极简入门TensorFlow C++源码
前一段时间,一直在忙框架方面的工作,偶尔也会帮业务同学去优化优化使用TensorFlow的代码,也加上之前看了dmlc/relay,nnvm的代码,觉得蛮有意思,也想分别看下TensorFlow的Graph IR、PaddlePaddle的Graph IR,上周五,看代码看的正津津有味的时候,看到某个数据竞赛群里面讨论东西,不记得具体内容,大概说的是框架的代码实现, 有几位算法大佬说看底层源码比较麻烦,因为比较早从框架,这块代码通常都还能看,问题都不大,和群里小伙伴吹水了半天之后,感觉是可以写篇如何看TensorFlow或者其他框架底层源码的劝退文了。
利其器
首先,一定是要找个好工作来看源码,很多人推荐vs code、sublime,我试过vs code+bazel的,好像也不错,但是后面做c++适应了clion之后,除了资源要求比较多,还是蛮不错的,使用c++一般推荐使用cmake来看编译项目,但是TensorFlow是bazel的,无法直接支持,最开始,这边是自己写简单的cmake,能够实现简单的代码跳转,但是涉及到比如protobuf之类的编译过后产生的文件无法跳转,比较麻烦,不够纯粹,很早之前知道clion有bazel的组件,但是不知道为啥一直搞不通,上周找时间再试了试,发现竟然通了,使用之后,这才是看tf源码的真正方式:
首先,选择合适版本的bazel,千万不能太高,也不能太低,这里我拉的是TF2.0的代码,使用bazel 0.24.0刚刚好,切记
千万别太高也比太低
,
千万别太高也比太低
,
千万别太高也比太低
。
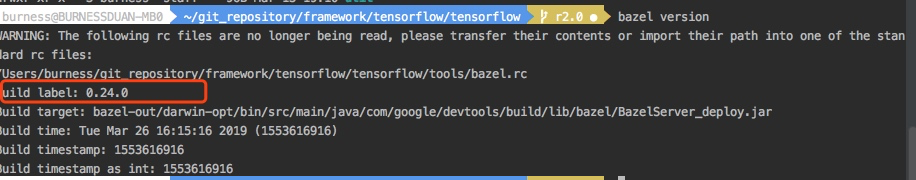

其次,clion上选择bazel的插件

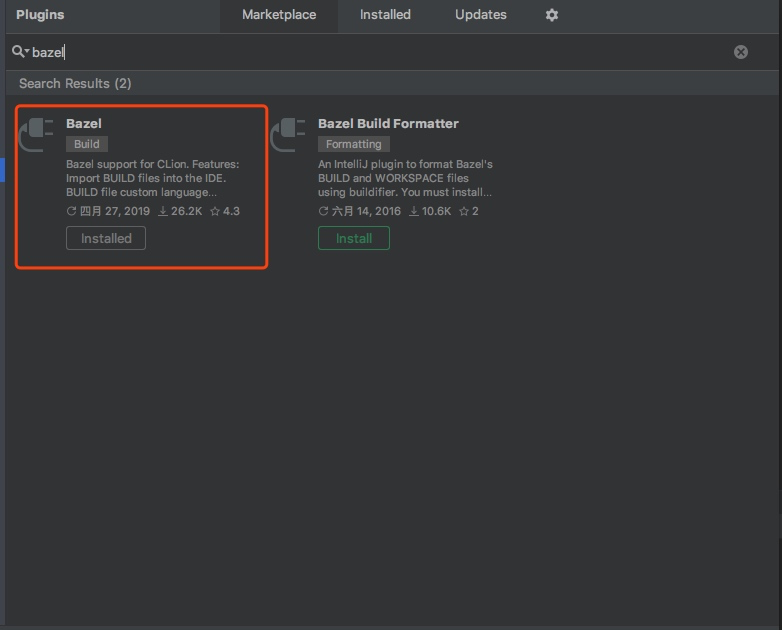
第三步,./configure,然后按你的意图选择合适的编译配置
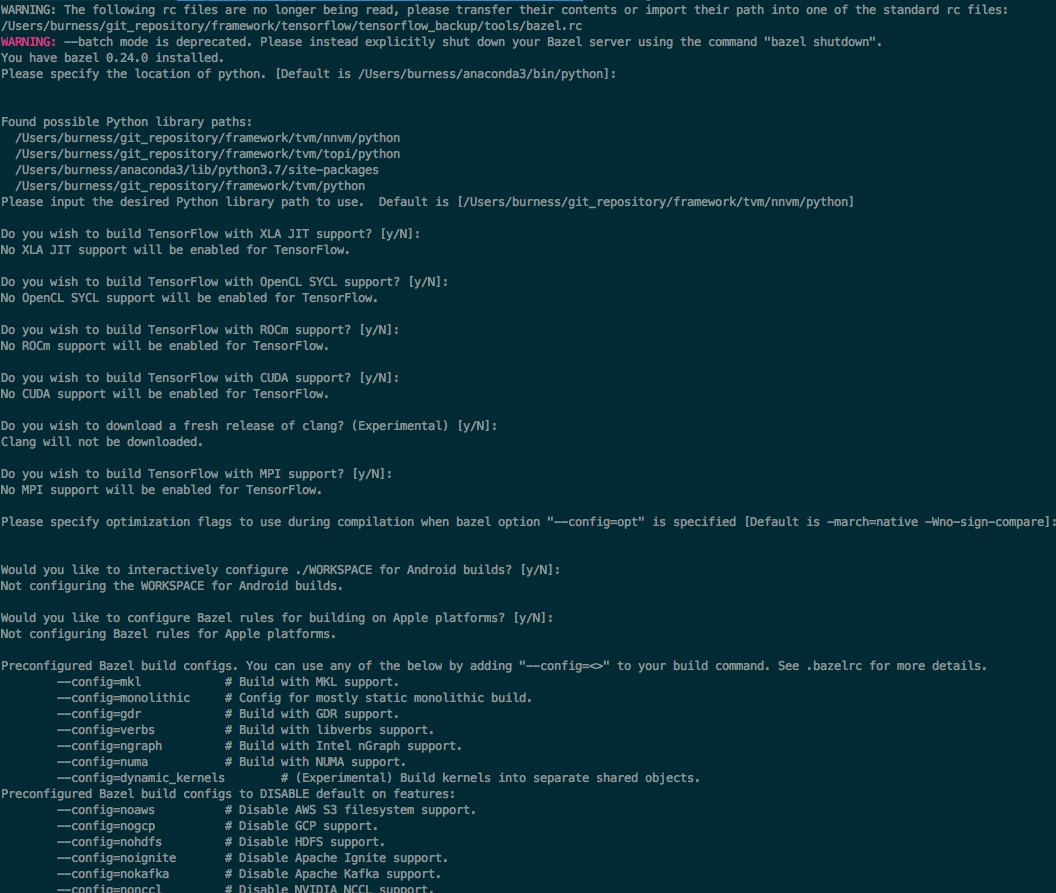

第四步,导入bazel项目:File=>Import Bazel Project
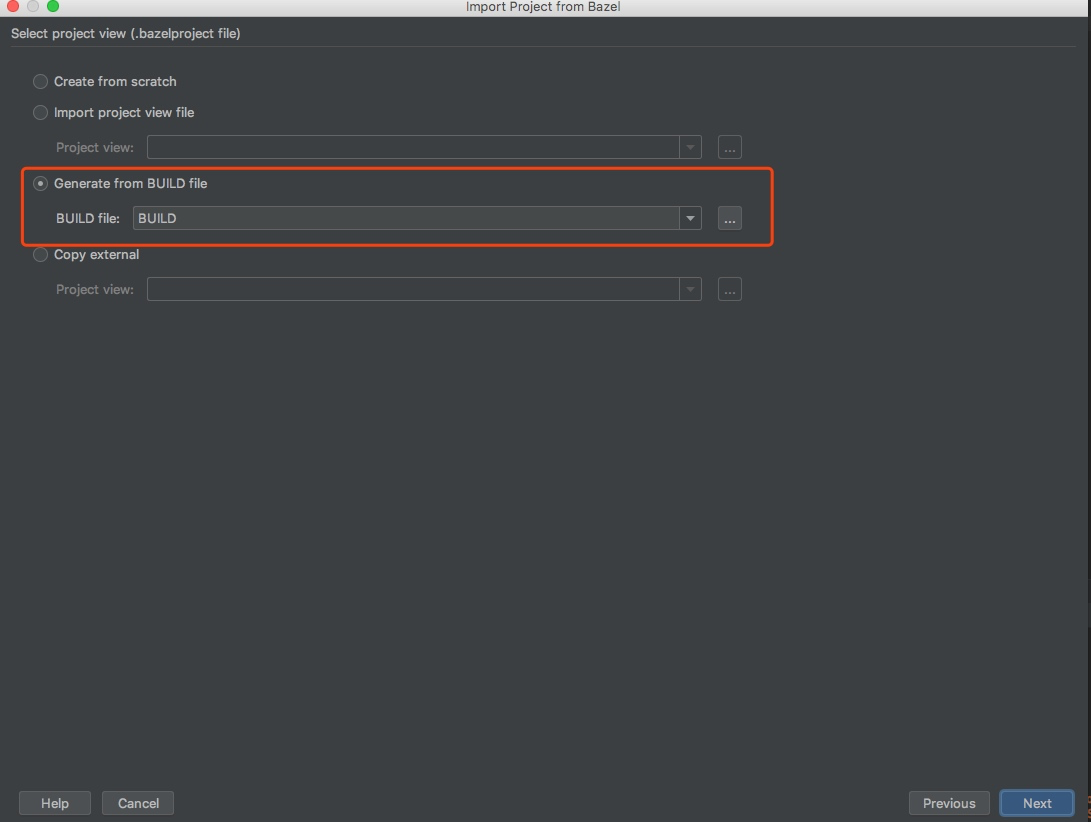
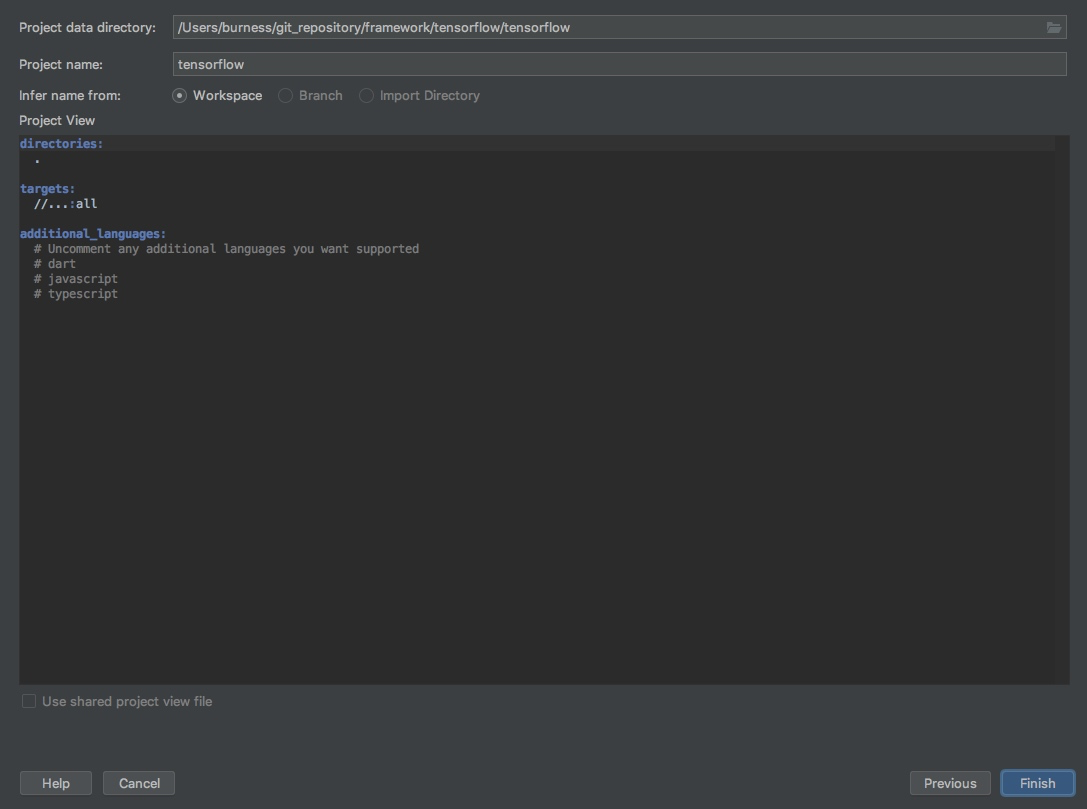
经过上面几步之后,接下来就要经过比较长时间的等待,clion会导入bazel项目,然后编译整个项目,这个耗时视你机器和网络而定(顺便提一句,最好保证比较畅通的访问github的网络,另外由于上面targets:all,会编译TensorFlow所有的项目,如果你知道是什么意思,可以自己修改,如果不知道的话我先不提了,默认就好,期间会有很多Error出现,放心,问题不大,因为会默认编译所有的模块)
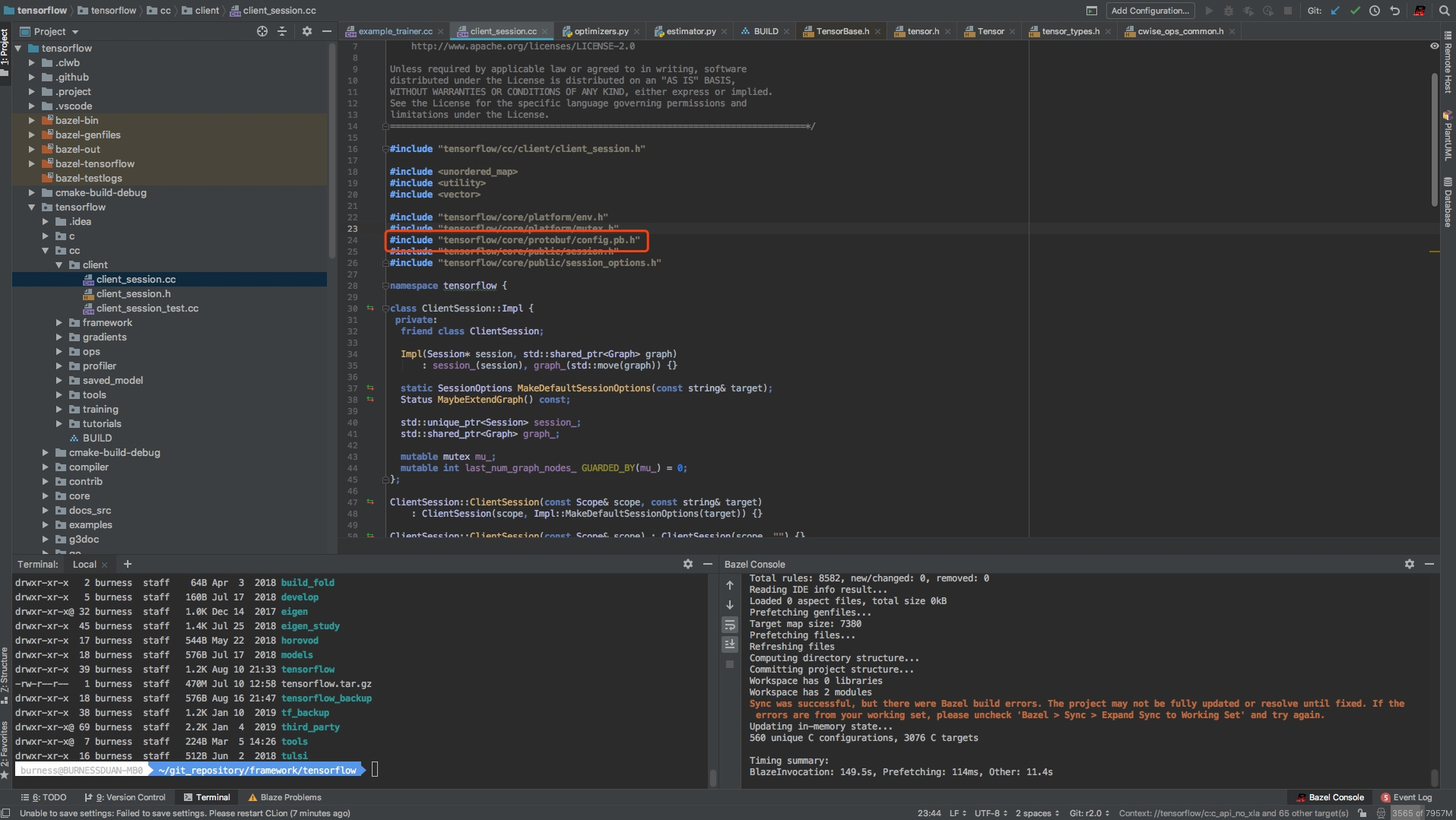
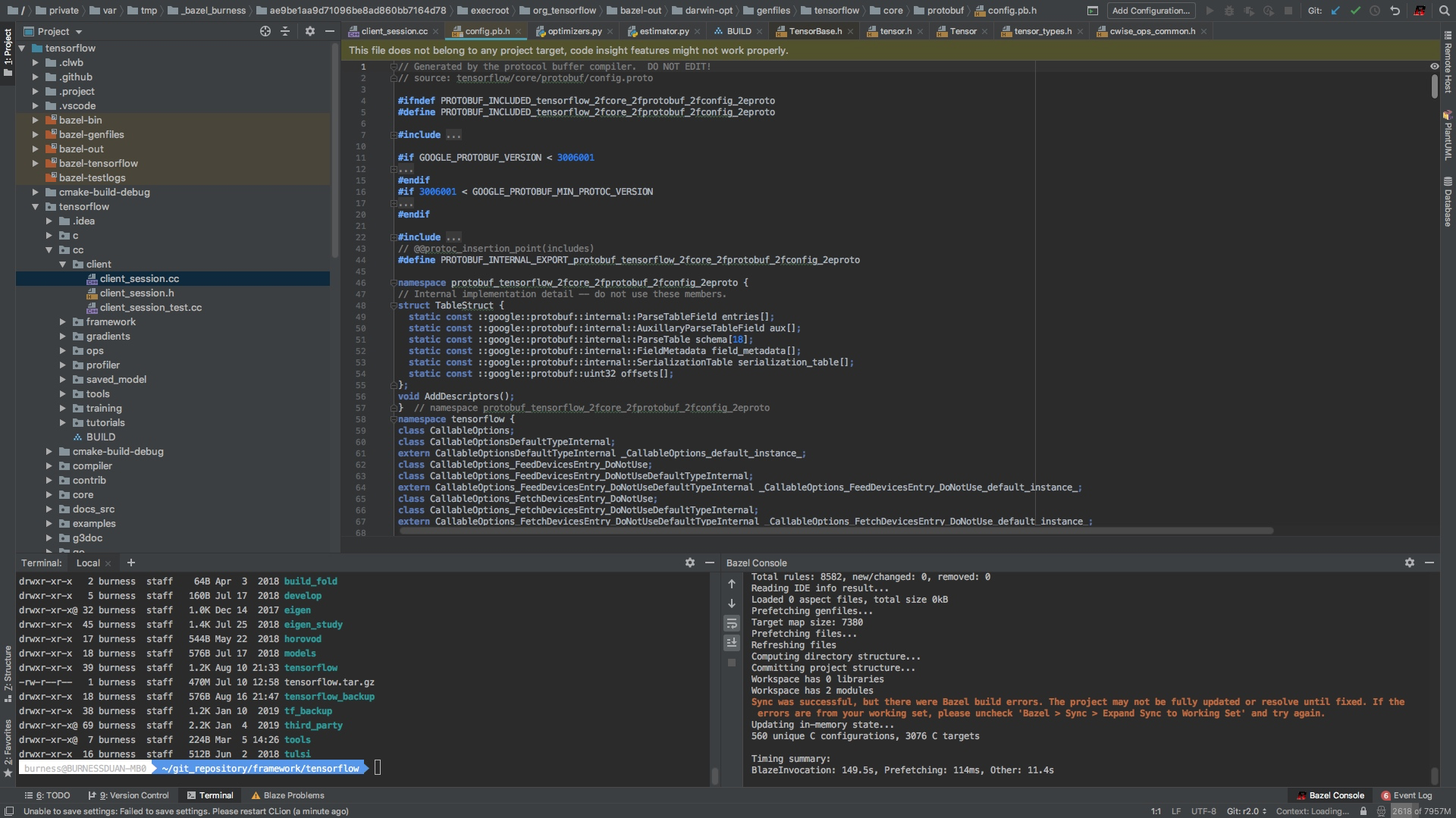
经过上面之后,我们就可以愉快的看代码啦,连protobuf生成的文件都很开心的跳转啦

极简版c++入门
TensorFlow大部分人都知道,底层是c++写的,然后外面包了一层python的api,既然底层是c++写的,那么用c++也是可以用来训练模型的,大部分人应该都用过c++或者java去载入frozen的模型,然后做serving应用在业务系统上,应该很少人去使用c++来训练模型,既然我们这里要读代码,我们先尝试看看用c++写模型,文件路径如下图:

主要函数就那么几个:CreateGraphDef, ConcurrentSteps, ConcurrentSessions:
CreateGraphDef 构造计算图
GraphDef CreateGraphDef() {
// TODO(jeff,opensource): This should really be a more interesting
// computation. Maybe turn this into an mnist model instead?
Scope root = Scope::NewRootScope();
using namespace ::tensorflow::ops; // NOLINT(build/namespaces)
// A = [3 2; -1 0]. Using Const<float> means the result will be a
// float tensor even though the initializer has integers.
auto a = Const<float>(root, {{3, 2}, {-1, 0}});
// x = [1.0; 1.0]
auto x = Const(root.WithOpName("x"), {{1.f}, {1.f}});
// y = A * x
auto y = MatMul(root.WithOpName("y"), a, x);
// y2 = y.^2
auto y2 = Square(root, y);
// y2_sum = sum(y2). Note that you can pass constants directly as
// inputs. Sum() will automatically create a Const node to hold the
// 0 value.
auto y2_sum = Sum(root, y2, 0);
// y_norm = sqrt(y2_sum)
auto y_norm = Sqrt(root, y2_sum);
// y_normalized = y ./ y_norm
Div(root.WithOpName("y_normalized"), y, y_norm);
GraphDef def;
TF_CHECK_OK(root.ToGraphDef(&def));
return def;
}
定义graph 节点 root, 然后定义常数变量a (shape为2*2), x (shape为2* 1),然后 y = A * x, y2 = y.2, y2_sum = sum(y2), y_norm = sqrt(y2_sum), y_normlized = y ./ y_norm。代码很简洁, 看起来一目了然,
然后是ConcurrentSteps
void ConcurrentSteps(const Options* opts, int session_index) {
// Creates a session.
SessionOptions options;
std::unique_ptr<Session> session(NewSession(options));
GraphDef def = CreateGraphDef();
if (options.target.empty()) {
graph::SetDefaultDevice(opts->use_gpu ? "/device:GPU:0" : "/cpu:0", &def);
TF_CHECK_OK(session->Create(def));
// Spawn M threads for M concurrent steps.
const int M = opts->num_concurrent_steps;
std::unique_ptr<thread::ThreadPool> step_threads(
new thread::ThreadPool(Env::Default(), "trainer", M));
for (int step = 0; step < M; ++step) {
step_threads->Schedule([&session, opts, session_index, step]() {
// Randomly initialize the input.
Tensor x(DT_FLOAT, TensorShape({2, 1}));
auto x_flat = x.flat<float>();
x_flat.setRandom();
std::cout << "x_flat: " << x_flat << std::endl;
Eigen::Tensor<float, 0, Eigen::RowMajor> inv_norm =
x_flat.square().sum().sqrt().inverse();
x_flat = x_flat * inv_norm();
// Iterations.
std::vector<Tensor> outputs;
for (int iter = 0; iter < opts->num_iterations; ++iter) {
outputs.clear();
TF_CHECK_OK(
session->Run({{"x", x}}, {"y:0", "y_normalized:0"}, {}, &outputs));
CHECK_EQ(size_t{2}, outputs.size());
const Tensor& y = outputs[0];
const Tensor& y_norm = outputs[1];
// Print out lambda, x, and y.
std::printf("%06d/%06d %s\n", session_index, step,
DebugString(x, y).c_str());
// Copies y_normalized to x.
x = y_norm;
// Delete the threadpool, thus waiting for all threads to complete.
step_threads.reset(nullptr);
TF_CHECK_OK(session->Close());
}新建一个session,然后设置10个线程来计算,来执行:
std::vector<Tensor> outputs;
for (int iter = 0; iter < opts->num_iterations; ++iter) {
outputs.clear();
TF_CHECK_OK(
session->Run({{"x", x}}, {"y:0", "y_normalized:0"}, {}, &outputs));
CHECK_EQ(size_t{2}, outputs.size());
const Tensor& y = outputs[0];
const Tensor& y_norm = outputs[1];
