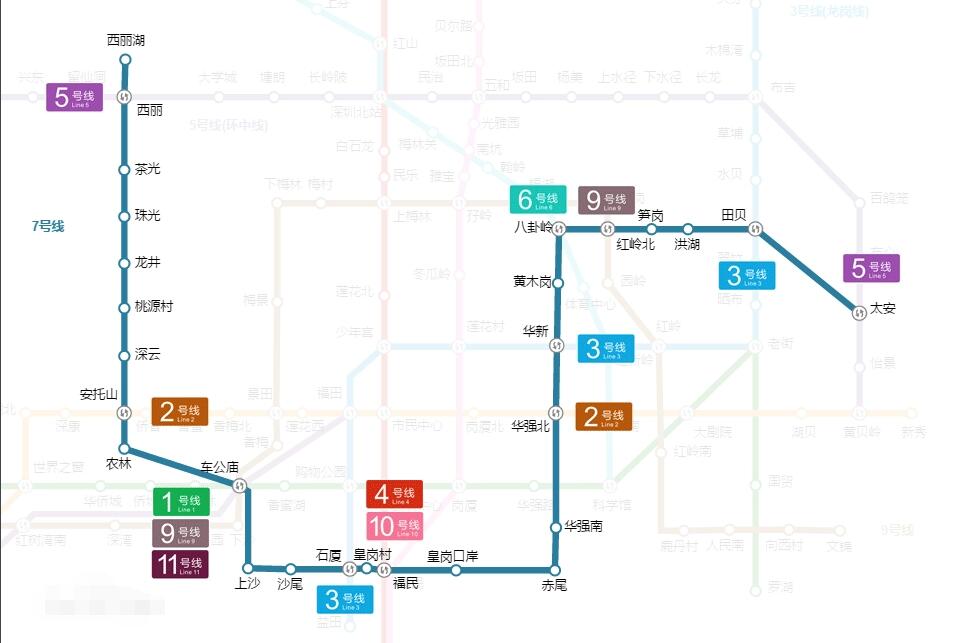
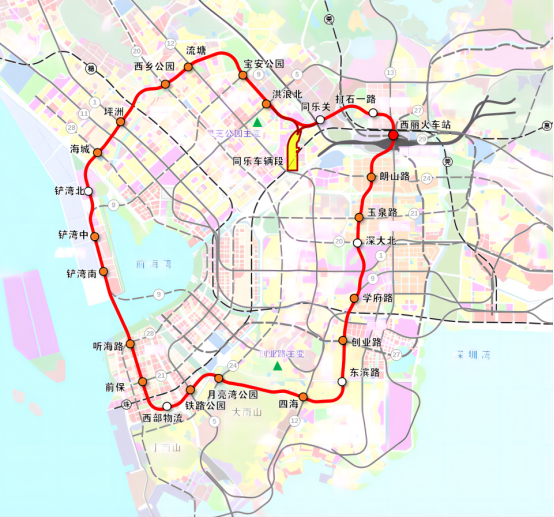
深圳地铁7号线站点线路图
深圳地铁7号线
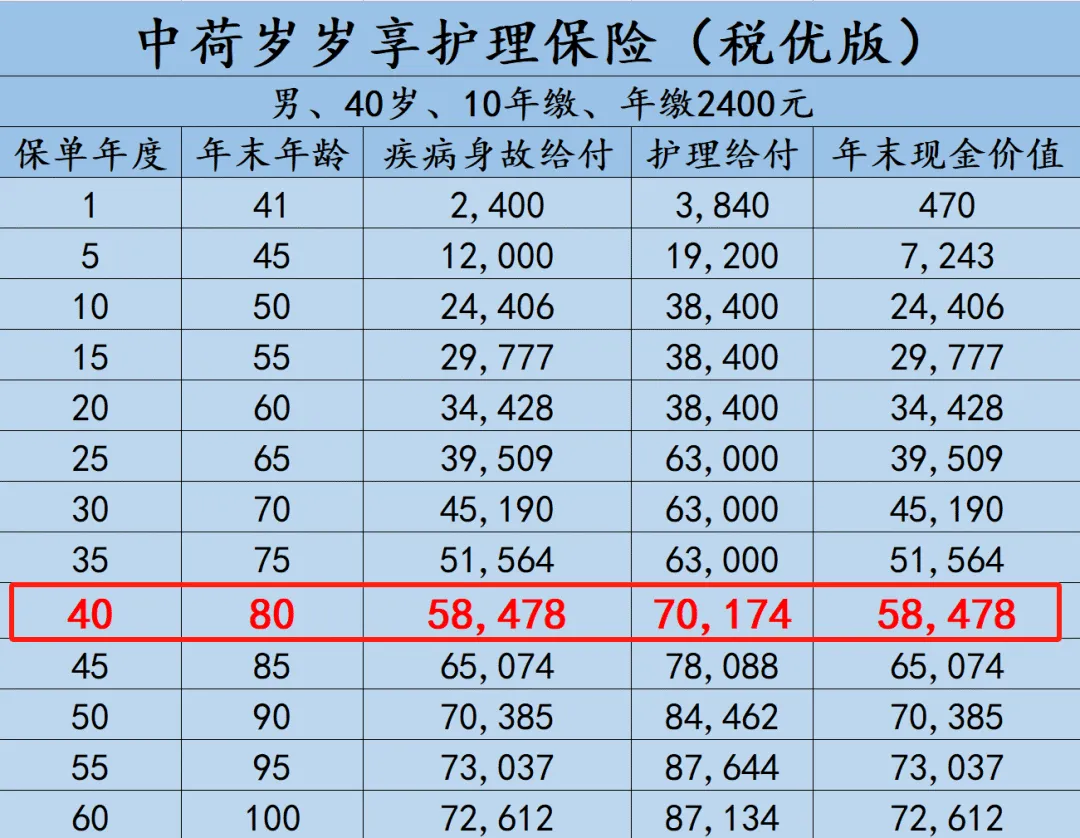
深圳地铁7号线是中国广东省深圳市境内的一条地铁线路,于2016年10月28日开通运营,其标志色为深蓝色。
深圳地铁7号线起于西丽湖站,途经南山区、福田区、罗湖区,贯穿龙珠大道、福民路、华强北路、田贝路,止于太安站。
截至2021年1月,深圳地铁7号线全长30.17千米,全部为地下线;共设28座车站,全部为地下车站;列车设计时速80千米/小时,采用6节编组A型列车。
地铁7号线停运消息
2022年2月23日起,因新冠疫情防控需要,深圳地铁7号线上沙站、沙尾站暂停运营服务,双方向列车不停站通过。其中,沙尾站已于2022年3月9日起恢复正常运营。
》》地铁暂停运营最新消息: 微信搜索公众号 【深圳城事攻略】 ,关注后在对话框发送消息 【地铁】 即可查看深圳地铁暂停运营站点相关信息、深圳地铁高清线路图下载。
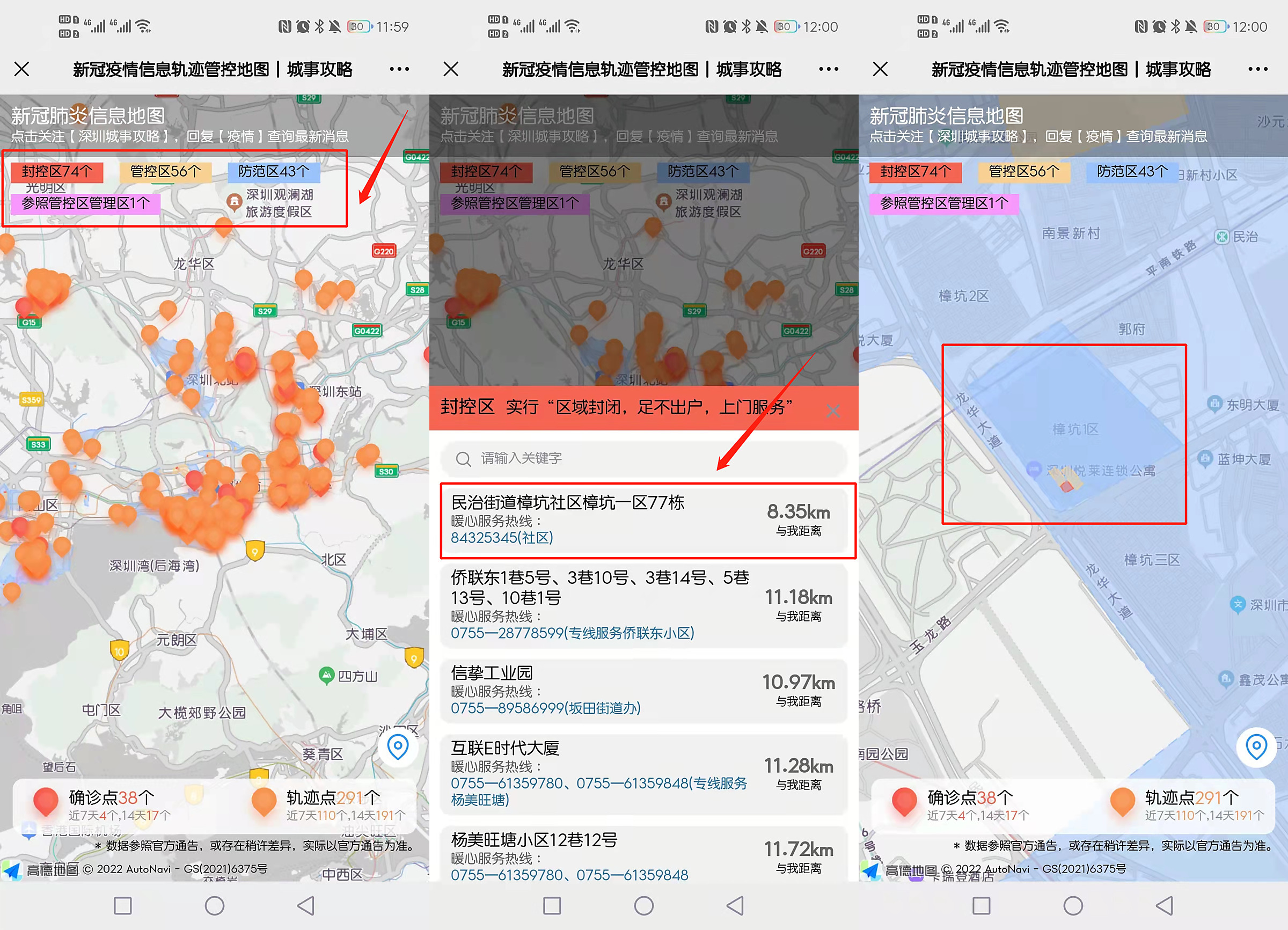
深圳疫情管控区地图查询入口
微信搜索公众号 【深圳城事攻略】, 关注后在对话框发送消息 【封控】 即可获取 深圳封控管控区域地图查看入口 、深圳疫情各区封控区、管控区和防范区名单(持续更新)。
【相关专题】:
【相关阅读推荐】: