Python JSON:编码(转储),解码(加载)json数据和文件(示例)
什么是JSON?
JSON是一种数据交换的标准格式,它受到JavaScript的启发。通常,JSON采用字符串或文本格式。json代表javascript对象表示法。
json:json的语法是作为键和值对编写的
{
"Key": "Value",
"Key": "Value",
}JSON与Python字典非常相似。python支持JSON,它有一个内置的库作为JSON
SON库的Python
是元帅和泡菜是在外部maintain modules of version of JSON的Python库。相关业务的性能和解码JSON编码的Python类You need to json图书馆和第一进出口文件在你的.py for that,
import jsonFollowing methods are available in the JSON modul
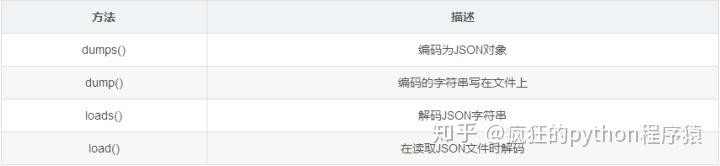
在读取JSON文件时解码
Python到JSON(编码)
默认情况下,JSON Library of Python执行以下Python对象转换为JSON对象
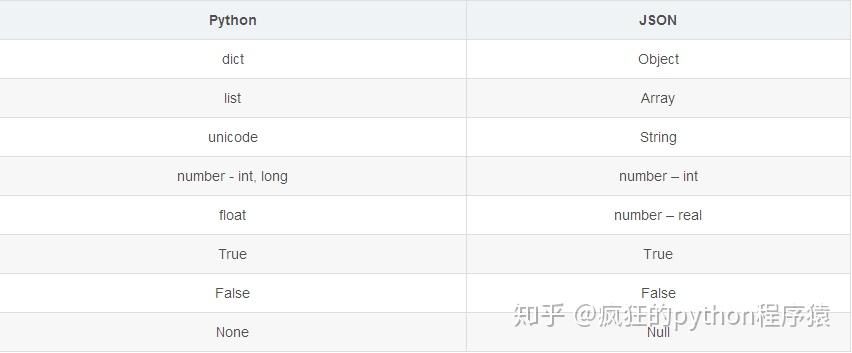
将Python数据转换为JSON称为编码操作。编码是在JSON库方法的帮助下完成的 - dumps() dumps()方法将python的字典对象转换为JSON字符串数据格式。
现在让我们用Python执行我们的第一个编码示例。
import json
x = {
"name": "Ken",
"age": 45,
"married": True,
"children": ("Alice","Bob"),
"pets": ['Dog'],
"cars": [
{"model": "Audi A1", "mpg": 15.1},
{"model": "Zeep Compass", "mpg": 18.1}
# sorting result in asscending order by keys:
sorted_string = json.dumps(x, indent=4, sort_keys=True)
print(sorted_string)输出:
{“person”:{“name”:“Kenn”,“sex”:“male”,“age”:28}})让我们使用相同的函数dump()创建字典的JSON文件
# here we create new data_file.json file with write mode using file i/o operation
with open('json_file.json', "w") as file_write:
# write json data into file
json.dump(person_data, file_write)输出:
无需显示...在您的系统中创建了json_file.json,您可以检查该文件。
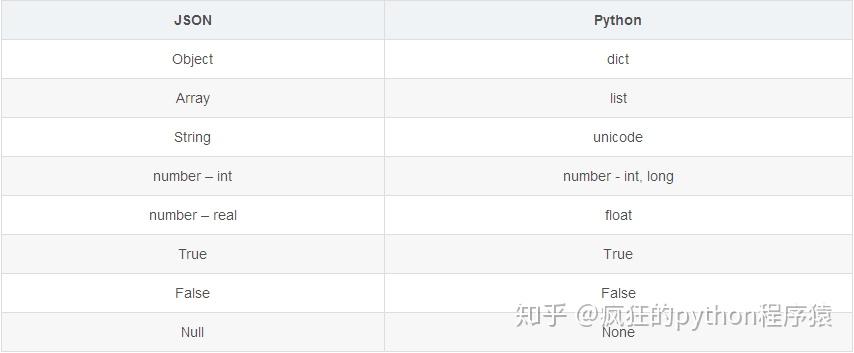
JSON到Python(解码)
JSON字符串解码是在Python的JSON库的内置方法load()和load()的帮助下完成的。这里的转换表显示了Python对象的JSON对象示例,这些对象有助于在Python中执行JSON字符串解码。
让我们看看在json.loads()函数的帮助下在Python中解码的基本示例
import json # json library imported
# json data string
person_data = '{ "person": { "name": "Kenn", "sex": "male", "age": 28}}'
# Decoding or converting JSON format in dictionary using loads()
dict_obj = json.loads(person_data)
print(dict_obj)
# check type of dict_obj
print("Type of dict_obj", type(dict_obj))
# get human object details
print("Person......", dict_obj.get('person'))输出:
{'person': {'name': 'Kenn', 'sex': 'male', 'age': 28}}
Type of dict_obj <class 'dict'>
Person...... {'name': 'John', 'sex': 'male'}

解码JSON文件或解析Python中的JSON文件
注意:解码JSON文件是文件输入/输出(I / O)相关的操作。JSON文件必须存在于您指定的程序中指定位置的系统上。
例:
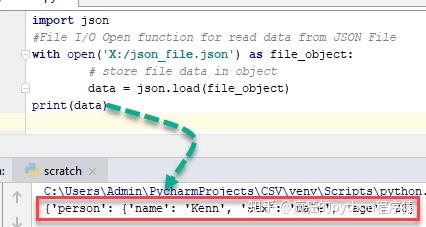
import json
#File I/O Open function for read data from JSON File
with open('X:/json_file.json') as file_object:
# store file data in object
data = json.load(file_object)
print(data)这里的数据是Python的字典对象。
输出:
{'person': {'name': 'Kenn', 'sex': 'male', 'age': 28}}
Python中的紧凑编码
当您需要减小JSON文件的大小时,可以在Python中使用紧凑编码。
例:
import json
# Create a List that contains dictionary
lst = ['a', 'b', 'c',{'4': 5, '6': 7}]
# separator used for compact representation of JSON.
# Use of ',' to identify list items
# Use of ':' to identify key and value in dictionary
compact_obj = json.dumps(lst, separators=(',', ':'))
print(compact_obj)输出:
'["a", "b", "c", {"4": 5, "6": 7}]'
Here output of JSON is represented in a single line which is the most compact representation by
removing the space character from compact_obj格式化JSON代码(漂亮打印)
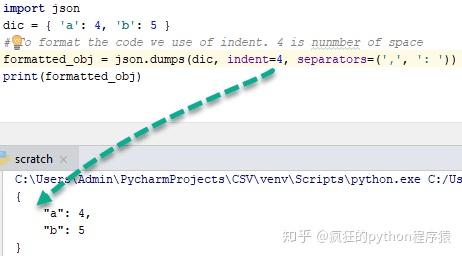
目的是为人类理解编写格式良好的代码。借助漂亮的打印功能,任何人都可以轻松理解代码。 例:
import json
dic = { 'a': 4, 'b': 5 }
''' To format the code use of indent and 4 shows number of space and use of separator is not
necessary but standard way to write code of particular function. '''
formatted_obj = json.dumps(dic, indent=4, separators=(',', ': '))
print(formatted_obj)输出:
{
"a" : 4,
"b" : 5
}
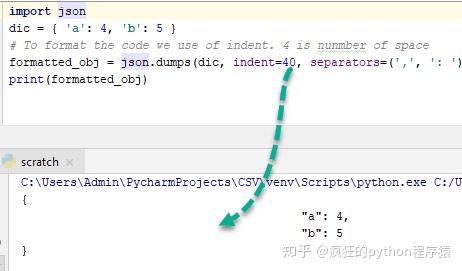
为了更好地理解这一点,将缩进更改为40并观察输出 -
订购JSON代码:
dumps中的sort_keys属性函数的参数将按升序对JSON中的键进行排序。sort_keys参数是一个布尔属性。当它是真正的排序时,否则不允许
例:
import json
x = {
"name": "Ken",
"age": 45,
"married": True,
"children": ("Alice", "Bob"),
"pets": [ 'Dog' ],
"cars": [
{"model": "Audi A1", "mpg": 15.1},
{"model": "Zeep Compass", "mpg": 18.1}
# sorting result in asscending order by keys:
sorted_string = json.dumps(x, indent=4, sort_keys=True)
print(sorted_string)输出:
{
"age": 45,
"cars": [ {
"model": "Audi A1",
"mpg": 15.1
"model": "Zeep Compass",
"mpg": 18.1
"children": [ "Alice",
"Bob"
"married": true,
"name": "Ken",
"pets": [
"Dog"
}您可能会看到钥匙的年龄,汽车,儿童等按升序排列。
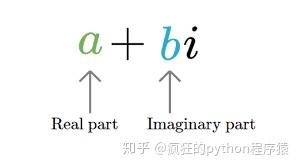
Python的复杂对象编码
Complex对象有两个不同的部分
- 真实的部分
- 想象中的一部分
在执行复杂对象的编码之前,需要检查变量是否复杂。您需要创建一个函数,该函数使用实例方法检查存储在变量中的值。
让我们为check对象创建特定的函数是复杂的还是有资格进行编码。
import json
# create function to check instance is complex or not
def complex_encode(object):
# check using isinstance method
if isinstance(object, complex):
return [object.real, object.imag]
# raised error using exception handling if object is not complex
raise TypeError(repr(object) + " is not JSON serialized")
# perform json encoding by passing parameter
complex_obj = json.dumps(4 + 5j, default=complex_encode)
print(complex_obj)输出:
'[4.0, 5.0]'Python中的复杂JSON对象解码
要在JSON中解码复杂对象,请使用object_hook参数,该参数检查JSON字符串是否包含复杂对象。
例:
import json
# function check JSON string contains complex object
def is_complex(objct):
if '__complex__' in objct:
return complex(objct['real'], objct['img'])
return objct
# use of json loads method with object_hook for check object complex or not
complex_object =json.loads('{"__complex__": true, "real": 4, "img": 5}', object_hook = is_complex)
#here we not passed complex object so it's convert into dictionary
simple_object =json.loads('{"real": 6, "img": 7}', object_hook = is_complex)
print("Complex_object......",complex_object)
print("Without_complex_object......",simple_object)输出:
Complex_object...... (4+5j)
Without_complex_object...... {'real': 6, 'img': 7}JSON序列化类JSONEncoder概述
JSONEncoder类用于在执行编码时对任何Python对象进行序列化。它包含三种不同的编码方法
- default(o) - 在子类中实现并返回o对象的serialize 对象。
- encode(o) - 与json.dumps()方法相同,返回Python数据结构的JSON字符串。
- iterencode(o) - 逐个表示字符串并编码对象o。
借助JSONEncoder类的encode()方法,我们还可以对任何Python对象进行编码。
# import JSONEncoder class from json
from json.encoder import JSONEncoder
colour_dict = { "colour": ["red", "yellow", "green" ]}
# directly called encode method of JSON
JSONEncoder().encode(colour_dict)
Output:输出:
'{"colour": ["red", "yellow", "green"]}'JSON反序列化类JSONDecoder概述
JSONDecoder类用于在执行解码时对任何Python对象进行反序列化。它包含三种不同的解码方法
- default(o) - 在子类中实现并返回反序列化的对象o对象。
- decode(o) - 与json.loads()方法相同,返回JSON字符串或数据的Python数据结构。
- raw_decode(o) - 逐个表示Python字典并解码对象o。
借助JSONDecoder类的decode()方法,我们还可以解码JSON字符串。
import json
# import JSONDecoder class from json
from json.decoder import JSONDecoder
colour_string = '{ "colour": ["red", "yellow"]}'
# directly called decode method of JSON
JSONDecoder().decode(colour_string)输出:
{'colour': ['red', 'yellow']}从URL解码JSON数据:Real Life Example
我们将从指定的URL( https:// feeds.citibikenyc.com/s tations/stations.json )获取CityBike NYC(自行车共享系统)的数据并转换为字典格式。
例:
注意: - 确保已在Python中安装了请求库,如果没有,则打开终端或CMD并键入
- (对于Python 3或更高版本)pip3安装请求
import json
import requests
# get JSON string data from CityBike NYC using web requests library
json_response= requests.get("https://feeds.citibikenyc.com/stations/stations.json")
# check type of json_response object
print(type(json_response.text))
# load data in loads() function of json library
bike_dict = json.loads(json_response.text)
#check type of news_dict
print(type(bike_dict))
# now get stationBeanList key data from dict
print(bike_dict['stationBeanList'][0])输出:
<class 'str'>
<class 'dict'>
'id': 487,
'stationName': 'E 20 St & FDR Drive',
'availableDocks': 24,
'totalDocks': 34,
'latitude': 40.73314259,
'longitude': -73.97573881,
'statusValue': 'In Service',
'statusKey': 1,
'availableBikes': 9,
'stAddress1': 'E 20 St & FDR Drive',
'stAddress2': '',
'city': '',
'postalCode': '',
'location': '',
'altitude': '',
'testStation': False,
'lastCommunicationTime': '2018-12-11 10:59:09 PM', 'landMark': ''
}与Python中的JSON库相关的异常:
- 类json.JSONDecoderError处理与解码操作相关的异常。它是ValueError的子类。
- 异常 - json.JSONDecoderError(msg,doc)
- 异常参数是,
- msg - 未格式化的错误消息
- doc - 解析JSON文档
- pos - 失败时的doc开始索引
- lineno - line no shows对应pos
- 冒号 - 列对应于pos
例:
import json
#File I/O Open function for read data from JSON File
data = {} #Define Empty Dictionary Object
with open('json_file_name.json') as file_object:
data = json.load(file_object)
except ValueError:
print("Bad JSON file format, Change JSON File")
Python中的无限和NaN数字
JSON数据交换格式(RFC - Request For Comments)不允许无限值或Nan值,但Python-JSON库中没有限制执行无限和Nan值相关操作。如果JSON获得INFINITE和Nan数据类型,则将其转换为文字。
例:
import json
# pass float Infinite value
infinite_json = json.dumps(float('inf'))
# check infinite json type
print(infinite_json)
print(type(infinite_json))
json_nan = json.dumps(float('nan'))
print(json_nan)
# pass json_string as Infinity
infinite = json.loads('Infinity')
print(infinite)
# check type of Infinity
print(type(infinite))输出:
Infinity
<class 'str'>
