【机器学习-因果推断】EconML 双重机器学习正交森林上手小案例 n(Python)
机器学习因果推断至今还没搞明白,但小案例模仿写了一堆。所以标题编号为了省事,就直接叫 n 了。
这个案例中,核心的函数是 DMLOrthoForest - 双重机器学习正交森林 ,是 因果森林 常见的实现形式之一。
函数形式:econml.orf.DMLOrthoForest( * , n_trees=500 , min_leaf_size=10 , max_depth=10 , subsample_ratio=0.7 , bootstrap=False , lambda_reg=0.01 , model_T='auto' , model_Y=<econml.sklearn_extensions.linear_model.WeightedLassoCVWrapperobject> , model_T_final=None , model_Y_final=None , global_residualization=False , global_res_cv=2 , discrete_treatment=False , categories='auto' , n_jobs=-1 , backend='loky' , verbose=3 , batch_size='auto' , random_state=None )
1. 准备工作和数据导入
## 基于微软的 EconML 包实现
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
#from econml.ortho_forest import ContinuousTreatmentOrthoForest as CausalForest
from econml.orf import DMLOrthoForest as CausalForest
#from econml.grf import CausalForest
## The econml.ortho_forest.ContinuousTreatmentOrthoForest class has been renamed to
## econml.orf.DMLOrthoForest; an upcoming release will remove support for the old name
df = pd.read_csv('https://vincentarelbundock.github.io/Rdatasets/csv/Ecdat/Crime.csv')
df = df.drop(columns = 'Unnamed: 0')
#df.shape ## (630, 25)
df.columns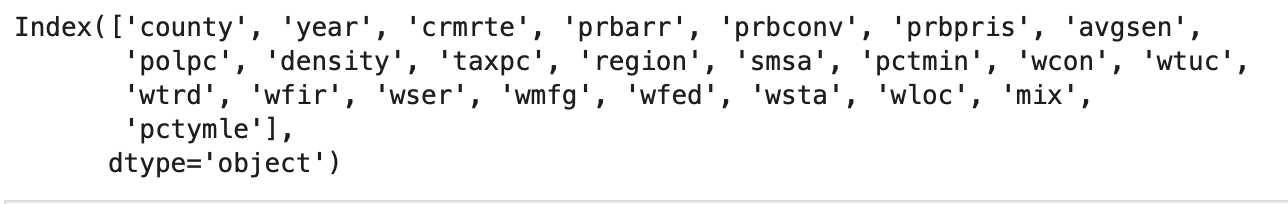
2. 处理分类型变量
## 处理分类变量
cat_vars = ['year', 'region', 'smsa']
xf = df.loc[:, cat_vars]
## 先拆开处理,删除,再合并
## 这里不可以直接 get dummies,除非先将那3个分类型列声明为 “category” 类型
xf.year = xf.year.astype('category')
xf = pd.get_dummies(xf) ## 没有删除哑变量中的第一个取值列
xf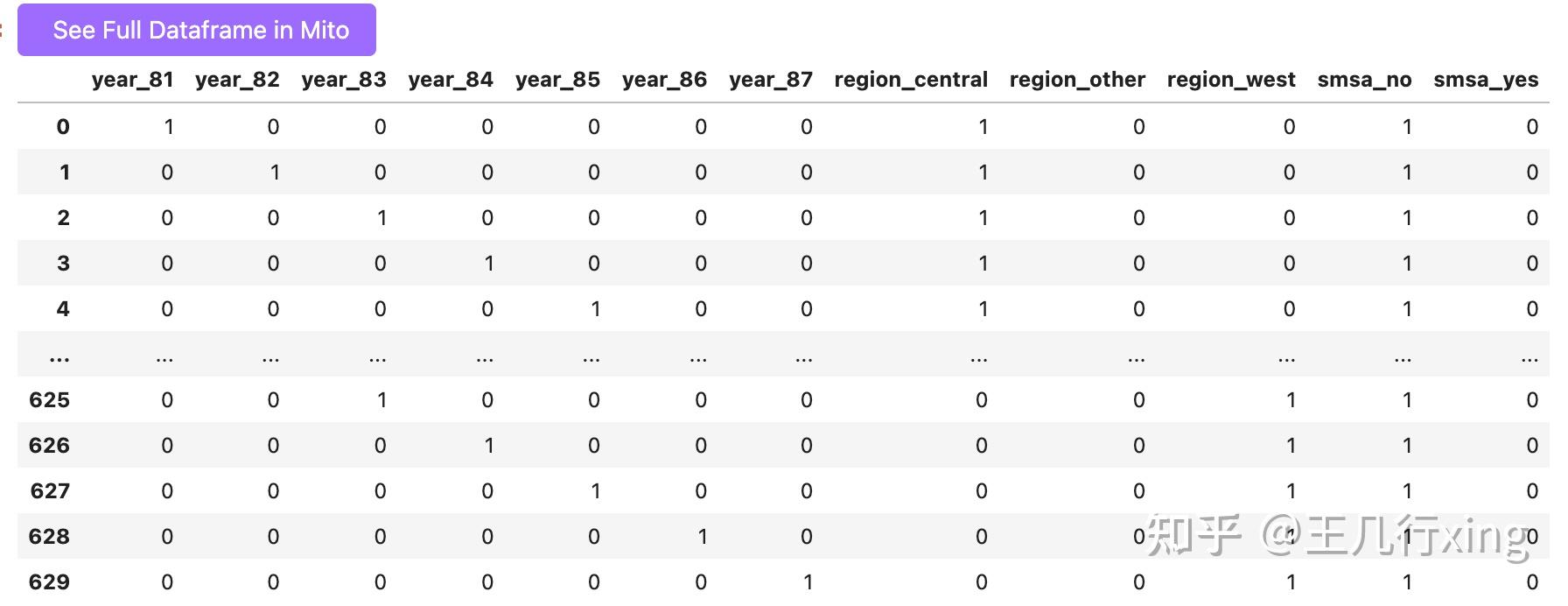
df = pd.concat([df.drop(cat_vars, axis=1), xf], axis=1) ##
cat_var_dummy_names = list(xf.columns)
regressors = ['prbarr', 'prbconv', 'prbpris',
'avgsen', 'polpc', 'density', 'taxpc',
'pctmin', 'wcon']
## 所有的变量名称
regressors = regressors + cat_var_dummy_names
regressors
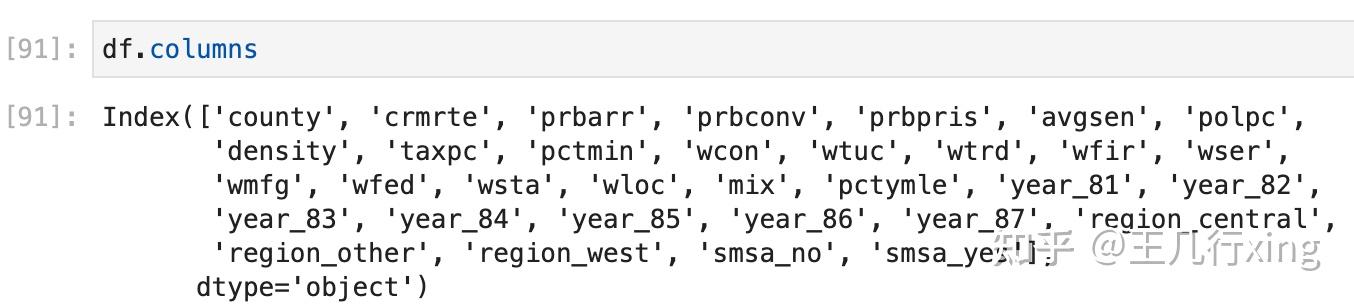
数据切割:
## 数据切割
train, test = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.2)3. 正交森林建模
## 因果森林建模
estimator = CausalForest(n_trees=100,
model_T=DecisionTreeRegressor(),
model_Y=DecisionTreeRegressor())
## OFFICIAL EXAMPLE####################################################
# T = np.array([0, 1]*60)
# W = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0]*30).reshape(-1, 1)
# Y = (.2 * W[:, 0] + 1) * T + .5
# est = DMLOrthoForest(n_trees=1, max_depth=1, subsample_ratio=1,
# model_T=sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression(),
# model_Y=sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression())
# est.fit(Y, T, X=W, W=W)
## OFFICIAL EXAMPLE####################################################
## 因果森林模型拟合
## from econml.orf import DMLOrthoForest
