c++映射map、multimap详解
首先map 容器存储的都是 pair 对象,也就是用 pair 类模板创建的键值对。其中,各个键值对的键和值可以是任意数据类型,包括 C++ 基本数据类型(int、double 等)、使用结构体或类自定义的类型。
其次在使用 map 容器存储多个键值对时,该容器会自动根据各键值对的键的大小,按照既定的规则进行排序。
默认情况下,其会根据键的大小对所有键值对做升序排序,即使用std::less<Key>;根据实际情况的需要,既可以选用 STL 标准库中提供的其它排序规则(比如std::greater<Key>),也可以自定义排序规则(在value为类时使用)。
需要注意的是,使用 map 容器存储的各个键值对,键的值既不能重复也不能被修改。换句话说,map 容器中存储的各个键值对不仅键的值独一无二,
键的类型也会用 const 修饰
,这意味着只要键值对被存储到 map 容器中,其键的值将不能再做任何修改。
map 容器定义
#include <map>
using namespace std;map 容器的模板定义如下:
template < class Key, // 指定键(key)的类型
class T, // 指定值(value)的类型
class Compare = less<Key>, // 指定排序规则
class Alloc = allocator<pair<const Key,T> > // 指定分配器对象的类型
> class map;构造函数:
- map(const Pred& comp=Pred(),const A& al=A()):创建空映射。
- map(const map& x):复制构造函数。
- map(const value_type * first,const value_type * last,const Pred& comp=Pred(),const A& al=A()):复制[first,last)之间元素构成新映射。
- multimap(const Pred& comp=Pred(),const A& al=A()):创建空映射。
- multimap(const multimap& x):复制构造函数。
- multimap(const value_type * first,const value_type * last,const Pred& comp=Pred(),const A& al=A()):复制[first, last)之间元素构成新映射。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
void Display(map<int, string>& m) {
map<int, string>::iterator te = m.begin();
while (te != m.end()) {
cout << (*te).first << "\t" << te->second << endl;
te++;
int main() {
map<int, string>mymap;
pair<int, string>s1(1, "zhangsan");
pair<int, string>s2(3, "lisi");
pair<int, string>s3(6, "wangwu");
pair<int, string>s4(5, "zhaoliu");
pair<int, string>s5(1, "zhangsan");
mymap.insert(s1);
mymap.insert(s2);
mymap.insert(s3);
mymap.insert(s4);
auto res = mymap.insert(s5);
cout<< typeid(res).name() <<endl;
if(!res.second){
cerr<< "Fail to insert a pair<K,V>" <<endl;
cout << "通过insert构建map: " << endl;
Display(mymap);
cout << "通过复制构造函数构建map: " << endl;
map<int, string>mymap2(mymap);
Display(mymap2);
return 0;
}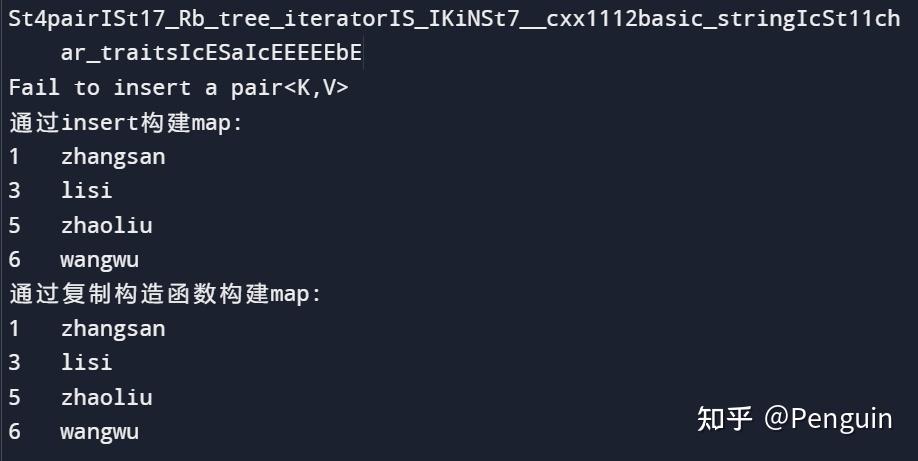
map不允许有重复键值,本例中有5个pair 对象,且 sl、s5有相同的键值,则在map 容器中只保留先存入的s1对象, s5则不能保存。如果把map换成multimap,则可以保存s5了。
特殊函数:
reference operator[](const Key& k):仅用在单映射map类中,可以以数组的形式给映射添加键值对,并可返回值的引用。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, string>mymap;
mymap["1-1"] = "元旦";
mymap["5-1"] = "五一劳动节";
mymap["7-1"] = "建党节";
mymap["8-1"] = "建军节";
mymap["10-1"] = "国庆节";
//mymap["6-1"] = "";
string s = mymap["1-1"];
if (s.length() > 0) {
cout << "1-1 is: " << s << endl;
else {
cout << "1-1 not resident" << endl;
try {
string s2 = mymap.at("6-1");
cout << s2 << endl;
catch (const out_of_range& e) {
cerr << e.what() << "\t" << "6-1" << "not find." << endl;
if (mymap.count("6-1")) {
cout << mymap["6-1"] << endl;
else {
cout << "6-1" << "not found." << endl;
string s1 = mymap["6-1"];
if (s1.length() > 0) {
cout << "6-1 is: " << s1 << endl;
else {
cout << "6-1 not resident" << endl;
return 0;
}
增加、删除函数:
- iterator insert(const value_type&. x):插人元素x。
- iterator insert(iterator it,const value_type& x):在迭代指针it处插入元素x。
- void insert(const value_type * first,const value_type * last):插入[first, last)间元素。
- iterator erase(iterator it):删除迭代指针it处元素。
- iterator erase(iterator first,iterator last):删除[first,last)迭代指针间元素。
- size_type erase(const Key& key):删除键值等于key的元素。
遍历函数:
- iterator begin():返回首元素的迭代器指针。
- iterator end():返回尾元素后的迭代器指针,而不是尾元素的迭代器指针。re
- verse_iterator rbegin():返回尾元素的逆向迭代器指针,用于逆向遍历容器。reverse_iterator
-
rend():返回首元素前的逆向迭代器指针,用于逆向遍历容器。
假设公司雇员属性有雇员姓名(没有重复的姓名)部门名称。编制管理雇员的集合类,仅包含:(1)添加雇员功能;(2)显示功能,要求按部门名称升序排列,若部门名相同,则按姓名升序排列。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
class CEMployee
public:
CEMployee(string name, string departname){
this->name = name;
this->departname = dapartname;
bool operator<(const CEMployee& e)const {
bool mark = (departname.compare(e.departname) < 0) ? true : false;
if (departname.compare(e.departname) == 0) {
mark = (name.compare(e.name) < 0) ? true : false;
return mark;
string GetName()const { return name; }
string GetDepart()const { return departname; }
private:
string name;
string departname;
class CManage {
multiset<CEMployee>myset;
public:
bool Add(CEMployee& e) {
myset.insert(e);
return true;
void show() {
multiset<CEMployee>::iterator te = myset.begin();
while (te != myset.end()) {
const CEMployee& obj = *te; //以引用的方式指向本身ref
cout << obj.GetName() << "\t" << obj.GetDepart() << endl;
te++;
int main() {
CEMployee e1("Jon", "人力部");
CEMployee e2("LiSa", "装配部");
CEMployee e3("BaTa", "制造部");
CEMployee e4("LiNa", "制造部");
CEMployee e5("Mack", "装配部");
CEMployee e6("Anna", "制造部");
CManage manage;
manage.Add(e1);
manage.Add(e2);
manage.Add(e3);
manage.Add(e4);
manage.Add(e5);
manage.Add(e6);
manage.show();
return 0;
}
由于一个部门可以有许多雇员﹐因此应当采用multiset类。应该利用集合类,在添加雇员时,直接完成先按部门升序排列,再按姓名升序排列,即在恰当的位置重载operator≤运算符,完成自定义排序规则功能。
如何获得有关multimap对象的信息呢?成员函数count()接受键作为参数,并返回具有该键的元素数目。成员函数 lower_bound()和 upper_bound()将键作为参数。成员函数equal_range()用键作为参数,且返回两个迭代器,它们表示的区间与该键匹配。为返回两个值,该方法将它们封装在一个pair对象中,这里pair 的两个模板参数都是迭代器。
操作函数:
- const_iterator lower_bound(const Key& key):返回键值大于等于key的迭代指针,否则返回end()。
- const_iterator upper_bound(const Key& key):返回键值大于 key的迭代指针,否则返回end()。
- int count(const Key&. key) const:返回容器中键值等于key的元素个数。
- pair≤const_iterator,const_iterator> equal_range(const Key& key) const:返回容器中键值等于key的迭代指针[first,last)。
- const_iterator find(const Key& key) const:查找功能,返回键值等于key的迭代器指针。
- void swap(map& s):交换单映射元素。
- void swap(multimap&. s):交换多映射元素。
例如,下面的代码打印 codes对象中区号为718的所有城市:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
typedef std::pair<const int, std::string> Pair;
typedef std::multimap<int, std::string> MapCode;
int main(){
using namespace std;
MapCode codes;
codes.insert(Pair(415, "北京"));
codes.insert(Pair(510, "大连"));
codes.insert(Pair(718, "太原"));
codes.insert(Pair(718, "拉萨"));
codes.insert(Pair(415, "上海"));
codes.insert(Pair(510, "广州"));
cout<< "Number of cities with area code 415: "
<< codes.count(415) <<endl;
cout<< "Number of cities with area code 718: "
<< codes.count(718) <<endl;
cout<< "Number of cities with area code 510: "
<< codes.count(510) <<endl;
pair<MapCode::iterator, MapCode::iterator> range
= codes.equal_range(718);
cout<< "Cities with area code 718: " <<endl;
for(auto it = range.first; it != range.second; it++){
cout<< (*it).second <<endl;
return 0;
}
编一个同义词字典功能类,每个单词后面跟着它的同义词
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class CWord {
private:
string mainword;
vector<string>vecword;
public:
CWord(string strLine) {
istringstream in(strLine);
in >> mainword;
string mid = "";
while (!in.eof()) {
in >> mid;
vecword.push_back(mid);
string GetMainWord() { return mainword; }
void Show() {
cout << endl;
cout << "单词是: " << "\t" << mainword << endl;
cout << "同义词是: " << "\t";
for_each(vecword.begin(), vecword.end(), [](string s) {
cout << s << "\t";
cout << endl;
class CWordManage {
multimap<string, CWord>mymap;
public:
bool Add(string strLine) {
CWord word(strLine);
pair<string, CWord>p(word.GetMainWord(), word);
mymap.insert(p);
return true;
void Show_Find(string strFind) {
multimap<string, CWord>::iterator itfind = mymap.find(strFind);
if (itfind != mymap.end()) {
CWord& obj = (*itfind).second;
obj.Show();
else {
cout << strFind << "字典里没有记录同义词" << endl;
void Show() {
multimap<string, CWord>::iterator te = mymap.begin();
while (te != mymap.end()) {
CWord& obj = (*te).second;
obj.Show();
te++;
int main() {
string s[5]{ string("one single unique"), string("correct true right"),
string("near close"), string("happy please"),
string("strong powerful") };
CWordManage manage;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
manage.Add(s[i]);
manage.Show();
