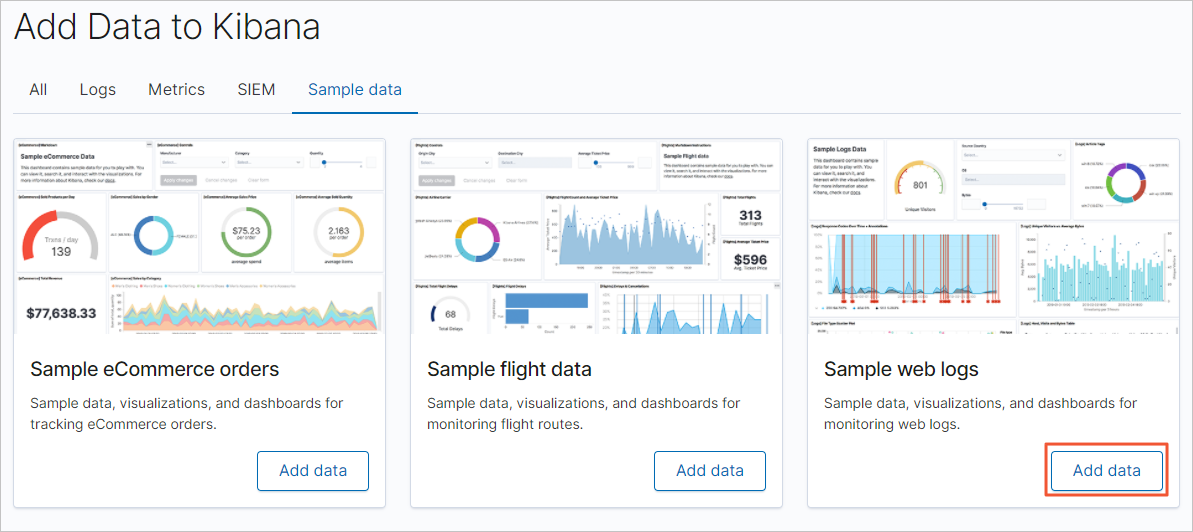
部署自建Kibana,并准备测试数据。
本文使用的自建Kibana版本为7.6.2,1个数据节点,具体操作步骤如下:
-
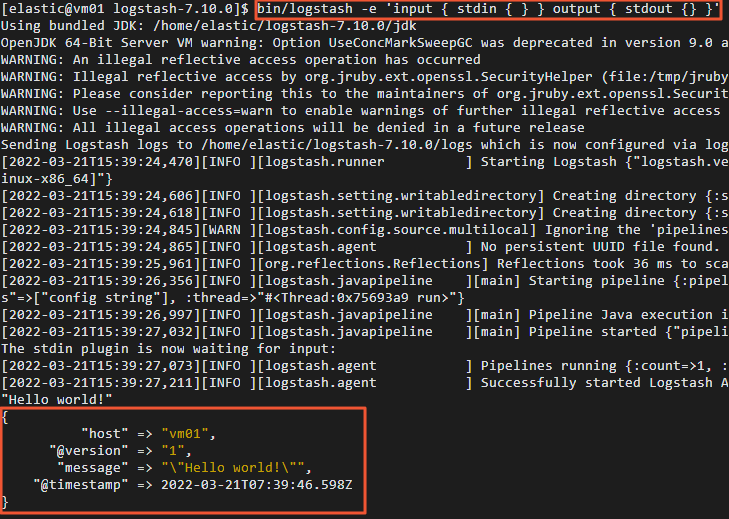
部署自建Logstash。
本文使用的Logstash版本为7.10.0,1个节点,具体操作步骤如下:
步骤二:迁移索引元数据(设置和映射)
在进行数据迁移时,Logstash会帮助您自动创建索引,但是自动创建的索引可能与您待迁移的索引存在差异,导致迁移前后数据的格式不一致。因此建议您在数据迁移前,在阿里云Elasticsearch中手动创建目标索引,确保迁移前后索引数据完全一致。
您可以通过Python脚本创建目标索引,具体操作步骤如下:
-
连接ECS服务器。
具体操作请参见 通过密码或密钥认证登录Linux实例 。说明 本文档以普通用户权限为例。
-
创建并打开Python脚本文件(本文以indiceCreate.py为例)。
sudo vi indiceCreate.py -
修改Python脚本文件,拷贝以下代码(注意修改集群的连接地址、用户名和密码)。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 文件名:indiceCreate.py import sys import base64 import time import httplib import json ## 源集群host。 oldClusterHost = "localhost:9200" ## 源集群用户名,可为空。 oldClusterUserName = "elastic" ## 源集群密码,可为空。 oldClusterPassword = "xxxxxx" ## 目标集群host,可在阿里云Elasticsearch实例的基本信息页面获取。 newClusterHost = "es-cn-zvp2m4bko0009****.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:9200" ## 目标集群用户名。 newClusterUser = "elastic" ## 目标集群密码。 newClusterPassword = "xxxxxx" DEFAULT_REPLICAS = 0 def httpRequest(method, host, endpoint, params="", username="", password=""): conn = httplib.HTTPConnection(host) headers = {} if (username != "") : 'Hello {name}, your age is {age} !'.format(name = 'Tom', age = '20') base64string = base64.encodestring('{username}:{password}'.format(username = username, password = password)).replace('\n', '') headers["Authorization"] = "Basic %s" % base64string; if "GET" == method: headers["Content-Type"] = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" conn.request(method=method, url=endpoint, headers=headers) else : headers["Content-Type"] = "application/json" conn.request(method=method, url=endpoint, body=params, headers=headers) response = conn.getresponse() res = response.read() return res def httpGet(host, endpoint, username="", password=""): return httpRequest("GET", host, endpoint, "", username, password) def httpPost(host, endpoint, params, username="", password=""): return httpRequest("POST", host, endpoint, params, username, password) def httpPut(host, endpoint, params, username="", password=""): return httpRequest("PUT", host, endpoint, params, username, password) def getIndices(host, username="", password=""): endpoint = "/_cat/indices" indicesResult = httpGet(oldClusterHost, endpoint, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword) indicesList = indicesResult.split("\n") indexList = [] for indices in indicesList: if (indices.find("open") > 0): indexList.append(indices.split()[2]) return indexList def getSettings(index, host, username="", password=""): endpoint = "/" + index + "/_settings" indexSettings = httpGet(host, endpoint, username, password) print (index + " 原始settings如下:\n" + indexSettings) settingsDict = json.loads(indexSettings) ## 分片数默认和源集群索引保持一致。 number_of_shards = settingsDict[index]["settings"]["index"]["number_of_shards"] ## 副本数默认为0。 number_of_replicas = DEFAULT_REPLICAS newSetting = "\"settings\": {\"number_of_shards\": %s, \"number_of_replicas\": %s}" % (number_of_shards, number_of_replicas) return newSetting def getMapping(index, host, username="", password=""): endpoint = "/" + index + "/_mapping" indexMapping = httpGet(host, endpoint, username, password) print (index + " 原始mapping如下:\n" + indexMapping) mappingDict = json.loads(indexMapping) mappings = json.dumps(mappingDict[index]["mappings"]) newMapping = "\"mappings\" : " + mappings return newMapping def createIndexStatement(oldIndexName): settingStr = getSettings(oldIndexName, oldClusterHost, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword) mappingStr = getMapping(oldIndexName, oldClusterHost, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword) createstatement = "{\n" + str(settingStr) + ",\n" + str(mappingStr) + "\n}" return createstatement def createIndex(oldIndexName, newIndexName=""): if (newIndexName == "") : newIndexName = oldIndexName createstatement = createIndexStatement(oldIndexName) print ("新索引 " + newIndexName + " 的setting和mapping如下:\n" + createstatement) endpoint = "/" + newIndexName createResult = httpPut(newClusterHost, endpoint, createstatement, newClusterUser, newClusterPassword) print ("新索引 " + newIndexName + " 创建结果:" + createResult) ## main indexList = getIndices(oldClusterHost, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword) systemIndex = [] for index in indexList: if (index.startswith(".")): systemIndex.append(index) else : createIndex(index, index) if (len(systemIndex) > 0) : for index in systemIndex: print (index + " 或许是系统索引,不会重新创建,如有需要,请单独处理~") -
执行Python脚本,创建目标索引。
sudo /usr/bin/python indiceCreate.py -
参见
登录Kibana控制台
,登录目标集群的Kibana控制台,查看已创建的索引。
GET /_cat/indices?v
步骤三:迁移全量数据
-
连接ECS服务器。
具体操作请参见 通过密码或密钥认证登录Linux实例 。
-
在config目录下,创建并打开Logstash配置文件。
cd logstash-7.10.0/config sudo vi es2es_all.conf -
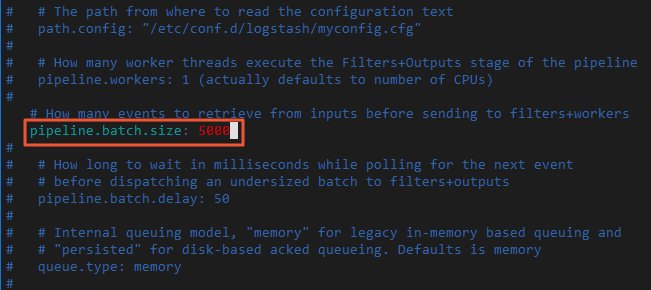
参考以下配置,修改Logstash配置文件。
input{ elasticsearch{ # 源端ES地址。 hosts => ["http://localhost:9200"] # 安全集群配置登录用户名密码。 user => "xxxxxx" password => "xxxxxx" # 需要迁移的索引列表,多个索引以英文以逗号(,)分隔。 index => "kibana_sample_data_*" # 以下三项保持默认即可,包含线程数和迁移数据大小和Logstash JVM配置相关。 docinfo=>true slices => 5 size => 5000 filter { # 去掉一些Logstash自己加的字段。 mutate { remove_field => ["@timestamp", "@version"] output{ elasticsearch{ # 目标端ES地址,可在阿里云Elasticsearch实例的基本信息页面获取。 hosts => ["http://es-cn-zvp2m4bko0009****.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:9200"] # 安全集群配置登录用户名密码。 user => "elastic" password => "xxxxxx" # 目标端索引名称,以下配置表示索引与源端保持一致。 index => "%{[@metadata][_index]}" # 目标端索引type,以下配置表示索引类型与源端保持一致。 document_type => "%{[@metadata][_type]}" # 目标端数据的id,如果不需要保留原id,可以删除以下这行,删除后性能会更好。 document_id => "%{[@metadata][_id]}" ilm_enabled => false manage_template => false }说明 为了保证迁移数据的准确性,建议您创建多个Logstash管道配置文件,分批次迁移数据,每个Logstash迁移部分数据。 -
启动Logstash全量迁移任务。
cd ../ sudo nohup bin/logstash -f config/es2es_all.conf >/dev/null 2>&1 &
步骤四:迁移增量数据
-
连接ECS服务器,在config目录下,创建并打开Logstash增量配置文件。
cd config sudo vi es2es_kibana_sample_data_logs.conf说明 本文档以普通用户权限为例。 -
参考以下配置,修改Logstash配置文件。
开启Logstash定时任务即可触发增量迁移,配置示例如下。
input{ elasticsearch{ # 源端ES地址。 hosts => ["http://localhost:9200"] # 安全集群配置登录用户名密码。 user => "xxxxxx" password => "xxxxxx" # 需要迁移的索引列表,多个索引使用英文逗号(,)分隔。 index => "kibana_sample_data_logs" # 按时间范围查询增量数据,以下配置表示查询最近5分钟的数据。 query => '{"query":{"range":{"@timestamp":{"gte":"now-5m","lte":"now/m"}}}}' # 定时任务,以下配置表示每分钟执行一次。 schedule => "* * * * *" scroll => "5m" docinfo=>true size => 5000 filter { # 去掉一些Logstash自己加的字段. mutate { remove_field => ["@timestamp", "@version"] output{ elasticsearch{ # 目标端ES地址,可在阿里云Elasticsearch实例的基本信息页面获取。 hosts => ["http://es-cn-zvp2m4bko0009****.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:9200"] # 安全集群配置登录用户名密码. user => "elastic" password => "xxxxxx" # 目标端索引名称,以下配置表示索引与源端保持一致。 index => "%{[@metadata][_index]}" # 目标端索引type,以下配置表示索引类型与源端保持一致。 document_type => "%{[@metadata][_type]}" # 目标端数据的id,如果不需要保留原id,可以删除以下这行,删除后性能会更好。 document_id => "%{[@metadata][_id]}" ilm_enabled => false manage_template => false }重要- Logstash记录的时间戳为UTC时间,如果您的本地时间为北京时间(东八区),那么两者会存在8个小时的时区差,此时将UTC时间转化为北京时间,可使用公式:UTC+时区差=北京时间。例如,以上示例中通过源端索引中的 @timestamp 字段进行range范围过滤查询获取增量数据,并在对应的时间上+8h转换为北京时间。
- 通过Logstash控制时间字段实现增量数据的同步,需确保原索引中有可控制的时间字段,如果原索引中没有时间字段数据,可使用 ingest pipeline 指定 _ingest.timestamp 获取元数据值,从而引入 @timestamp 时间字段。
-
启动Logstash增量迁移任务。
sudo nohup bin/logstash -f config/es2es_kibana_sample_data_logs.conf >/dev/null 2>&1 & -
在目标端Elasticsearch集群的Kibana中,查询最近更新的记录,验证增量数据是否同步。
以下示例的查询条件为:索引名称为kibana_sample_data_logs、最近时间范围为5分钟。
GET kibana_sample_data_logs/_search "query": { "range": { "@timestamp": { "gte": "now-5m", "lte": "now/m" "sort": [ "@timestamp": { "order": "desc"
步骤五:查看数据迁移结果
-
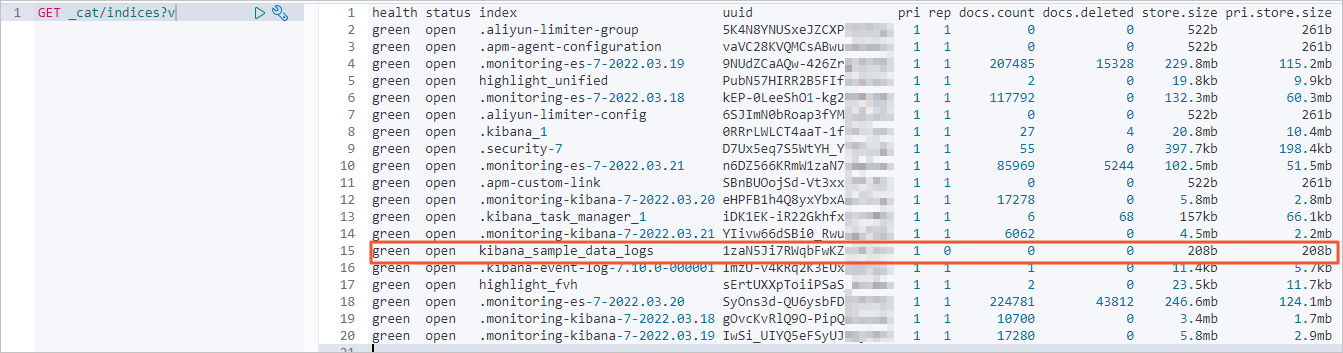
查看是否完成全量迁移。
-
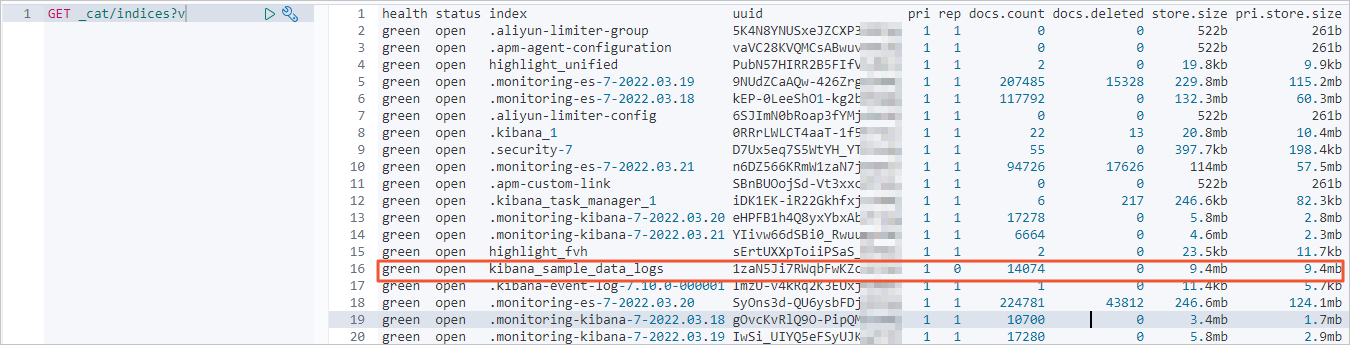
查看是否完成增量迁移。
查看自建Elasticsearch集群的最近更新记录。
GET kibana_sample_data_logs/_search "query": { "range": { "@timestamp": { "gte": "now-5m", "lte": "now/m" "sort": [ "@timestamp": { "order": "desc" }返回结果如下。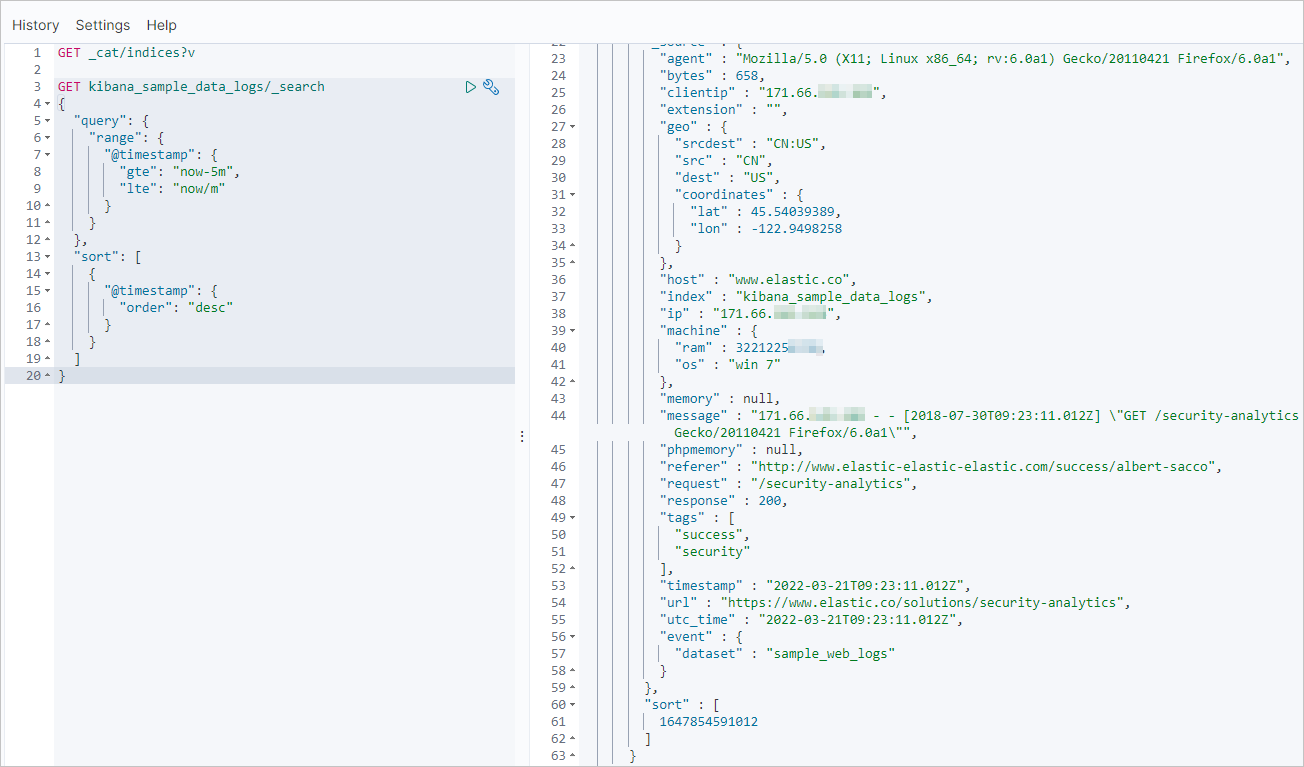
增量迁移完成后,使用同样命令查看阿里云Elasticsearch集群最近的更新记录。正常情况下,阿里云Elasticsearch集群的更新记录会与自建集群一致。