一、碎片虽然是嵌入在活动中显示的,但是碎片和活动都是各自存在不同的类当中的,并没有什么明显的方式来直接进行通信的。那么如果要在活动中调用碎片里的方法,在碎片里调用活动的方法,一个碎片调用另一碎片的方法,应该怎么实现呢?
1、活动中调用碎片的方法:
为了方便碎片与活动之间进行通信,FragmentManager提供了一个类似于findViewById()的方法,专门从布局文件中获取碎片的实例,代码如下:
Fragment2 fragment2=(Fragment2)getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.fragment2)
调用 FragmentManager 的 findFragmentById()方法,可以在活动中得到相应碎片的实例,这样就可以调用碎片的方法了。
2、碎片中调用活动的方法:
在每个碎片中都可以通过调用 getActivity()方法来得到和当前碎片相关联
的活动实例,代码如下:
MainActivity activity=(MainActivity)getActivity();
获得活动实例后,就可以在碎片中调用活动的方法。另外当碎片中需要
使用 Context 对象时,也可以使用 getActivity()方法,因为获取到的活动本身就是一个Context对象了。
3、一个碎片中调用另一碎片的方法:
首先,在一个碎片中得到与此碎片相关联的活动实例,然后可以通过这个活动实例去获取另外一个碎片的实例,这样就可以实现一个碎片中与另一碎片之间的通信功能,代码如下:
MainActivity activity=(MainActivity)getActivity()
Fragment2 fragment2=(Fragment2)activity.getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.fragment2)
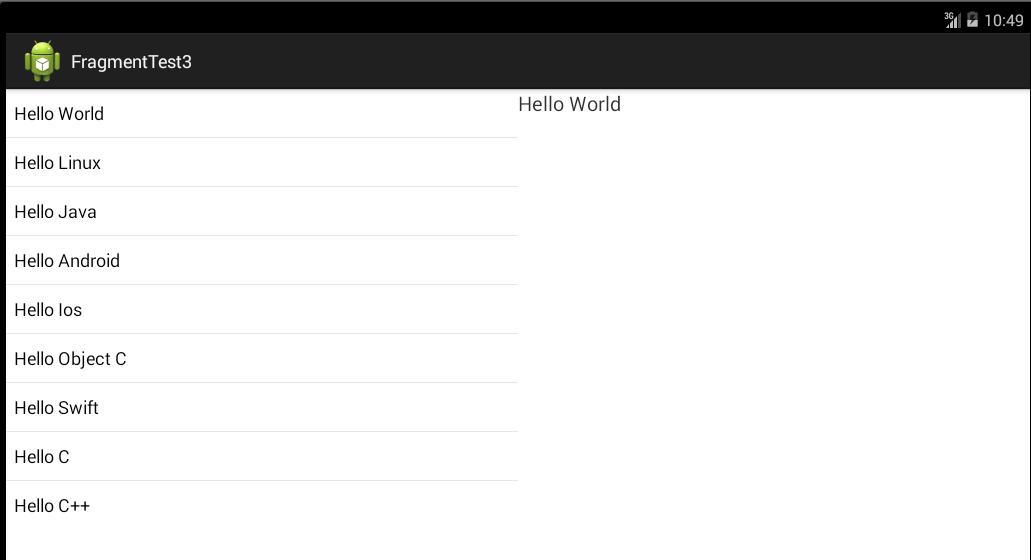
二、接下来附上一个简单的例子,该例子实现了一个碎片与另一个碎片通信的功能,实现效果如下:
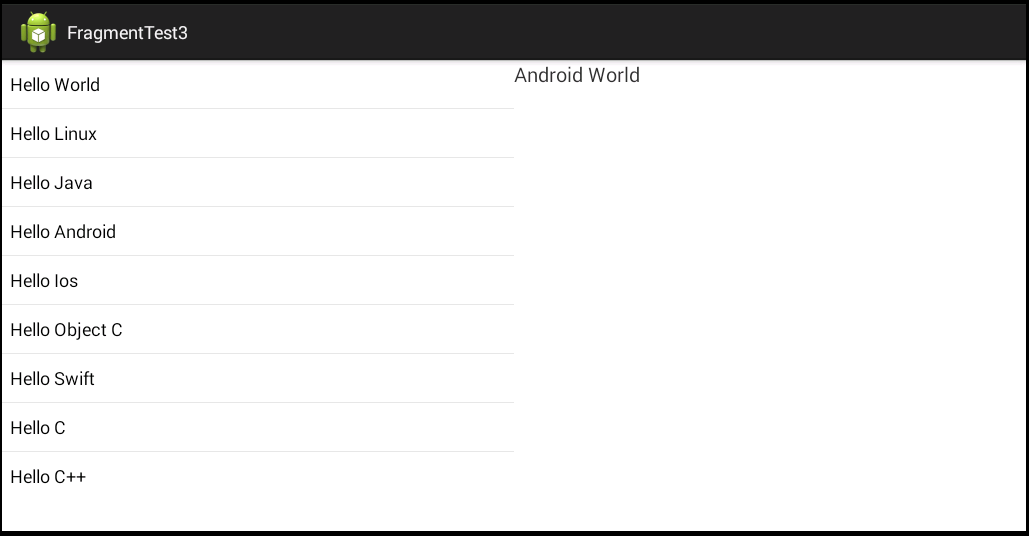
运行项目后的效果,然后点击左侧列表中的某一项,在右侧会显示你所点击的那一项的文本,如下图所示:
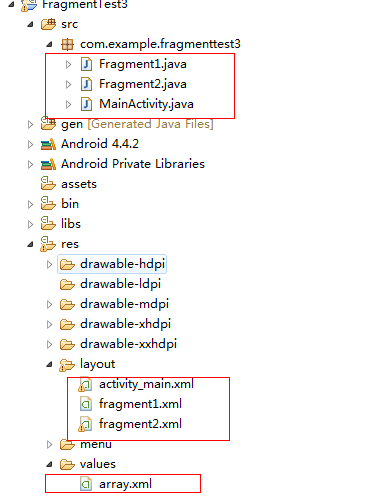
三、首先,新建一个android项目,项目名为Fragment3Test,项目结构图如下:
1、首先,在res目录下的values目录下新建一个array.xml文件,用来绑定左边碎片的列表数据,array.xml代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string-array name="list">
<item>Hello World</item>
<item>Hello Linux</item>
<item>Hello Java</item>
<item>Hello Android</item>
<item>Hello Ios</item>
<item>Hello Object C</item>
<item>Hello Swift</item>
<item>Hello C</item>
<item>Hello C++</item>
</string-array>
</resources>
2、在layout目录下新建两个布局文件,分别为fragment1.xml和fragment2.xml,代码分别如下:
fragment1.xml,用来在左边碎片展示一个列表:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:entries="@array/list"/>
</LinearLayout>
fragment2.xml,用来显示右边碎片的内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Android World"
android:textSize="20sp"/>
</LinearLayout>
3、在src目录下新建两个类,分别为Fragment1和Fragment2类,都继承于android.app.Fragment类,代码分别如下:
Fragment1.java,左边碎片,其中代码中实现了与右边碎片的通信,即实现点击左边碎片列表的哪个项,右边碎片的文本就为点击的哪个项的文本内容:
package com.example.fragmenttest3
import android.app.Fragment
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import android.view.ViewGroup
import android.widget.AdapterView
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener
import android.widget.ListView
public class Fragment1 extends Fragment {
private ListView listView
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment1, container, false)
listView=(ListView)view.findViewById(R.id.listView)
//列表点击时的事件监听器
listView.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> arg0, View arg1, int arg2,
long arg3) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
MainActivity activity=(MainActivity)getActivity()
Fragment2 fragment2=(Fragment2)activity.getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.fragment2)
//当选择列表的项,设置右边碎片中的TextView的内容
switch (arg2) {
case 0:
fragment2.textView.setText(listView.getItemAtPosition(0).toString())
break
case 1:
fragment2.textView.setText(listView.getItemAtPosition(1).toString())
break
case 2:
fragment2.textView.setText(listView.getItemAtPosition(2).toString())
break
case 3:
fragment2.textView.setText(listView.getItemAtPosition(3).toString())
break
case 4:
fragment2.textView.setText(listView.getItemAtPosition(4).toString())
break
case 5:
fragment2.textView.setText(listView.getItemAtPosition(5).toString())
break
case 6:
fragment2.textView.setText(listView.getItemAtPosition(6).toString())
break
case 7:
fragment2.textView.setText(listView.getItemAtPosition(7).toString())
break
case 8:
fragment2.textView.setText(listView.getItemAtPosition(8).toString())
break
default:
break
return view
上述代码中的:
MainActivity activity=(MainActivity)getActivity()
Fragment2 fragment2=(Fragment2)activity.getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.fragment2)
这两行代码可以获得Fragment2碎片的实例,便可以调用Fragment2碎片的方法和变量了。
Fragment2.java,右边碎片,代码如下:
package com.example.fragmenttest3;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class Fragment2 extends Fragment {
public TextView textView;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container,false);
textView=(TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.textView);
return view;
上述两个类都是加载了相应的碎片,但是我在其中加了一些逻辑。
4、修改默认的activity_main布局文件,用来添加两个碎片,代码如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment1"
android:name="com.example.fragmenttest3.Fragment1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment2"
android:name="com.example.fragmenttest3.Fragment2"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
5、默认的MainActivity不需要修改,部署此项目便得到上面第二点的效果了。
四、以上内容仅供大家参考学习,谢谢!
源码下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/download/u012561176/9262143
一、碎片虽然是嵌入在活动中显示的,但是碎片和活动都是各自存在不同的类当中的,并没有什么明显的方式来直接进行通信的。那么如果要在活动中调用碎片里的方法,在碎片里调用活动的方法,一个碎片调用另一碎片的方法,应该怎么实现呢? 1、活动中调用碎片的方法: 为了方便碎片与活动之间进行通信,FragmentManager提供了一个类似于findViewById()的方法,专门从布局文件中获取碎片的实例,代码
由于Android设备的碎片特性,关于屏幕适配的话题一直绵绵不休,这篇文章是Android开发者官网的屏幕适配教程,算是非常官方的解决方案,我们可以从这里学到很多。
这节课教你如何通过以下几种方式支持多屏幕:
☞确保你的布局能自适应屏幕
☞根据你的屏幕配置提供合适的UI布局
☞确保你当前的布局适合当前的屏幕
☞提供合适的位图(bitmap)
4.1 碎片的使用方式
4.1.1 碎片的简单用法
1、新建一个左侧碎片布局left_fragment.xml和右侧碎片布局right_fragment,并实现其代码
2、在主包下创建一个LeftFragment类和RightFragment类,均继承Fragment类,重写onCreateView()方法,这样就创造了两个碎片
3、在主活动布局activity_m
Activity调用Fragment中方法:
可以通过FragmentManager提供的fingFragmentById(id)方法,专门从布局文件中获取碎片的实例,然后就可以轻松的调用碎片里面的方法了
Fragment调用Activity中的方法:
每个碎片都可以通过调用getActivity()方法来得到和当前碎片相关联的Activity实例:
例:MainActivity
所谓进行通信,就是你使用我的数据和方法,你使用我的数据和方法。
第一步:新建一个安卓项目,代码使用https://blog.csdn.net/jintingbo/article/details/104745290中的代码,即本实验是在那篇文章的基础上的继续。
第二步:新建一个碎片,随便取一个名字,比中叫左碎片LeftFragment;
第三步:在LeftFragment中新建一个自定义的方法...
为了方便碎片和活动之间进行通信,FragmentManager提供了一个类似于findViewById()的方法,专门用于从布局文件中获取碎片实例、RightFragment rightFragment = (RightFragment)getFragmentManager()findFragmentById(R.id.right);碎片调用活动中的方法
MainActivity activity
利用intent在活动和碎片与活动之间传递数据是比较简单的,intent方法提供了许多putExtra方法的重载可供我们的各种需求。intent可以把一些数据暂存,当跳转到另一个页面之后数据也会随着跳转到相应的页面,这样就可以在之后的页面对数据进行处理.我所了解的有传递方法有(当然其他的实现方法还有很多,我会继续努力探索更多的实现方法分享给大家)
第一种:活动之间数据的传递(FiratActiv...
碎片和活动之间进行通信
虽然碎片都是嵌入在活动中显示的,可是实际上它们的关系并没有那么亲密。你可以看
出,碎片和活动都是各自存在于一个独立的类当中的,它们之间并没有那么明显的方式来直
接进行通信。如果想要在活动中调用碎片里的方法,或者在碎片中调用活动里的方法,应该
如何实现呢?
为了方便碎片和活动之间进行通信,FragmentManager 提供了一个类似于findViewById()
sugarjo:
Hyperledger Fabric学习笔记(二)- Fabric 2.2.1环境搭建
玛卡巴卡吴:


