|
|
眉毛粗的匕首 · Vue集成Iframe页面-阿里云开发者社区· 1 年前 · |
|
|
曾经爱过的小笼包 · 新格局下 传统出口强市如何应对挑战?· 1 年前 · |
|
|
狂野的金针菇 · docker-compose设置容器中sys ...· 1 年前 · |
|
|
想出国的拐杖 · ModuleNotFoundError: ...· 2 年前 · |
|
|
狂野的啄木鸟 · 哪种Python循环方式最快?-python ...· 2 年前 · |
以上实例编译运行结果如下:
runoob 注意: String 类是不可改变的,所以你一旦创建了 String 对象,那它的值就无法改变了(详看笔记部分解析)。
如果需要对字符串做很多修改,那么应该选择使用 StringBuffer & StringBuilder 类 。
字符串长度
用于获取有关对象的信息的方法称为访问器方法。
String 类的一个访问器方法是 length() 方法,它返回字符串对象包含的字符数。
下面的代码执行后,len 变量等于 14:
StringDemo.java 文件代码:
以上实例编译运行结果如下:
菜鸟教程网址长度 : 14连接字符串
String 类提供了连接两个字符串的方法:
"我的名字是 ".concat("Runoob");
更常用的是使用'+'操作符来连接字符串,如:
"Hello," + " runoob" + "!" 结果如下:
"Hello, runoob!" 下面是一个例子:
StringDemo.java 文件代码:
以上实例编译运行结果如下:
1、菜鸟教程网址:www.runoob.com创建格式化字符串
我们知道输出格式化数字可以使用 printf() 和 format() 方法。
String 类使用静态方法 format() 返回一个String 对象而不是 PrintStream 对象。
String 类的静态方法 format() 能用来创建可复用的格式化字符串,而不仅仅是用于一次打印输出。
如下所示:
你也可以这样写
String 方法
下面是 String 类支持的方法,更多详细,参看 Java String API 文档:
boolean regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase, int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len)测试两个字符串区域是否相等。 boolean regionMatches(int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len)
测试两个字符串区域是否相等。 String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)
返回一个新的字符串,它是通过用 newChar 替换此字符串中出现的所有 oldChar 得到的。 String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement)
使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串所有匹配给定的正则表达式的子字符串。 String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement)
使用给定的 replacement 替换此字符串匹配给定的正则表达式的第一个子字符串。 String[] split(String regex)
根据给定正则表达式的匹配拆分此字符串。 String[] split(String regex, int limit)
根据匹配给定的正则表达式来拆分此字符串。 boolean startsWith(String prefix)
测试此字符串是否以指定的前缀开始。 boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset)
测试此字符串从指定索引开始的子字符串是否以指定前缀开始。 CharSequence subSequence(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
返回一个新的字符序列,它是此序列的一个子序列。 String substring(int beginIndex)
返回一个新的字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串。 String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
返回一个新字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串。 char[] toCharArray()
将此字符串转换为一个新的字符数组。 String toLowerCase()
使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为小写。 String toLowerCase(Locale locale)
使用给定 Locale 的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为小写。 String toString()
返回此对象本身(它已经是一个字符串!)。 String toUpperCase()
使用默认语言环境的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为大写。 String toUpperCase(Locale locale)
使用给定 Locale 的规则将此 String 中的所有字符都转换为大写。 String trim()
返回字符串的副本,忽略前导空白和尾部空白。 static String valueOf(primitive data type x)
返回给定data type类型x参数的字符串表示形式。 contains(CharSequence chars)
判断是否包含指定的字符系列。 isEmpty()
判断字符串是否为空。
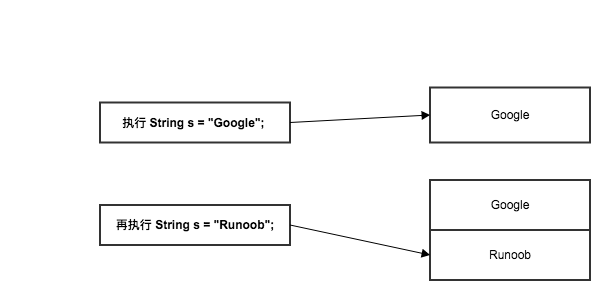
从结果上看是改变了,但为什么说 String 对象是不可变的呢?
原因在于实例中的 s 只是一个 String 对象的引用,并不是对象本身,当执行 s = "Runoob"; 创建了一个新的对象 "Runoob",而原来的 "Google" 还存在于内存中。
tianqixin
429***967@qq.com
豆妮的小奴隶
861***743@qq.com
length() 方法,length 属性和 size() 方法的区别:
1、 length() 方法是针对字符串来说的,要求一个字符串的长度就要用到它的length()方法; 2、 length 属性 是针对 Java 中的数组来说的,要求数组的长度可以用其 length 属性; 3、Java 中的 size() 方法是针对泛型集合说的, 如果想看这个泛型有多少个元素, 就调用此方法来查看!这个例子来演示这两个方法和一个属性的用法:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { String array[] = { "First", "Second", "Third" }; String a = "HelloWorld"; List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); list.add(a); System.out.println("数组array的长度为" + array.length); System.out.println("字符串a的长度为" + a.length()); System.out.println("list中元素个数为" + list.size()); 输出的值为: 数组array的长度为3 字符串a的长度为10 list中元素个数为11.对整数进行格式化:%[index$][标识][最小宽度]转换方式
格式化字符串由4部分组成,特殊的格式常以%index$开头,index从1开始取值,表示将第index个参数拿进来进行格式化,[最小宽度]的含义也很好理解,就是最终该整数转化的字符串最少包含多少位数字。剩下2个部分的含义:
'-' 在最小宽度内左对齐,不可以与"用0填充"同时使用 '#' 只适用于8进制和16进制,8进制时在结果前面增加一个0,16进制时在结果前面增加0x '+' 结果总是包括一个符号(一般情况下只适用于10进制,若对象为BigInteger才可以用于8进制和16进制) ' ' 正值前加空格,负值前加负号(一般情况下只适用于10进制,若对象为BigInteger才可以用于8进制和16进制) '0' 结果将用零来填充 ',' 只适用于10进制,每3位数字之间用","分隔 '(' 若参数是负数,则结果中不添加负号而是用圆括号把数字括起来(同'+'具有同样的限制)转换方式:
d-十进制 o-八进制 x或X-十六进制
上面的说明过于枯燥,我们来看几个具体的例子。需要特别注意的一点是:大部分标识字符可以同时使用。
System.out.println(String.format("%1$,09d", -3123));
System.out.println(String.format("%1$9d", -31));
System.out.println(String.format("%1$-9d", -31));
System.out.println(String.format("%1$(9d", -31));
System.out.println(String.format("%1$#9x", 5689));
//结果为:
//-0003,123
// -31
//-31
// (31)
// 0x1639
2.对浮点数进行格式化:%[index$][标识][最少宽度][.精度]转换方式
我们可以看到,浮点数的转换多了一个"精度"选项,可以控制小数点后面的位数。
- '-' 在最小宽度内左对齐,不可以与"用0填充"同时使用
- '+' 结果总是包括一个符号
- ' ' 正值前加空格,负值前加负号
- '0' 结果将用零来填充
- ',' 每3位数字之间用","分隔(只适用于fgG的转换)
-
'(' 若参数是负数,则结果中不添加负号而是用圆括号把数字括起来(只适用于eEfgG的转换)
转换方式:
- 'e', 'E' -- 结果被格式化为用计算机科学记数法表示的十进制数
- 'f' -- 结果被格式化为十进制普通表示方式
- 'g', 'G' -- 根据具体情况,自动选择用普通表示方式还是科学计数法方式
-
'a', 'A' -- 结果被格式化为带有效位数和指数的十六进制浮点数
3.对字符进行格式化:
对字符进行格式化是非常简单的,c表示字符,标识中'-'表示左对齐,其他就没什么了。
hunter
hun***es@126.com
hunter
hun***es@126.com
Java:String、StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 的区别
String :字符串常量,字符串长度不可变。Java中String 是immutable(不可变)的。用于存放字符的数组被声明为final的,因此只能赋值一次,不可再更改。
StringBuffer :字符串变量(Synchronized,即线程安全)。如果要频繁对字符串内容进行修改,出于效率考虑最好使用 StringBuffer,如果想转成 String 类型,可以调用 StringBuffer 的 toString() 方法。Java.lang.StringBuffer 线程安全的可变字符序列。在任意时间点上它都包含某种特定的字符序列,但通过某些方法调用可以改变该序列的长度和内容。可将字符串缓冲区安全地用于多个线程。
StringBuilder :字符串变量(非线程安全)。在内部 StringBuilder 对象被当作是一个包含字符序列的变长数组。
基本原则:
- 如果要操作少量的数据用 String ;
- 单线程操作大量数据用StringBuilder ;
- 多线程操作大量数据,用StringBuffer。
阿颖
553***793@qq.com
GritHub
147***6963@qq.com
String 类中 concat() 方法和 + 号的区别:
pubic class Demo{ pulic satic void main(String[] args){ String str1 = "a".concat("b").concat("c"); String str2 = "a"+"b"+"c"; String str3 = "abc"; String str4 = new String("abc"); System.out.println(str1 == str2); //运行结果为false System.out.println(str1 == str3); //运行结果为false System.out.println(str2 == str3); //运行结果为ture System.out.println(str2 == str4); //运行结果为false System.out.println(str1.equals(str4)); //运行结果为true执行结果为:
false false false首先关于 new 出来的对象和 String s = "字符串" 的 == 执行结果为 false 就不多赘述了,因为 == 比较的是两个对象的地址值,equals() 比较的是字面值。那么 concat 方法和 + 号的区别在这里有体现了,我们查看concat方法的源码可以看到,它是通过复制数组在通过 char 数组进行拼接生成一个新的对象,所以地址值会有变动,而 + 号不会。(作者很菜,初来乍到,前辈多包涵)
|
|
眉毛粗的匕首 · Vue集成Iframe页面-阿里云开发者社区 1 年前 |
|
|
曾经爱过的小笼包 · 新格局下 传统出口强市如何应对挑战? 1 年前 |