Spring Security核心API讲解
前言
经过前面几个章节的学习,威哥带大家实现了基于内存和数据库模型的认证与授权,尤其是基于自定义的数据库模型更是可以帮助我们进行灵活开发。但是前面章节的内容,属于让我们达到了 "会用" 的层级,但是 "为什么这么用",很多小伙伴就会一脸懵逼了。对于技术学习来说,我们追求的不仅要 "知其然",更要 "知其所以然"!
本篇文章中,威哥就跟各位小伙伴一起来了解剖析Spring Security源码内部,实现认证授权的具体过程及底层原理。接下来请各位做好心理准备,以下的学习过程可能会让你心理 “稍有不适” 哦,因为每次看源码都懵懵的......
一. Spring Security认证请求完整流程图
在开始分析Spring Security关于认证授权的源码之前,威哥先借用网上的一张图片,先让各位对认证授权有个大致的了解。
下图展示了从发起一个web请求,到经过内存或数据库层面的查询,最后再得到整个用户认证信息的全过程。
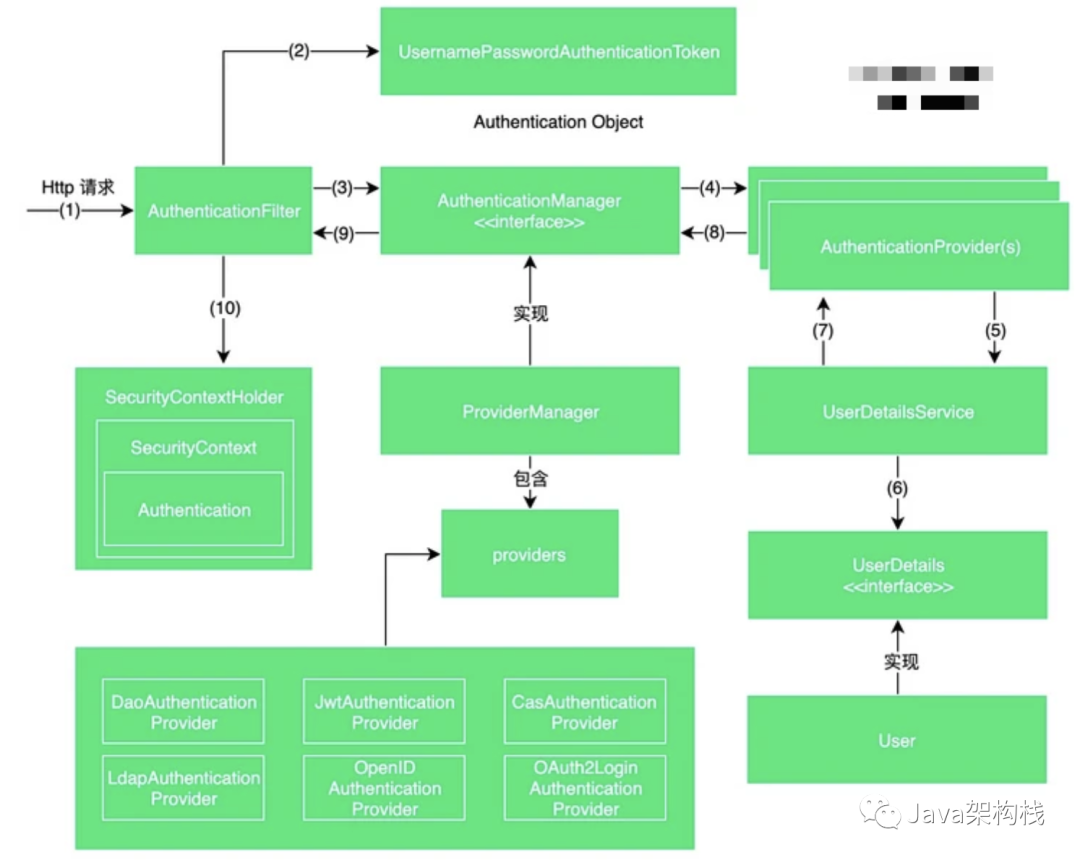
上图详细的给大家展示了Spring Security是如何实现认证授权的流程及运行原理的,并展示了Spring Security里的核心API,其中涉及到了Spring Security关于认证授权的众多核心API,威哥对这些核心API进行分析讲解,从而帮助各位掌握认证授权的执行流程。为了能让各位更好的理解掌握本文,这张图一定要背下来!
由于Spring Security中关于认证授权相关的API很多,我先把这些API归为如下几类分别进行阐述,这样显得结构会更清晰一些。
二. 核心API之一(3个)
1. Authentication
1.1 Authentication类关系
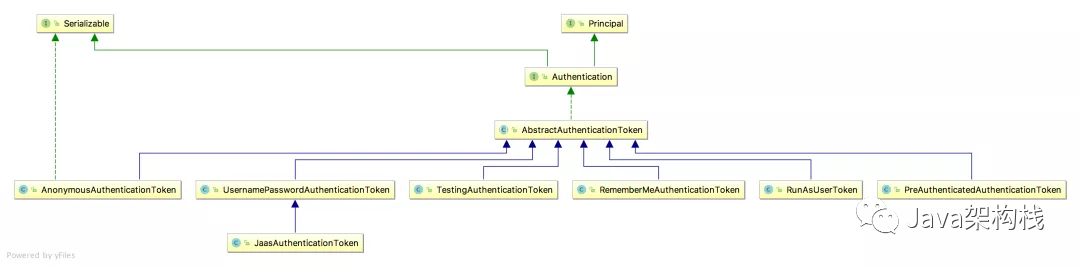
注:实线箭头表示继承,虚线箭头表示实现;绿线表示接口与接口之间的关系,蓝线表示类与类之间的关系。
Authentication 是 spring-security-core 核心包中的接口,直接继承自 Principal 接口,而 Principal 是位于 java.security包中,由此可知Authentication是SpringSecurity中的核心接口。Authentication接口中封装了用户信息,它有个很重要的子类,一定要记住:UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.
1.2 Authentication功能
在用户登录认证之前,用户名密码等信息会被封装为一个Authentication的具体实现类对象。在登录认证成功之后又会生成一个信息更全面的Authentication对象,从该对象中可以 得到用户的权限信息列表、密码、用户细节信息、用户身份信息、认证信息等。
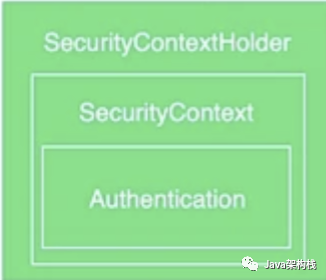
Authen tication对象会被保存在Security Context Holder所持有的Security Context 中,供后续的程序进行调用,如访问权限的鉴定等。
1.3 Authentication核心方法
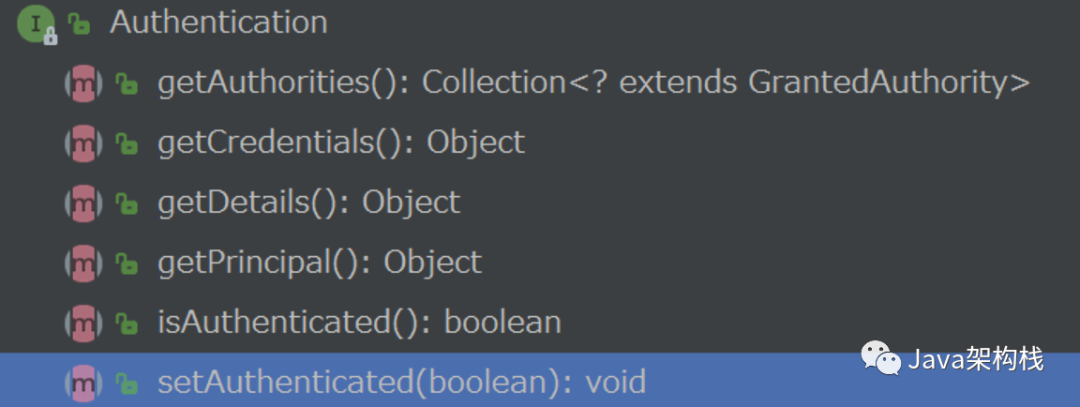
我们利用上面这些方法就可以获取到关于用户相关的信息,比如用户名、密码、角色等。
2. SecurityContext
安全上下文,该类用于存储认证授权的相关信息,实际上就是存储 "当前用户" 的账号信息和相关权限,即代表当前用户信息的 Authentication 对象会被 SecurityContext 所持有(引用),SecurityContext上下文对象则被SecurityContextHolder 所持有(引用)。
2.1 SecurityContext类源码
下面是SecurityContext的源码内容,这个接口中只有两个方法,Authentication对象的getter、setter:
public interface SecurityContext extends Serializable {
// ~ Methods
// ========================================================================================================
* Obtains the currently authenticated principal, or an authentication request token.
* @return the <code>Authentication</code> or <code>null</code> if no authentication
* information is available
Authentication getAuthentication();
* Changes the currently authenticated principal, or removes the authentication
* information.
* @param authentication the new <code>Authentication</code> token, or
* <code>null</code> if no further authentication information should be stored
void setAuthentication(Authentication authentication);
}从源码中可以得知,利用SecurityContext的getAuthentication()方法就可以拿到用户信息。
2.2 获取当前用户信息
如果是在自己的项目中,该如何获取当前已登录的用户信息呢?
因为Authentication身份信息与当前执行线程已经绑定在一起,所以我们可以使用以下代码在应用程序中获取当前已认证用户的用户名。
public String getCurrentUsername() {
//得到当前认证后的用户信息
Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
if (principal instanceof UserDetails) {
return ((UserDetails) principal).getUsername();
if (principal instanceof Principal) {
return ((Principal) principal).getName();
return String.valueOf(principal);
}3. SecurityContextHolder
3.1 SecurityContextHolder简介
由于一个请求从开始到结束都由一个线程处理,这个线程中途不会去处理其他的请求,所以在这段时间内,这个线程就相当于跟当前用户是一一对应的。
SecurityContextHolder工具类就是用于把SecurityContext存储当前线程中,Web环境,SecurityContextHolder是利用ThreadLocal来存储SecurityContext对象的。
所以SecurityContextHolder可以用来设置和获SecurityContext对象,该类主要是给框架内部使用,我们可以利用它获取当前用户的SecurityContext对象,进而进行请求检查,和访问控制等。
Security Context Holder用于存储当前应用程序的Security Context安全上下文对象,而Security Context中则存储着当前正在访问系统的Authentication用户的详细信息,如当前操作的用户是谁,该用户是否已经被认证,拥有哪些角色权限等。
我们可以用下图展示SecurityContextHolder、SecurityContext与Authentication三者之间的关系:

3.2 SecurityContextHolder的线程安全性保障
默认情况下,Security Context Holder使用 Thread Local来保存Security Context,这就意味着只要是同一线程中的方法,都可以从 ThreadLocal 中获取到当前的 SecurityContext对象。
因为Sevlet中的线程都是被池化复用的,一旦处理完当前的请求,这个线程可能马上就会被分配去处理其他的请求,而且也不能保证用户下次的请求会被分配到与上次相同的线程。
也就是我们每次在请求完成后,Spring Security都会将 Thread Local 进行清除,即在每一次 请求 结束后都会自动清除当前线程的 ThreadLocal对象。
你可能会问,这时候如果我们的认证信息没有被保存,岂不是每次请求后都要重新认证登录?这明显不行,我们肯定要保存用户的认证信息!这个保存工作是由SecurityContextPersistenceFilter来完成的!
Security Context Persistence Filter是Security中的一个拦截器,它的执行时机非常早,当请求来临时它会从Security Context Repository中把SecurityContext对象取出来,然后放入SecurityContextHolder的ThreadLocal中。
在所有拦截器都处理完成后,再把SecurityContext存入SecurityContextRepository,并清除SecurityContextHolder内的SecurityContext引用。这样就实现了用户认证信息的保存,也保证了线程的安全性!
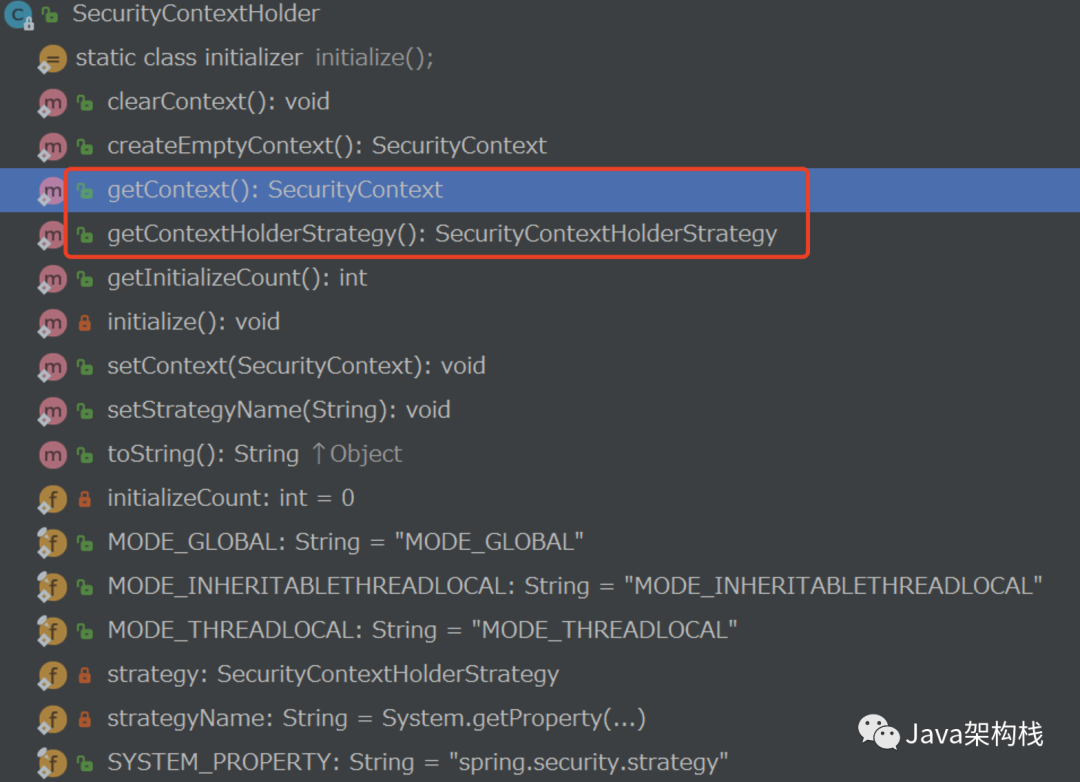
3.3 SecurityContextHolder中的方法及属性
在 SecurityContextHolder 中定义了一系列的静态方法,而这些静态方法的内部逻辑基本上都是通过 Security Context Holder 所持有的Security Context Holder Strategy对象来实现的,如getContext()、setContext()、clearContext()等。如下图所示:
3.4 SecurityContextHolder中的3种存储策略
SecurityContextHolder中定义了3种策略来管理SecurityContext对象的存储,默认使用的 strategy是基于ThreadLocal的Thread Local Security Context Holder Strategy,另外还有Global Security Context Holder Strategy 和 Inheritable Thread Local Security Context Holder Strategy两种策略。
SecurityContextHolder可以通过设置来调整3种存储策略,三种策略详情如下:
- MODE_THREADLOCAL:表示将 Security Context对象 存储在当前线程中;
- MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL:表示将 SecurityContext对象 存储在线程中,但子线程可以获取到父线程中的 SecurityContext;
- MODE_GLOBAL:表示 SecurityContext对象内容 在所有线程中都相同。
Security Context Holder默认使用MODE_THREADLOCAL模式,即存储在当前线程中,一般我们使用默认的 strategy 就可以了。
4. SecurityContextHolder、SecurityContext、Authentication总结
经过以上3个小节的学习,下面我们来简单总结一下 Security Context Holder、Security Context 和 Authentication 这三个对象之间的关系。
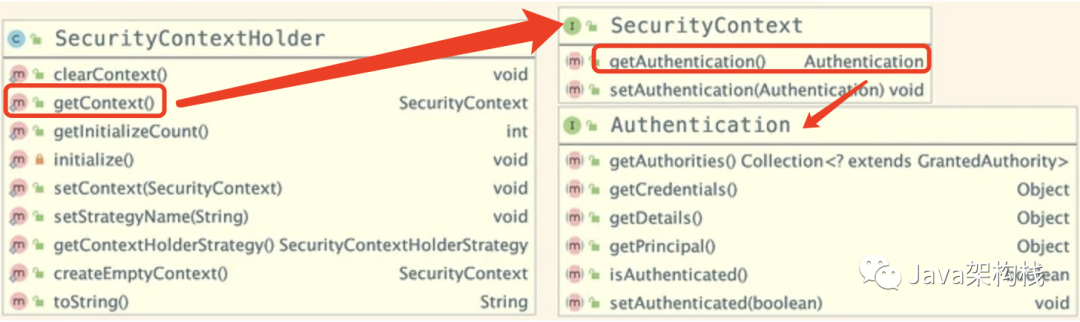
SecurityContextHolder 用来保存 SecurityContext (安全上下文对象),利用SecurityContextHolder的getContext()方法可以得到SecurityContext对象;然后再通过调用 SecurityContext 对象中的getAuthentication()方法,就可以获取 Authentication 对象;最后我们利用Authentication对象,可以进一步获取已认证用户的详细信息。
三. 核心API之二:Filter相关API
1. Filter概念
Spring Security 的底层是通过一系列的 Filter 来管理认证和授权请求的,形成了一组核心的过滤器链,每个 Filter 都有其自身的功能,而且各个 Filter 在功能上还有关联关系,项目启动后将会自动配置生效。其中最核心的就是BasicAuthenticationFilter ,该Filter用来认证用户的身份。
接下来我们先简单讲解一下各个Filter及其执行顺序。
2. Filter顺序
Spring Security 中定义的一些列Filter,不管实际应用中我们会用到哪些,它们都应当保持如下顺序。
- ChannelProcessingFilter:如果你访问的 channel 错了,那首先就会在 channel 之间进行跳转,如 http 变为 https。
- SecurityContextPersistenceFilter:在一开始进行 请求 的时候就会在 Security Context Holder 中建立一个 Security Context,然后在请求结束的时候,任何对 SecurityContext 的改变都会被 copy 到 HttpSession中。
- ConcurrentSessionFilter:因为它需要使用 Security Context Holder 的功能,而且更新对应 session 的最后更新时间,以及通过 Session Registry 获取当前的 Session Information 以检查当前的 session 是否已经过期,过期则会调用 LogoutHandler。
- 认证处理机制:如Username Password Authen tication Filter,Cas Authen tication Filter,Basic Authentication Filter 等,以至于Security Context Holder可以被更新为包含一个有效的Authentication请求。
- SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter:它将会把 Http Servlet Request 封装成一个继承自 Http Servlet Request Wrapper 的 Security Context Holder Aware Request Wrapper,同时使用Security Context实现了 HttpServletRequest 中与安全相关的方法。
- JaasApiIntegrationFilter:如果 Security Context Holder 中拥有的 Authen tication 是一个 Jaas Authen tication Token,那么该 Filter 将使用包含在 Jaas Authentication Token中的Subject继续执行FilterChain。
- RememberMeAuthenticationFilter:如果之前的认证处理机制没有更新 SecurityContextHolder,并且用户请求包含了一个 Remember-Me 对应的 cookie,那么一个对应的 Authentication 将会设给 SecurityContextHolder。
- AnonymousAuthenticationFilter:如果之前的认证机制都没有更新 Security Context Holder 拥有的 Authen tication,那么一个 Anonymous Authentication Token 将会设给 Security Context Holder。
- ExceptionTransactionFilter:用于处理在 FilterChain 范围内抛出的 Access Denied Exception 和 Authen tication Exception,并把它们转换为对应的 Http 错误码返回或者对应的页面。
- FilterSecurityInterceptor:保护 Web URI,并且在访问被拒绝时抛出异常。
3. Filter整体执行流程图
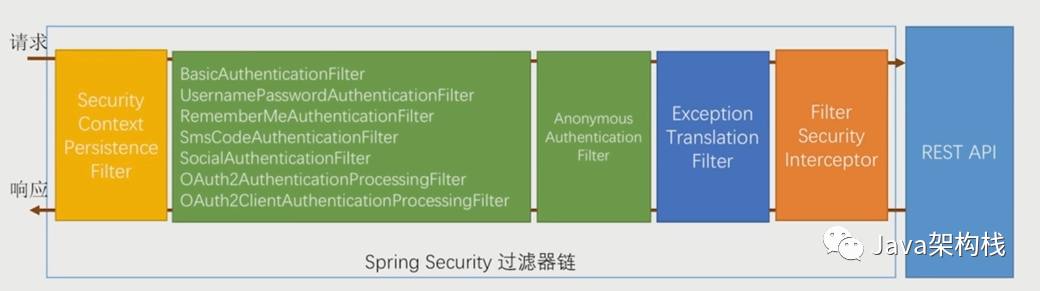
我们这个章节中暂时对过滤器链的执行流程不做详细描述,下一章节再做阐述。
四. 核心API之三:认证管理相关类
1. AuthenticationManager
Authentication Manager的作用是校验Authentication,如果验证失败会抛出Authentication Exception异常。Authen tication Exception是抽象类,因此并不能实例化一个AuthenticationException异常并抛出,实际抛出的通常是其实现子类,如Disabled Exception、Locked Exception、Bad Credentials Exception等。Authentication Manager的核心认证方法authenticate()如下所示:
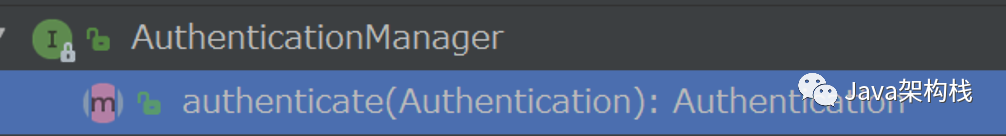
AuthenticationManager是认证相关的核心接口,也是发起认证的起点。
在实际开发中,我们可能会允许用户使用 用户+密码登录,同时允许用户使用 邮箱+密码,手机号码+密码登录,甚至可能允许用户使用 指纹 登录,所以要求认证系统支持多种认证方式。几种不同的认证方式:用户名 + 密码(Username Password Authen tication Token),邮箱+密码,手机号码+密码登录,可以分别对应三种不同的 AuthenticationProvider 子类。
2. ProviderManager
Spring Security中Authentication Manager接口的默认实现类是ProviderManager,但它本身并不直接处理身份认证请求,它会委托给内部配置的Authentication Provider列表providers。
该列表会进行循环遍历,依次对比匹配以查看它是否可以执行身份验证,每个Provider 验证程序在验证后,将会抛出异常或返回一个完全填充的Authentication对象。源码如下所示:
// org/springframework/security/authentication/ProviderManager.java
public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware,
InitializingBean {
//维护一个AuthenticationProvider列表
private List<AuthenticationProvider> providers = Collections.emptyList();
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
AuthenticationException parentException = null;
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 遍历providers列表,判断是否支持当前authentication对象的认证方式
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
try {
// 执行provider的认证方式并获取返回结果
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
catch (AccountStatusException | InternalAuthenticationServiceException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
throw e;
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
// 若当前ProviderManager无法完成认证操作,且其包含父级认证器,则允许转交给父级认证器尝试进行认证
if (result == null && parent != null) {
try {
result = parentResult = parent.authenticate(authentication);
catch (ProviderNotFoundException e) {
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = parentException = e;
if (result != null) {
if (eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication
&& (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
// 完成认证,从authentication对象中移除私密数据
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
// 若父级AuthenticationManager认证成功,则派发AuthenticationSuccessEvent事件
if (parentResult == null) {
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
return result;
// 未认证成功,抛出ProviderNotFoundException异常
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(messages.getMessage(
"ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() },
"No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
if (parentException == null) {
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
throw lastException;
}在 Provider Manager 进行认证的过程中,会遍历providers列表,判断是否支持对当前 authen tication 对象的认证方式。若支持该认证方式时,就会调用所匹配 provider (Authentication Provider)对象的 authenticate()方法进行认证操作;
若认证失败则返回 null,下一个Authentication Provider 会继续尝试认证。如果所有认证器都无法认证成功,则 Provider Manager 会抛出一个 Provider NotFound Exception 异常。
五. 核心API之四:认证实现类AuthenticationProvider
1. UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
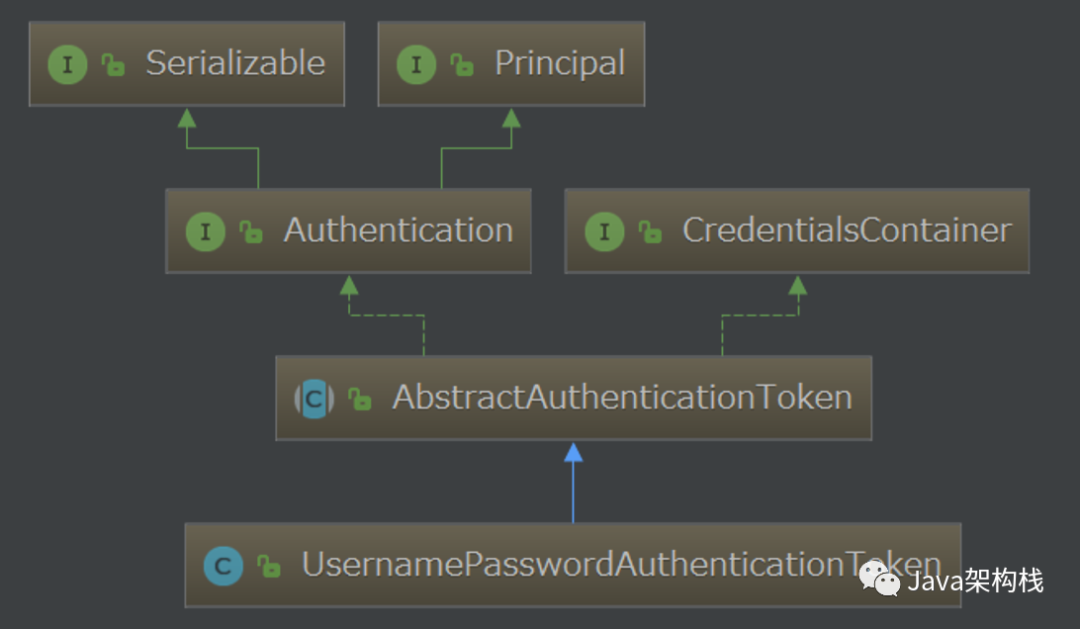
Username Password Authentication Token继承自Abstract Authentication Token类,实现了Authentication接口。在Spring Security 中,当我们使用用户名和密码进行登录认证的时候,用户在登录表单中提交的用户名和密码信息,都会被封装到 Username Password Authentication Token 对象中。
这个生成的Token(Authentication)对象,接下来会被交由Authentication Manager来进行管理,而Authentication Manager内部又管理了一系列的Authentication Provider对象,每一个Provider都会调用User Details Service和User Detail类,来查询返回一个Authentication对象,该对象中包含有用户名、密码、权限等信息。
2. AuthenticationProvider简介
Authentication Manager是负责管理协调认证工作的,但并不负责认证功能的真正实现,认证功能的真正实现是由 Authen tication Manager 中引用的 Authen tication Provider 类来完成的,通过源码我们可以看到Authen tication Manager 中引用了一个providers列表,如下所示:
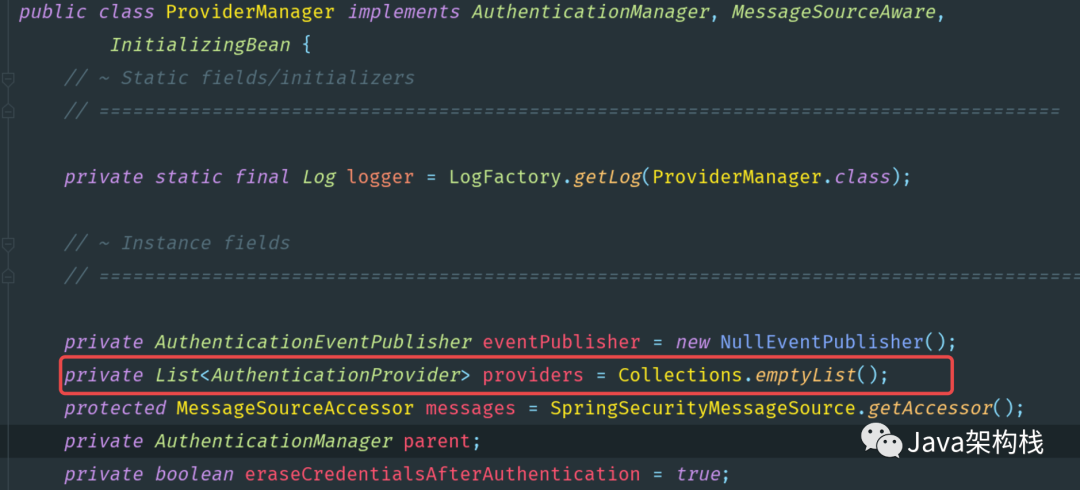
providers集合的泛型是Authen tication Provider接口,Authen tication Provider接口有多个实现子类,如下图:
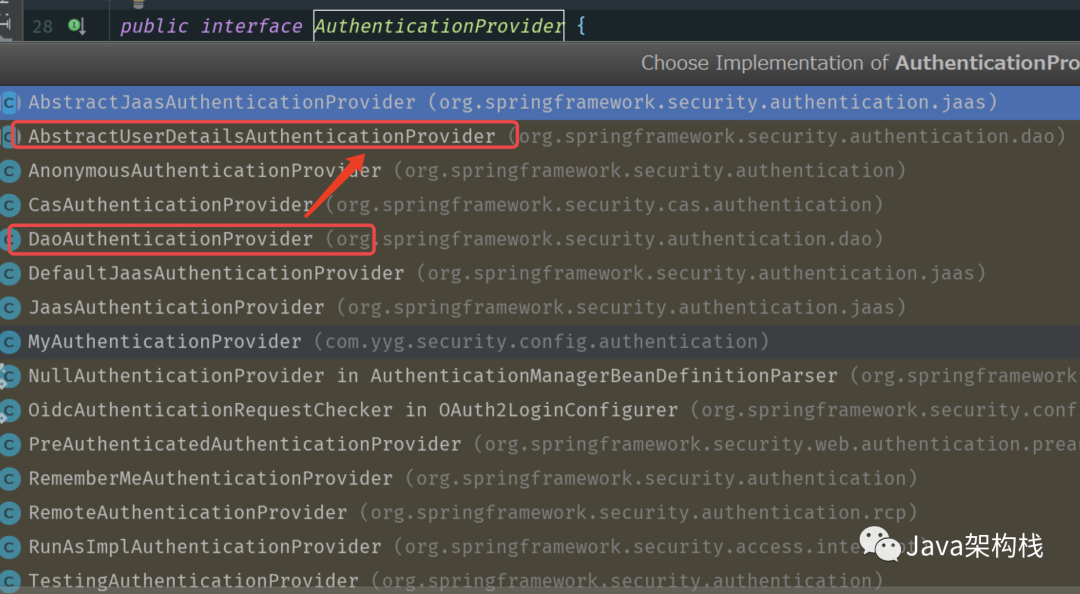
3. DaoAuthenticationProvider类关系
Authen tication Provider接口的一个直接子类是Abstract User Details Authentication Provider,该类又有一个直接子类Dao Authen tication Provider,这三个类之间的关系图如下:
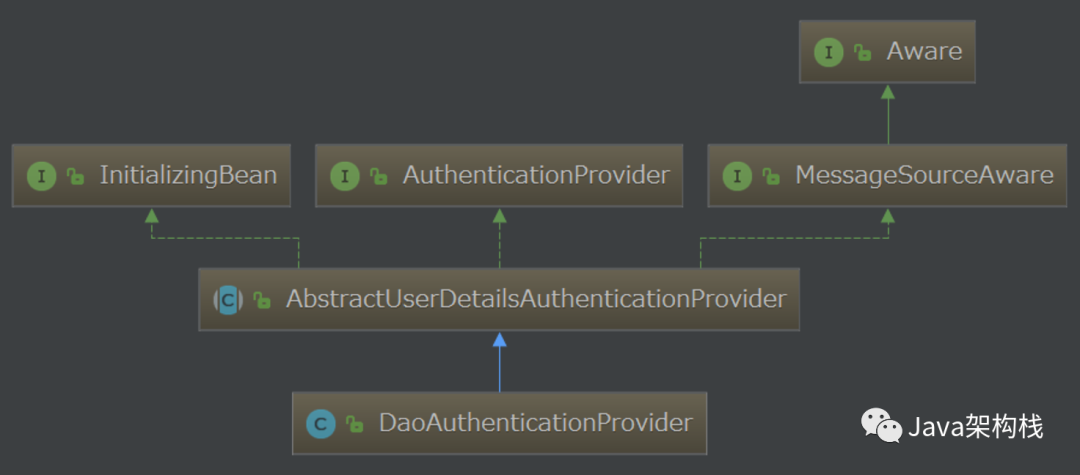
Spring Security中默认就是使用Dao Authentication Provider来实现基于数据库模型认证授权工作的!
Dao Authentication Provider 在进行认证的时候,需要调用 User Details Service 对象的load User By Username() 方法来获取用户信息 User Details,其中包括用户名、密码和所拥有的权限等。所以如果我们需要改变认证方式,可以实现自己的 Authentication Provider;如果需要改变认证的用户信息来源,我们可以实现 User Details Service。
4. authenticate()认证方法源码剖析
在实际项目中,最常见的认证方式是基于数据库模型,使用用户名和密码进行认证,具体是由Dao Authentication Provider类实现的。对于已注册的用户,因为我们在数据库中已保存了正确的用户名和密码,所以认证就是对比用户在登录表单中提交的用户名、密码,与数据库中所保存的用户名、密码是否相同。这个认证的实现,主要是基于如下源码来实现的。
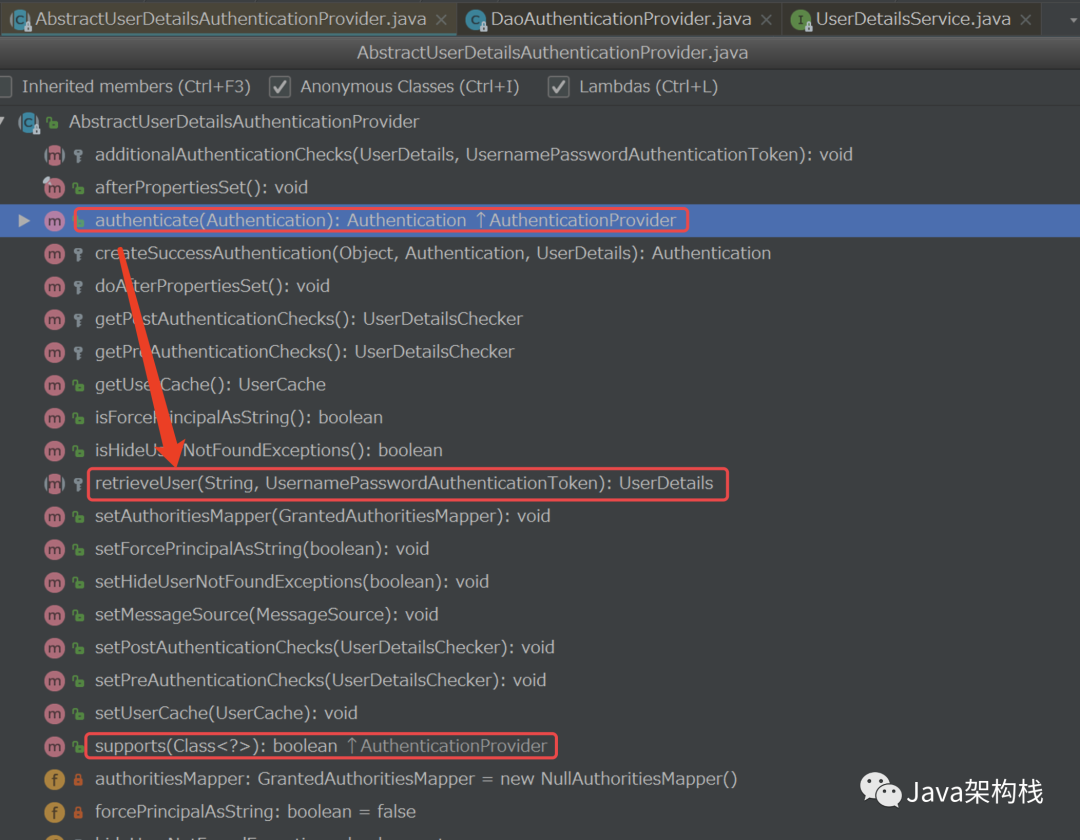
首先我们知道,在Authentication Provider接口中有个authen ticate()方法,但是该方法并没有默认实现,如下所示:
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}这个authenticate()方法是在Authen tication Provider的子类Abstract User Details Authentication Provider中实现的,实现源码如下:
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Assert.isInstanceOf(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class, authentication,
() -> messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.onlySupports",
"Only UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken is supported"));
// Determine username
//从认证对象中得到用户名
String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED"
: authentication.getName();
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
//根据用户名获取缓存的用户对象
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
//在缓存为空的情况下,调用retrieveUser()方法,根据用户名查询用户对象。
//其中的retrieveUser()方法是个抽象方法,由子类DaoAuthenticationProvider来实现。
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
catch (UsernameNotFoundException notFound) {
logger.debug("User '" + username + "' not found");
if (hideUserNotFoundExceptions) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
else {
throw notFound;
Assert.notNull(user,
"retrieveUser returned null - a violation of the interface contract");
try {
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
catch (AuthenticationException exception) {
if (cacheWasUsed) {
// There was a problem, so try again after checking
// we're using latest data (i.e. not from the cache)
cacheWasUsed = false;
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
else {
throw exception;
postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}5. retrieveUser()检索用户方法源码剖析
在上面的authenticate()方法内部,调用了retrieveUser()方法,该方法是抽象方法,根据用户名查询用户信息,由子类Dao Authen tication Provider来具体实现,如下所示:
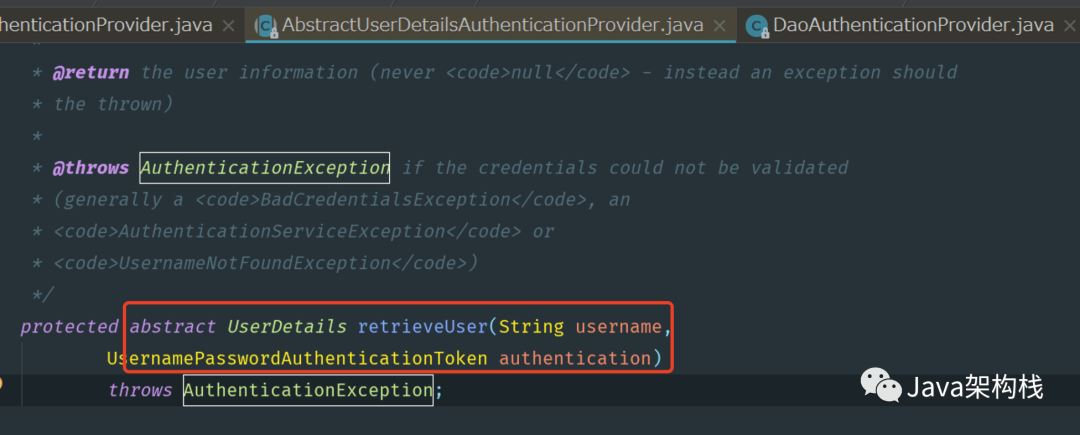
当我们使用用户名和密码进行认证时,用户在登录页面表单中提交的用户名和密码,会被封装成了 Username Password Authen tication Token对象。在 Dao Authen tication Provider 类中,会对retrieve User()方法进行具体实现,来根据用户名加载用户的信息。
该方法虽然有两个参数,但只有第一个参数起主要作用,该方法会返回一个 UserDetails对象。retrieveUser 方法的具体实现如下:
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)throws AuthenticationException {
prepareTimingAttackProtection();
try {
//这里调用了我们自己编写的UserDetailsService对象中的loadUserByUsername()方法!
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
return loadedUser;
}catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(authentication);
throw ex;
}catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
throw ex;
}catch (Exception ex) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}在 Dao Authentication Provider 类的 retrieve User() 方法中,会以传入的 username 作为参数,再调用 User Details Service 对象的 loadUserByUsername() 方法加载用户。
6. 完整的authenticate流程
(1)在ProviderManager类中遍历List providers集合,判断AuthenticationProvider类是否支持对当前对象进行认证;
(2)如果支持,则调用AuthenticationProvider接口对象的authenticate (authentication)方法进行认证;
(3)结合当前具体的认证实现模型,如果是基于数据库模型来进行表单认证,则执行AbstractUser Details Authentication Provider类中的authenticate (authentication)方法具体进行认证;
(4)AbstractUserDetails Authentication Provider类中的authenticate (authentication)方法内部会调用retrieveUser()抽象方法加载对象;
(5)在DaoAuthenticationProvider类中具体执行retrieveUser()方法,在该方法中调用User Details Service对象的loadUser By Username (username)方法,从而实现根据用户名从数据库中查询用户信息。
六. 核心API之五(4个)
1. UserDetails接口
UserDetails 是 Spring Security 中的核心接口,它表示用户的详细信息,这个接口涵盖了一些必要的用户信息字段。我们可以将UserDetails视为自己的用户数据库和SecurityContextHolder所需的适配器,通过具体的实现类对它进行扩展。通常我们可以将UserDetails强制转换为应用程序提供的原始对象,以便我们调用特定的业务方法(例如getEmail(),getEmployeeNumber()等)。UserDetails接口的源码定义如下:
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
//获取用户权限,本质上是用户的角色信息
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
//获取密码
String getPassword();
//获取用户名
String getUsername();
//判断账户是否未过期
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
//判断账户是否未锁定
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
//判断密码是否未过期
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
