Json library implemented by boost variant
boost variant 介绍
boost variant 是一个不同union的泛型类,用于存储和操作不同类型但在使用时存在相同抽象的对象。variant 在实现不同类型的泛型的同时,提供对其包括的具体类型的安全访问。
基于此性质,boost variant 可以应用于json 这种数据结构,我们把json 中的Object, Array, String, Number, True, False, Null 统一当做同一种variant 类型。需要注意的是,json 中的Object 和 Array 类型是递归的variant 类型,在声明时需要使用
boost::recursive_wrapper
修饰。
boost::recursivee_wrapper
用于创建包含创建的variant类型的表达式.
在访问varint 类型时,可以使用
boost::get<T>
以及
boost::apply_visitor
的形式。
更多关于 boost variant 的介绍见
https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_62_0/doc/html/variant/reference.html
json 数据结构
json 的数据类型实现在
json_type.hpp
#ifndef JSON_TYPE_HPP
#define JSON_TYPE_HPP
#include <boost/variant.hpp>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
namespace json
struct Object;
struct Array;
struct String
String() {}
String(const char* value) : value{value} {}
String(std::string value) : value{std::move(value)} {}
std::string value;
struct Number
Number() {};
Number(const double value) : value{value} {}
double value;
struct True
struct False
struct Null
using Value = boost::variant<String,
Number,
boost::recursive_wrapper<Object>,
boost::recursive_wrapper<Array>,
True,
False,
Null>;
struct Object
bool isMember(const std::string& key) const
return values.count(key) != 0;
const Value& at(const std::string& key) const
return values.at(key);
const Value& operator[](const std::string& key) const
return values.at(key);
std::unordered_map<std::string, Value> values;
struct Array
const Value& at(const size_t idx) const
return values.at(idx);
const Value& operator[](const size_t idx) const
return values.at(idx);
size_t size() const
return values.size();
const Value& front() const
return values.front();
const Value& back() const
return values.back();
std::vector<Value> values;
}
#endif
json 数据访问
本节只介绍使用
boost::get<T>
访问varint 数据。
boost::apply_visitor
的方式在序列化的部分介绍
代码示例如下
namespace access
inline const Object& asObject(const Value& value)
return boost::get<Object>(value);
inline const Array& asArray(const Value& value)
return boost::get<Array>(value);
inline const String& asString(const Value& value)
return boost::get<String>(value);
inline const Number& asNumber(const Value& value)
return boost::get<Number>(value);
inline const True& asTrue(const Value& value)
return boost::get<True>(value);
inline const False& asFalse(const Value& value)
return boost::get<False>(value);
inline const Null& asNull(const Value& value)
return boost::get<Null>(value);
}
json 序列化
json 序列化利用
boost::apply_visitor
.
boost::apply_visitor
需要实现一个visitor 函数对象,函数对象针对不同实际类型实现不同的序列化方式,针对Object以及Array 这两种类型需要递归调用visitor。
示例代码如下
#ifndef JSON_SERIALIZE_HPP
#define JSON_SERIALIZE_HPP
#include "json_type.hpp"
#include "json_util.hpp"
#include <vector>
#include <ostream>
namespace json
struct SerializeToOstream : boost::static_visitor<void>
explicit SerializeToOstream (std::ostream& out) : out(out) {}
void operator() (const String& string) const
out << "\"";
out << string.value;
out << "\"";
void operator() (const Number& number) const
out << util::cast::to_string_with_percision(number.value);
void operator() (const Object& object) const
out << "{";
for (auto it = object.values.begin(); it != object.values.end();)
out << "\"" << it->first << "\":";
boost::apply_visitor(SerializeToOstream(out), it->second);
if (++it != object.values.end())
out << ",";
out << "}";
void operator() (const Array& array) const
out << "[";
for (auto it = array.values.cbegin(); it != array.values.cend();)
boost::apply_visitor(SerializeToOstream(out), *it);
if (++it != array.values.cend())
out << ",";
out << "]";
void operator() (const True&) const
out << "ture";
void operator() (const False&) const
out << "false";
void operator() (const Null&) const
out << "null";
private:
std::ostream& out;
struct SerializeToString : boost::static_visitor<void>
explicit SerializeToString (std::string& out) : out(out) {}
void operator() (const String& string) const
out.push_back('\"');
out.append(string.value);
out.push_back('\"');
void operator() (const Number& number) const
const std::string number_str = util::cast::to_string_with_percision(number.value);
out.append(std::move(number_str));
void operator() (const Object& object) const
out.push_back('{');
for (auto it = object.values.begin(); it != object.values.end();)
out.push_back('\"');
out.append(it->first);
out.push_back('\"');
out.push_back(':');
boost::apply_visitor(SerializeToString(out), it->second);
if (++it != object.values.end())
out.push_back(',');
out.push_back('}');
void operator() (const Array& array) const
out.push_back('[');
for (auto it = array.values.cbegin(); it != array.values.cend();)
boost::apply_visitor(SerializeToString(out), *it);
if (++it != array.values.cend())
out.push_back(',');
out.push_back(']');
void operator() (const True&) const
out.append("true");
void operator() (const False&) const
out.append("false");
void operator() (const Null&) const
out.append("null");
private:
std::string& out;
void serialize(std::ostream& out, const Object& object)
Value value = object;
boost::apply_visitor(SerializeToOstream(out), value);
void serialize(std::string& out, const Object& object)
Value value = object;
boost::apply_visitor(SerializeToString(out), value);
}
#endif
构造json 结构
针对String,Number,True,False,Null 这类简单类型可以直接使用构造函数构造。
Array 类型内部使用vector 类型,构造时使用vector 的 push_back, emplace_back 方法增加Array的元素。
Object 类型内部使用unordered_map 类型,构造时可以使用 unordered_map 的内建方法。
示例代码如下:
Object obj
obj.values["string"] = "v1"
obj.values["bool"] = True()
obj.values["null"] = Null()
obj.values["number"] = Number(9)
Array arr
arr.values.emplace_back(Number(1.02))
arr.values.emplace_back(Number(2.2))
arr.values.emplace_back(Number(3))
arr.values.emplace_back(True())
arr.values.emplace_back(False())
obj.values["array"] = std::move(arr)
示例代码测试构建json对象,访问json对象,以及序列化json 对象。
示例代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include "json.hpp"
using namespace json;
int main()
Object obj;
obj.values["string"] = "v1";
obj.values["bool"] = True();
obj.values["null"] = Null();
obj.values["number"] = Number(9);
Array arr;
arr.values.emplace_back(Number(1.02));
arr.values.emplace_back(Number(2.2));
arr.values.emplace_back(Number(3));
arr.values.emplace_back(True());
arr.values.emplace_back(False());
obj.values["array"] = std::move(arr);
std::cout << "Test json access.\n";
const auto& arr1 = access::asArray(obj["array"]);
std::cout << "first number in arr is "
<< access::asNumber(arr1.front()).value << std::endl;
std::cout << "Test serialize to ostream.\n";
serialize(std::cout, obj);
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "Test serialize to string.\n";
std::string str;
serialize(str, obj);
std::cout << str << std::endl;
return 0;
g++ –std=c++11 test_json.cpp -o test_json
执行结果如下
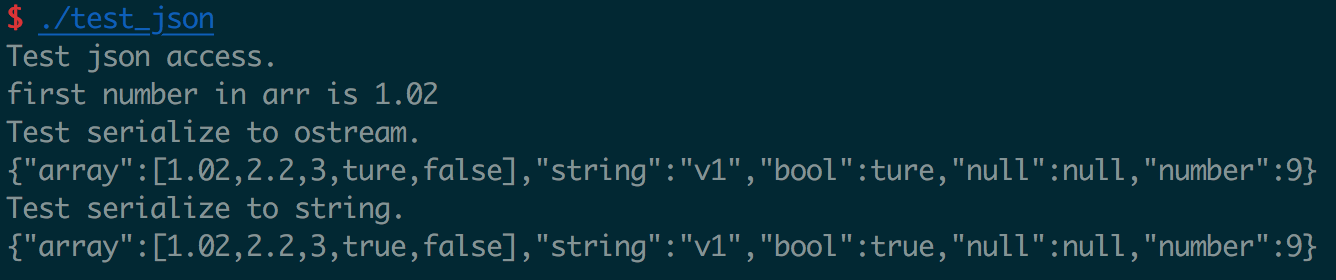
使用boost spirit 实现json 的反序列化
https://github.com/ce39906/self-practices/tree/master/cppcode/variant_json
Json library implemented by boost variantboost variant 介绍boost variant 是一个不同union的泛型类,用于存储和操作不同类型但在使用时存在相同抽象的对象。variant 在实现不同类型的泛型的同时,提供对其包括的具体类型的安全访问。 基于此性质,boost variant 可以应用于json 这种数据结构,我们把j...
C++没有元对象,无法实现
json和对象的映射(比如GSon),或者数据库的对象关系映射(比如GreenDao)。
C++可以获取变量的字符串(#define name2str(name) (#name))和变量的类型(#define getType(value) typeid(value).name()),但是并没有办法遍历类的成员属性。解决办法是给类添加一个map,在构造函数中实现成员变量名称和成员变量类型的map,但这比较复杂。QT有Q
Variant,可以很好的实现映射。
Q
Variant与对象
Awesome list of C++ GameDev project
A curated list of awesome C++ (mainly) things for Game Development. Inspired by awesome-... stuff.
~2000 projects listed here!
If you want to add projects here, do a push request or open an issue!
(Maybe some new cat
javascript模块by Kamlesh Chandnani 由Kamlesh Chandnani
了解JavaScript模块系统的基础知识,并建立自己的库 (Learn the basics of the JavaScript module system and build your own library)
Lately we all have been hearing a lot ...
/*************************************************************************
&gt; File Name: cout_uint8.cpp
&gt; Author: liuce03
&gt; Mail: liuce03@meituan.com
&gt; Creat...
两者都会调用移动构造
push 2我的理解就是有一个拷贝构造呀,然后使用placement new来进行移动构造
另外push也是能实现移动语义的吧,也有const左值引用和右值版本
c++11 右值引用,移动构造函数,emplace_back 解析
20要继续努力哦!:
c++11 右值引用,移动构造函数,emplace_back 解析
Nnboylhj:
linux shell 确保脚本只有一个运行实例
yong1585855343:
