[观赏]超级快速的大数质因数分解模板
[观赏]超级快速的大数质因数分解模板
众所周知,大数的质因数分解向来是数学界的一大难题,4096位的RSA密码破解,如果用现在已知的质因数分解模板去跑的话,那么估计到我挥手离开这个世界的时候可能都跑不完,可能子辈,孙辈,往后几个世代都跑不完。所谓现代版的"愚公移山"大抵如此,一个世代接着一个世代地跑同一个模型,总有能跑完的那一刻(但是电脑只会在那之前先报废,报废的话就得从头再来了罢,悲)。
分享一位知友提过的一个非常有趣的问题,稍微看一看就这道这个领域到底有多棘手了。
我们先来细数一下我们从刚刚学习程序设计的时候,都学习过了质因数分解的哪些做法呢?
- 暴力地从 1 枚举到 \sqrt n ,只要能够整除当前的数,即可将其添加为因子
-
Pollard-Rho大质因数分解,一般可以结合Miller-Rabin素数判定,一般适用于 n\le 2^{64} 的情况。由于其实现上差异较大,不同的做法在时间上差距极大。 -
Pollard-Rho + euler_sieve + quadratic_sieve多个数论模板缝合的大质因数分解,一般适用于 n\le 2^{128} 的情况,具体实现可以参照 Tangjz大佬的示例代码 ,一般也可以跑出相当快的速度。
以上可能你没听说过最后一个,或者没听说过后面两个,或者这几个都没听说过,不过都无所谓了,反正这几个都不过是小case罢了,大家直接打开链接去看代码就完事了,本文不负责讲解。(其实最后这个最强力的做法, 我也看不懂,也不想讲 ,主要是不想让前菜占太多的版面hhh)
SPOJ 大质因数分解系列题目
评测网址:
- Integer Factorization (15 digits)
- Integer Factorization (20 digits)
- Integer Factorization (29 digits)
顾名思义,这三道评测题目全部都是单纯的质因数分解,每一组数据的输出为 "底数(必须是一个质数质数)^幂数" 的组合形式,按照底数从小到大的顺序输出。最后用一行0作为结尾。具体如下:
样例输入
3111989
13091989
2432902008176640000
77145199750673
0样例输出
317^1 9817^1
17^2 89^1 509^1
2^18 3^8 5^4 7^2 11^1 13^1 17^1 19^1
328439^1 234884407^1数据范围
-
FACT0的范围:数据组数为
10
,每组数据的范围为
n\le10^{15}
,需要用
long long数据类型表示,时间上限为 1138\text{ms} -
FACT1的范围:数据组数为
10
,每组数据的范围为
n\le 10^{20}
,需要用
__int128数据类型表示,时间上限为 3065\text{ms} -
FACT2的范围: 数据组数为
10
,每组数据的范围为
n\le 10^{29}
,需要用
__int128数据类型表示,时间上限为 2014\text{ms}
那么前两个数据范围,正好对应上面所讲的三种方法中的后两种(虽然据说FACT0用第一种最暴力的方法也能过),虽然最后一种在数据的表示范围上一样,但是运行时间远远不够。
在github上寻找题目的题解时,颗粒无收,就在即将扫兴而归时,直接搜索质因数分解的相关项目,结果找到了一个大佬用
python 2.7
标准完成的快速质因数分解项目。
抱着试试看的态度,我将所有的子模块整合在同一个文件中,并将其修改为
python 3.9
标准,在进行测试后,跑出了以下的效果:
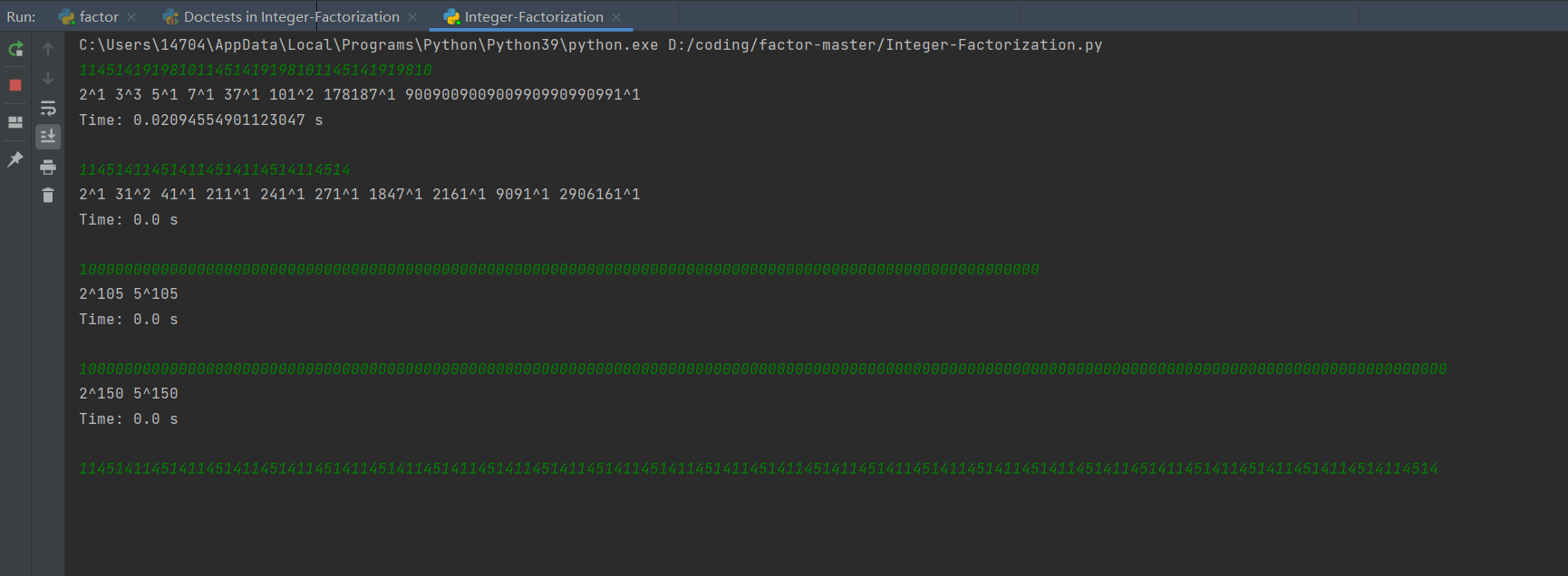
可以看到,当输入的大数规模在 [10^{30},10^{40}] 左右时,或者数较为庞大但是其质因数组成较为简单的时候,可以在非常短的时间内运行出结果。但是稍微复杂一点,就不行了,比如说我最后一组是连续复制了25次的114514,数据量级接近 10^{150} ,我从AC上述3题,写了本文的部分内容,出去跑步5km,洗澡完毕,总共约70分钟的时间,这个程序依旧没有跑完。可见要想将其用在解决RSA加密算法问题还遥遥无期。
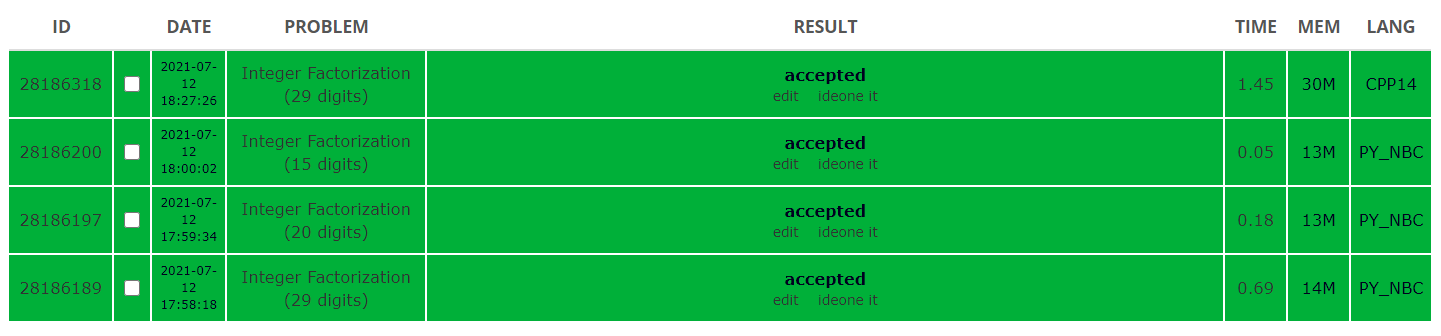
但是针对上述题目的数据范围,就算是绰绰有余啦。上述3题的运行结果如下:
笔者将自己的
python 3.9
代码与另一个大佬的
C++
程序进行对比,发现其在性能上有着本质性的差别。
在最极端的情况下,当一个量级为
10^{30}
的质数,等于两个不相等的量级在
10^{15}
上下的质数相乘时,本代码需要跑约
300\text{ms}
,而上述进行对比的
C++
代码则需要跑约
1000\text{ms}
左右。
上面的时间数据指的是在单组数据下的运行时间。当然,对比代码的码量较小,也不是专门攻克和优化该问题的项目型代码,所以运行起来空间消耗也非常大。拿来说语言之间的优势和劣势显然是不公平的(听说还有大小为20KB的C++代码,跑SPOJ的数据范围只需要 60\text{ms} ,这个版本我就找不到了,其他我见到的C++代码,时间都在 1\text{s} 以上)。但是笔者之前在写牛顿迭代法求高精度整数开根的问题时,采用了码量较大,优化相当优秀,单组高精度除法快于python的C++模板时,在时间上却远慢于python,这说明C++在手写高精度上下的功夫远没有python内部实现来的快,使得运算量较大时,python有机会弥补在评测机运行时与生俱来的时间劣势。所以如果日后要攻克该问题时,应该也都是通过python这些内部实现了高精度整数的语言来进行实验。
那么话不多说,直接上代码了。该代码长度大约在30KB左右,总长度为993行,相当硬核。每个函数拆开看我大概能看懂是二分查找、不同规模的欧拉筛和区间筛、
Pollard-Rho
函数本体。但是和在一块看我就看不懂了,实在是过于复杂...
该代码所采用的标准为
Python 3.9
,在本地运行时请务必注意使用对应的标准。另外本代码的输入输出是完全对标上述SPOJ的3道题的。
AC代码
# coding=utf-8
import math
import random
import fractions
import sys
import time
from decimal import Decimal
# coding=utf-8
# Prime sieve constants
SMALL_THRESHOLD = 60
ERAT_THRESHOLD = 35 * 10 ** 5
ATKIN_THERSHOLD = 10 ** 10
LOWER_SEG_SIZE = 65536
UPPER_SEG_SIZE = 2097152
# Pollard rho constants
PRIME_THRESHOLD_RHO = 500
SIZE_THRESHOLD_RHO = 10 ** 20
# Pollard (p-1) constants
MAX_B1_PM1 = 10 ** 8
MAX_B2_PM1 = 10 ** 10
MAX_D_PM1 = 500
# ECM constants
MAX_CURVES_ECM = 10000
MAX_RND_ECM = 2 ** 63
MAX_B1_ECM = 43 * 10 ** 7
MAX_B2_ECM = 2 * 10 ** 10
# General factorization constants
PRIME_THRESHOLD_BF = 25000
# Names of factoring routines for displaying purposes
NAME_ECM = "ECM"
NAME_RHO = "Pollard Rho"
NAME_PM1 = "Pollard p-1"
PRIME_THRESHOLD = 100000
MR_THRESHOLD = 10 ** 36
def binary_search(x, arr, include_equal=False):
if x > arr[-1]:
return len(arr)
elif x < arr[0]:
return 0
l, r = 0, len(arr) - 1
while l <= r:
m = (l + r) >> 1
if arr[m] == x:
return m + 1 if not include_equal else m
elif arr[m] < x:
l = m + 1
else:
r = m - 1
return l
def gcd(a, b):
return int(math.gcd(a, b))
def xgcd(a, b):
r, s = 0, 1
while b != 0:
c, d = divmod(a, b)
r, s = s, r - c * s
a, b = b, d
return r
def is_prime_bf(n):
if n < 2: return False
if n == 2 or n == 3: return True
if not n & 1: return False
if not n % 3: return False
if n < 9: return True
sqrt_n = int(math.sqrt(n)) + 1
for i in range(5, sqrt_n, 6):
if not n % i or not n % (i + 2): return False
return True
def is_prime_fast(n, use_probabilistic=False, tolerance=30):
firstPrime = [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47,
53, 59, 61, 67, 71]
# Determine bases for deterministic Miller-Rabin test
if n >= MR_THRESHOLD:
logn = math.log(n)
if not use_probabilistic:
w = range(2, 2 * int(logn * math.log(logn) / math.log(2)))
else:
w = range(tolerance)
elif n >= 1543267864443420616877677640751301:
w = firstPrime[:20]
elif n >= 564132928021909221014087501701:
w = firstPrime[:18]
elif n >= 59276361075595573263446330101:
w = firstPrime[:16]
elif n >= 6003094289670105800312596501:
w = firstPrime[:15]
elif n >= 3317044064679887385961981:
w = firstPrime[:14]
elif n >= 318665857834031151167461:
w = firstPrime[:13]
elif n >= 3825123056546413051:
w = firstPrime[:12]
# [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23]
elif n >= 341550071728321:
w = firstPrime[:9]
# [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17]
elif n >= 3474749660383:
w = firstPrime[:7]
elif n >= 2152302898747:
w = firstPrime[:6]
# [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13]
elif n >= 4759123141:
w = firstPrime[:5]
# [2, 3, 5, 7, 11]
elif n >= 9006403:
w = [2, 7, 61]
elif n >= 489997:
# Some Fermat stuff
if not (not (n & 1) or not (n % 3) or not (n % 5) or not (n % 7) or not (n % 11) or not (n % 13) or not (
n % 17) or not (n % 19) or not (n % 23) or not (n % 29) or not (n % 31) or not (n % 37) or not (
n % 41) or not (n % 43) or not (n % 47) or not (n % 53) or not (n % 59) or not (n % 61) or not (
n % 67) or not (n % 71) or not (n % 73) or not (n % 79) or not (
n % 83)) and n % 89 and n % 97 and n % 101:
hn, nm1 = n >> 1, n - 1
p = pow(2, hn, n)
if p == 1 or p == nm1:
p = pow(3, hn, n)
if p == 1 or p == nm1:
p = pow(5, hn, n)
return p == 1 or p == nm1
return False
elif n >= 42799:
return n & 1 and n % 3 and n % 5 and n % 7 and n % 11 and n % 13 and n % 17 \
and n % 19 and n % 23 and n % 29 and n % 31 and n % 37 and n % 41 and n % 43 \
and pow(2, n - 1, n) == 1 and pow(5, n - 1, n) == 1
elif n >= 841:
return not (((((not (n & 1) or not (n % 3) or not (n % 5) or not (n % 7) or not (n % 11) or not (
n % 13) or not (
n % 17)) or not (n % 19)) or not (n % 23) or not (n % 29) or not (n % 31) or not (n % 37) or not (
n % 41) or not (n % 43) or not (
n % 47)) or not (n % 53) or not (n % 59) or not (n % 61) or not (n % 67) or not (n % 71) or not (
n % 73) or not (n % 79)) or not (n % 83) or not (n % 89) or not (n % 97) or not (n % 101) or not (
n % 103) or not (pow(2, n - 1, n) == 1))
elif n >= 25:
return not (not (n & 1) or not (n % 3) or not (n % 5) or not (n % 7) or not (
n % 11)) and n % 13 and n % 17 and n % 19 and n % 23
elif n >= 4:
return n & 1 and n % 3
else:
return n > 1
if not (
n & 1 and n % 3 and n % 5 and n % 7 and n % 11 and n % 13 and n % 17 and n % 19 and n % 23 and n % 29 and n % 31 and n % 37 and n % 41 and n % 43 and n % 47 and n % 53 and n % 59 and n % 61 and n % 67 and n % 71 and n %
73 and n % 79 and n % 83 and n % 89): return False
# Miller-Rabin
s = 0
d = n - 1
while not d & 1:
d >>= 1
s += 1
for k in w:
# Pick a random witness if probabilistic
if use_probabilistic:
p = random.randint(2, n - 2)
else:
p = k
x = pow(p, d, n)
if x == 1: continue
for _ in range(s):
if x + 1 == n: break
x = x * x % n
else:
return False
return True
def is_prime(n, use_probabilistic=False, tolerance=30):
if n < PRIME_THRESHOLD:
return is_prime_bf(n)
else:
if use_probabilistic:
return is_prime_fast(n, use_probabilistic, tolerance)
else:
if n < MR_THRESHOLD:
return is_prime_fast(n)
else:
return is_prime_fast(n, True, 40)
# Sieve bits
segs = [[] for _ in range(60)]
# Primes under 60
under60 = [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59]
# delta's in the solutions to the congruences in algorithms 4.1, 4.2, 4.3
# in the paper
dAll = [1, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 49, 53, 59]
# All (d, f, g) where 4f^2 + g^2 = d (mod 60), d � 60, f � 15, g � 30
DFG1 = [[1, 0, 1], [1, 0, 11], [1, 0, 19],
[1, 0, 29], [1, 2, 15], [1, 3, 5], [1, 3, 25], [1, 5, 9],
[1, 5, 21], [1, 7, 15], [1, 8, 15], [1, 10, 9],
[1, 10, 21], [1, 12, 5], [1, 12, 25], [1, 13, 15],
[13, 1, 3], [13, 1, 27], [13, 4, 3], [13, 4, 27],
[13, 6, 7], [13, 6, 13], [13, 6, 17], [13, 6, 23],
[13, 9, 7], [13, 9, 13], [13, 9, 17], [13, 9, 23],
[13, 11, 3], [13, 11, 27], [13, 14, 3], [13, 14, 27],
[17, 2, 1], [17, 2, 11], [17, 2, 19], [17, 2, 29],
[17, 7, 1], [17, 7, 11], [17, 7, 19], [17, 7, 29],
[17, 8, 1], [17, 8, 11], [17, 8, 19], [17, 8, 29],
[17, 13, 1], [17, 13, 11], [17, 13, 19], [17, 13, 29],
[29, 1, 5], [29, 1, 25], [29, 4, 5], [29, 4, 25],
[29, 5, 7], [29, 5, 13], [29, 5, 17], [29, 5, 23],
[29, 10, 7], [29, 10, 13], [29, 10, 17], [29, 10, 23],
[29, 11, 5], [29, 11, 25], [29, 14, 5], [29, 14, 25],
[37, 2, 9], [
37, 2, 21], [37, 3, 1], [37, 3, 11],
[37, 3, 19], [37, 3, 29], [37, 7, 9], [37, 7, 21],
[37, 8, 9], [37, 8, 21], [37, 12, 1], [37, 12, 11],
[37, 12, 19], [37, 12, 29], [37, 13, 9], [37, 13, 21],
[41, 2, 5], [41, 2, 25], [41, 5, 1], [41, 5, 11],
[41, 5, 19], [41, 5, 29], [41, 7, 5], [41, 7, 25],
[41, 8, 5], [41, 8, 25], [41, 10, 1], [41, 10, 11],
[41, 10, 19], [41, 10, 29], [41, 13, 5], [41, 13, 25],
[49, 0, 7], [49, 0, 13], [49, 0, 17], [49, 0, 23],
[49, 1, 15], [49, 4, 15], [49, 5, 3], [49, 5, 27],
[49, 6, 5], [49, 6, 25], [49, 9, 5], [49, 9, 25],
[49, 10, 3], [49, 10, 27], [49, 11, 15], [49, 14, 15],
[53, 1, 7], [53, 1, 13], [53, 1, 17], [53, 1, 23],
[53, 4, 7], [53, 4, 13], [53, 4, 17], [53, 4, 23],
[53, 11, 7], [53, 11, 13], [53, 11, 17], [53, 11, 23],
[53, 14, 7], [53, 14, 13], [53, 14, 17], [53, 14, 23]]
# All (d, f, g) where 3f^2 + g^2 = d (mod 60), d � 60, f � 10, g � 30
DFG2 = [[7, 1, 2], [7, 1, 8], [7, 1, 22],
[7, 1, 28], [7, 3, 10], [7, 3, 20], [7, 7, 10],
[7, 7, 20], [7, 9, 2], [7, 9, 8], [7, 9, 22], [7, 9, 28],
[19, 1, 4], [19, 1, 14], [19, 1, 16], [19, 1, 26],
[19, 5, 2], [19, 5, 8], [19, 5, 22], [19, 5, 28],
[19, 9, 4], [19, 9, 14], [19, 9, 16], [19, 9, 26],
[31, 3, 2], [31, 3, 8], [31, 3, 22], [31, 3, 28],
[31, 5, 4], [31, 5, 14], [31, 5, 16], [31, 5, 26],
[31, 7, 2], [31, 7, 8], [31, 7, 22], [31, 7, 28],
[43, 1, 10], [43, 1, 20], [43, 3, 4], [43, 3, 14],
[43, 3, 16], [43, 3, 26],
[43, 7, 4], [43, 7, 14],
[43, 7, 16], [43, 7, 26], [43, 9, 10], [43, 9, 20]]
# All (d, f, g) where 3f^2 - g^2 = d (mod 60), d < 60, f � 10, g � 30
DFG3 = [[11, 0, 7], [11, 0, 13], [11, 0, 17],
[11, 0, 23], [11, 2, 1], [11, 2, 11], [11, 2, 19],
[11, 2, 29], [11, 3, 4], [11, 3, 14], [11, 3, 16],
[11, 3, 26], [11, 5, 2], [11, 5, 8], [11, 5, 22],
[11, 5, 28], [11, 7, 4], [11, 7, 14], [11, 7, 16],
[11, 7, 26], [11, 8, 1], [11, 8, 11], [11, 8, 19],
[11, 8, 29], [23, 1, 10], [23, 1, 20], [23, 2, 7],
[23, 2, 13], [23, 2, 17], [23, 2, 23], [23, 3, 2],
[23, 3, 8], [23, 3, 22], [23, 3, 28], [23, 4, 5],
[23, 4, 25], [23, 6, 5], [23, 6, 25], [23, 7, 2],
[23, 7, 8], [23, 7, 22], [23, 7, 28], [23, 8, 7],
[23, 8, 13], [23, 8, 17], [23, 8, 23], [23, 9, 10],
[23, 9, 20], [47, 1, 4], [47, 1, 14], [47, 1, 16],
[47, 1, 26], [47, 2, 5], [47, 2, 25], [47, 3, 10],
[47, 3, 20], [47, 4, 1], [47, 4, 11], [47, 4, 19],
[47, 4, 29], [47, 6, 1], [47, 6, 11], [47, 6, 19],
[47, 6, 29], [47, 7, 10], [47, 7, 20], [47, 8, 5],
[47, 8, 25], [47, 9, 4], [47, 9, 14], [47, 9, 16],
[47, 9, 26], [59, 0, 1], [59, 0, 11], [59, 0, 19],
[59, 0, 29], [59, 1, 2], [59, 1, 8], [59, 1, 22],
[59, 1, 28], [59, 4, 7], [59, 4, 13], [59, 4, 17],
[59, 4, 23], [59, 5, 4], [59, 5, 14], [59, 5, 16],
[59, 5, 26], [59, 6, 7], [59, 6, 13], [59, 6, 17],
[59, 6, 23], [59, 9, 2], [59, 9, 8], [59, 9, 22],
[59, 9, 28]]
def small_sieve(n):
correction = (n % 6 > 1)
n = {0:
n, 1: n - 1, 2: n + 4, 3: n + 3, 4: n + 2, 5: n + 1}[n % 6]
sieve = [True] * (n // 3)
sieve[0] = False
limit = (int(math.sqrt(n)) // 3) + 1
# Use a wheel (mod 6)
for i in range(limit):
if sieve[i]:
k = 3 * i + 1 | 1
sieve[((k * k) // 3):: (k << 1)] = \
[False] * ((n // 6 - (k * k) // 6 - 1) // k + 1)
sieve[(k * k + (k << 2) -
(k << 1) * (i & 1)) // 3:: (k << 1)] = \
[False] * ((n // 6 - (k * k + (k << 2) -
2 * k * (i & 1)) // 6 - 1) // k + 1)
return [2, 3] + [3 * i + 1 | 1 for i in range(1, n // 3 - correction) if sieve[i]]
def enum1(d, f, g, L, B, segs):
x, y0, temp = f, g, L + B
k0 = (4 * f * f + g * g - d) // 60
while k0 < temp:
k0 += x + x + 15
x += 15
while True:
x -= 15
k0 -= x + x + 15
if x <= 0:
return
while k0 < L:
k0 += y0 + 15
y0 += 30
k, y = k0, y0
while k < temp:
segs[d][(k - L) >> 5] ^= 1 << ((k - L) & 31)
k += y + 15
y += 30
def enum2(d, f, g, L, B, segs):
x, y0, temp = f, g, L + B
k0 = (3 * f * f + g * g - d) // 60
while k0 < temp:
k0 += x + 5
x += 10
while True:
x -= 10
k0 -= x + 5
if x <= 0:
return
while k0 < L:
k0 += y0 + 15
y0 += 30
k, y = k0, y0
while k < temp:
segs[d][(k - L) >> 5] ^= 1 << ((k - L) & 31)
k += y + 15
y += 30
def enum3(d, f, g, L, B, segs):
x, y0, temp = f, g, L + B
k0 = (3 * f * f - g * g - d) // 60
while True:
while k0 >= temp:
if x <= y0:
return
k0 -= y0 + 15
y0 += 30
k, y = k0, y0
while k >= L and y < x:
segs[d][(k - L) >> 5] ^= 1 << ((k - L) & 31)
k -= y + 15
y += 30
k0 += x + 5
x += 10
def sieve_of_atkin(n):
sqrt_n, u, r = int(math.sqrt(n)), n + 32, 17
B, lu = 60 * sqrt_n, math.log(u)
primes = small_sieve(sqrt_n)
ret = under60 + [0] * int(u / lu + u / (lu * lu) * 1.5 - r)
for d in dAll:
segs[d] = [0] * ((B >> 5) + 1
)
# Do computations in segments of size 60�n
lim = n // 60 + 1
for L in range(1, lim, B):
for d in dAll:
for k in range(len(segs[d])):
segs[d][k] = 0
# Sieve off the primes (i.e. solutions to the various quadratic
# Diophantine equations)
lim2 = 60 * (L + B)
for d, f, g in DFG1:
enum1(d, f, g, L, B, segs)
for d, f, g in DFG2:
enum2(d, f, g, L, B, segs)
for d, f, g in DFG3:
enum3(d, f, g, L, B, segs)
# Sieve off non-squarefree numbers
for p in primes:
p2 = p * p
if p2 > lim2:
break
if p >= 7:
b = -xgcd(p2, 60)
if b < 0: b += p2
for d in dAll:
x = b * (60 * L + d) % p2
while x < B:
segs[d][x >> 5] &= ~(1 << (x & 31))
x += p2
# Compute primes
for j in range((B >> 5) + 1):
for x in range(32):
k = 60 * (L + x + (j << 5))
for d in dAll:
if k + d > n:
return ret[:r]
# If a_k = 1, 60k + d is a prime
if ((segs[d][j] << 31 - x) & 0xFFFFFFFF) >= 0x80000000:
ret[r] = 60 * k + d
r += 1
def prime_sieve(n):
if n <= SMALL_THRESHOLD:
return under60[:binary_search(n, under60)]
elif n <= ERAT_THRESHOLD:
return small_sieve(n)
elif n <= ATKIN_THERSHOLD:
return sieve_of_atkin(n)
else:
return segmented_sieve(2, n)
def segmented_sieve(lo, hi):
if hi < lo: return []
max_prime, pos = int(math.sqrt(hi)), 0
base_primes = prime_sieve(max_prime)
primes = [0] * int(math.ceil(1.5 * hi / math.log(hi)) - math.floor(1.5 * lo / math.log(lo)))
# Include primes below �hi if necessary
if lo < max_prime:
lo_pos = binary_search(lo, base_primes, include_equal=True)
for k in range(lo_pos, len(base_primes)):
primes[pos] = base_primes[k]
pos += 1
lo = max_prime
# Compute segment size
delta = UPPER_SEG_SIZE if hi - lo >= UPPER_SEG_SIZE else LOWER_SEG_SIZE
l1, l = len(base_primes), (delta >> 4) + 1
int_size, sieve = l << 3, bytearray([0x0] * l)
lo_1, hi_1 = lo, lo + delta
# Compute stuff in segments
while lo_1 <= hi:
# Re-zero sieve bits if necessary
if lo_1 != lo:
for i in range(l):
sieve[i] = 0
if (lo_1 & 1) == 0:
lo_1 += 1
# Sieve off primes
for i in range(1, l1):
p = base_primes[i]
k = (p - (lo_1 % p)) % p
if (k & 1) == 1:
k += p
k >>= 1
while k < int_size:
sieve[k >> 3] |= 1 << (k & 7)
k += p
# Compute primes and put them in the prime list
end = min(hi_1, hi) + 1
for n in range(lo_1, end, 2):
d = n - lo_1
if ((sieve[d >> 4] >> ((d >> 1) & 0x7)) & 0x1) == 0x0:
primes[pos] = n
pos += 1
# Update segment boundaries
lo_1 =
hi_1 + 1
hi_1 = lo_1 + delta
return primes[:pos]
RESOLUTION = 40
def compute_bounds(n):
log_n = len(str(n))
if log_n <= 30:
B1, B2 = 2000, 147396
elif log_n <= 40:
B1, B2 = 11000, 1873422
elif log_n <= 50:
B1, B2 = 50000, 12746592
elif log_n <= 60:
B1, B2 = 250000, 128992510
elif log_n <= 70:
B1, B2 = 1000000, 1045563762
elif log_n <= 80:
B1, B2 = 3000000, 5706890290
else:
# Anything greater and my computer runs out of memory -- prolly need to fix this
B1, B2 = MAX_B1_ECM, MAX_B2_ECM
return B1, B2
def point_add(px, pz, qx, qz, rx, rz, n):
u = (px - pz) * (qx + qz)
v = (px + pz) * (qx - qz)
upv, umv = u + v, u - v
x = (rz * upv * upv)
if x >= n:
x %= n
z = rx * umv * umv
if z >= n:
z %= n
return x, z
def point_double(px, pz, n, a24):
u, v = px + pz, px - pz
u2, v2 = u * u, v * v
t = u2 - v2
x = (u2 * v2)
if x >= n:
x %= n
z = (t * (v2 + a24 * t))
if z >= n:
z %= n
return x, z
def scalar_multiply(k, px, pz, n, a24):
sk = bin(k)
lk = len(sk)
qx, qz = px, pz
rx, rz = point_double(px, pz, n, a24)
for i in range(3, lk):
if sk[i] == '1':
qx, qz = point_add(rx, rz, qx, qz, px, pz, n)
rx, rz = point_double(rx, rz, n, a24)
else:
rx, rz = point_add(qx, qz, rx, rz, px, pz, n)
qx, qz = point_double(qx, qz, n, a24)
return qx, qz
###########################################################
ADD_COST = 6
DUP_COST = 5
def lucas_cost(k, v):
d = k
r = int(Decimal(d) * Decimal(v) + Decimal(0.5))
if r >= k:
return ADD_COST * k
d, e, c = k - r, 2 * r - k, DUP_COST + ADD_COST
while d != e:
# Want d >= e so swap if d < e
if d < e:
d, e = e, d
# Condition 1
if 4 * d <= 5 * e and (d + e) % 3 == 0:
d, e = (2 * d - e) / 3, (2 * e - d) / 3
c += 3 * ADD_COST
# Condition 2
elif 4 * d <= 5 * e and (d - e) % 6 == 0:
d = (d - e) / 2
c += ADD_COST + DUP_COST
# Condition 3
elif d <= 4 * e:
d -= e
c += ADD_COST
# Condition 4
elif (d + e) % 2 == 0:
d = (d - e) / 2
c += ADD_COST + DUP_COST
# Condition 5
elif d % 2 == 0:
d /= 2
c += ADD_COST + DUP_COST
# Condition 6
elif d % 3 == 0:
d = d / 3 - e
c += 3 * ADD_COST + DUP_COST
# Condition 7
elif (d + e) % 3 == 0:
d = (d - 2 * e) / 3
c += 3 * ADD_COST + DUP_COST
# Condition 8
elif (d -
e) % 3 == 0:
d = (d - e) / 3
c += 3 * ADD_COST + DUP_COST
# Condition 9
else:
e /= 2
c += ADD_COST + DUP_COST
return c
def multiply_prac(k, px, pz, n, a24):
ax, bx, cx, tx, t2x = px, 0, 0, 0, 0
az, bz, cz, tz, t2z = pz, 0, 0, 0, 0
v = [0.61803398874989485, 0.5801787282954641, 0.6179144065288179, 0.6180796684698958]
# Find best value of v
r, i = lucas_cost(k, v[0]), 0
for d in range(len(v)):
e = lucas_cost(k, v[d])
if e < r:
r, i = e, d
r = int(Decimal(k) * Decimal(v[i]) + Decimal(0.5))
d, e = k - r, 2 * r - k
bx, bz, cx, cz = ax, az, ax, az
ax, az = point_double(ax, az, n, a24)
while d != e:
# Want d >= e so swap if d < e
if d < e:
d, e = e, d
ax, az, bx, bz = bx, bz, ax, az
# Condition 1
if 4 * d <= 5 * e and (d + e) % 3 == 0:
d, e = (2 * d - e) / 3, (2 * e - d) / 3
tx, tz = point_add(ax, az, bx, bz, cx, cz, n)
t2x, t2z = point_add(tx, tz, ax, az, bx, bz, n)
bx, bz = point_add(bx, bz, tx, tz, ax, az, n)
ax, az, t2x, t2z = t2x, t2z, ax, az
# Condition 2
elif 4 * d <= 5 * e and (d - e) % 6 == 0:
d = (d - e) / 2
bx, bz = point_add(ax, az, bx, bz, cx, cz, n)
ax, az = point_double(ax, az, n, a24)
# Condition 3
elif d <= 4 * e:
d -= e
# tx, tz = point_add(bx, bz, ax, az, cx, cz, n)
# bx, tx, cx = tx, cx, bx
# bz, tz, cz = tz, cz, bz
cx, cz = point_add(bx, bz, ax, az, cx, cz, n)
bx, bz, cx, cz = cx, cz, bx, bz
# Condition 4
elif (d + e) % 2 == 0:
d = (d - e) / 2
bx, bz = point_add(bx, bz, ax, az, cx, cz, n)
ax, az = point_double(ax, az, n, a24)
# Condition 5
elif d % 2 == 0:
d /= 2
cx, cz = point_add(cx, cz, ax, az, bx, bz, n)
ax, az = point_double(ax, az, n, a24)
# Condition 6
elif d % 3 == 0:
d = d / 3 - e
tx, tz = point_double(ax, az, n, a24)
t2x, t2z = point_add(ax, az, bx, bz, cx, cz, n)
ax, az = point_add(tx, tz, ax, az, ax, az, n)
# tx, tz = point_add(tx, tz, t2x, t2z, cx, cz, n)
# cx, bx, tx = bx, tx, cx
# cz, bz, tz = bz, tz, cz
cx, cz = point_add(tx, tz, t2x, t2z, cx, cz, n)
bx, bz, cx, cz = cx, cz, bx, bz
# Condition 7
elif (d + e) % 3 == 0:
d = (d - 2 * e) / 3
tx, tz
= point_add(ax, az, bx, bz, cx, cz, n)
bx, bz = point_add(tx, tz, ax, az, bx, bz, n)
tx, tz = point_double(ax, az, n, a24)
# TODO: Check order of a and t here
ax, az = point_add(ax, az, tx, tz, ax, az, n)
# Condition 8
elif (d - e) % 3 == 0:
d = (d - e) / 3
tx, tz = point_add(ax, az, bx, bz, cx, cz, n)
# TODO: Check whether c = f(a, c, b) or c = f(c, a, b)
cx, cz = point_add(cx, cz, ax, az, bx, bz, n)
bx, bz, tx, tz = tx, tz, bx, bz
tx, tz = point_double(ax, az, n, a24)
# TODO: Check order of a and t here
ax, az = point_add(ax, az, tx, tz, ax, az, n)
# Condition 9
else:
e /= 2
cx, cz = point_add(cx, cz, bx, bz, ax, az, n)
bx, bz = point_double(bx, bz, n, a24)
x, z = point_add(ax, az, bx, bz, cx, cz, n)
return x, z
###########################################################
def factorize_ecm(n, verbose=False):
if n == 1 or is_prime(n):
return n
B1, B2 = compute_bounds(n)
# if verbose:
# print "Number of digits:", len(str(n))
# print "Bounds:", B1, B2
D = int(math.sqrt(B2))
beta = [0] * (D + 1)
S = [0] * (2 * D + 2)
# ----- Stage 1 and Stage 2 precomputations -----
curves, log_B1 = 0, math.log(B1)
# if verbose:
# print "Sieving primes..."
primes = prime_sieve(B2)
num_primes = len(primes)
idx_B1 = binary_search(B1, primes)
# Compute a B1-powersmooth integer 'k'
k = 1
for i in range(idx_B1):
p = primes[i]
k = k * pow(p, int(log_B1 / math.log(p)))
g = 1
while (g == 1 or g == n) and curves <= MAX_CURVES_ECM:
curves += 1
sigma = random.randint(6, MAX_RND_ECM)
# if verbose and curves % RESOLUTION == 0:
# print "Tried", curves, "random curves..."
# Generate a new random curve in Montgomery form with Suyama's parametrization
u = ((sigma * sigma) - 5) % n
v = (4 * sigma) % n
vmu = v - u
A = ((vmu * vmu * vmu) * (3 * u + v) // (4 * u * u * u * v) - 2) % n
a24 = (A + 2) // 4
# ----- Stage 1 -----
px, pz = ((u * u * u) // (v * v * v)) % n, 1
qx, qz = scalar_multiply(k, px, pz, n, a24)
g = gcd(n, qz)
# If stage 1 is successful, return a non-trivial factor else
# move on to stage 2
if g != 1 and g != n:
# print "Stage 1 found factor!"
return g
# ----- Stage 2 -----
S[1], S[2] = point_double(qx, qz, n, a24)
S[3], S[4] = point_double(S[1], S[2], n, a24)
beta[1] = (S[1] * S[2]) % n
beta[2] = (S[3] * S[4]) % n
for d in range(3, D + 1):
d2 = 2 * d
S[d2 - 1], S[d2] = point_add(S[d2 - 3], S[d2 - 2], S[1], S[2], S[d2 - 5], S[d2 - 4], n)
beta
[d] = (S[d2 - 1] * S[d2]) % n
g, B = 1, B1 - 1
rx, rz = scalar_multiply(B, qx, qz, n, a24)
tx, tz = scalar_multiply(B - 2 * D, qx, qz, n, a24)
q, step = idx_B1, 2 * D
for r in range(B, B2, step):
alpha, limit = (rx * rz) % n, r + step
while q < num_primes and primes[q] <= limit:
d = (primes[q] - r) // 2
f = (rx - S[2 * d - 1]) * (rz + S[2 * d]) - alpha + beta[d]
g = (g * f) % n
q += 1
trx, trz = rx, rz
rx, rz = point_add(rx, rz, S[2 * D - 1], S[2 * D], tx, tz, n)
tx, tz = trx, trz
g = gcd(n, g)
# No non-trivial factor found, return -1
if curves > MAX_CURVES_ECM:
return -1
else:
# print "Stage 2 found factor!"
return g
small_primes = prime_sieve(PRIME_THRESHOLD_RHO)
def factorize_rho(n, verbose=False):
if n == 1 or is_prime(n):
return n
# If no factor is found, return -1
for i in range(len(small_primes) - 1, -1, -1):
r, c, y = 1, small_primes[i], random.randint(1, n - 1)
# if verbose:
# print "Trying offset:", c
m, g, q, ys = random.randint(1, n - 1), 1, 1, y
min_val, k = 0, 0
while g == 1:
x, k = y, 0
for j in range(r):
y = y * y + c
if y > n: y %= n
while k < r and g == 1:
ys, min_val = y, min(m, r - k)
for j in range(min_val):
y = y * y + c
if y > n: y %= n
q = q * abs(x - y)
if q > n: q %= n
g = gcd(q, n)
k += m
r <<= 1
if g == n:
# If no factor found, try again.
while True:
ys = ys * ys + c
if ys > n: ys %= n
g = gcd(abs(x - ys), n)
if g > 1:
break
if g != n:
return g
else:
return -1
small_primes = prime_sieve(PRIME_THRESHOLD_BF)
def merge_factorizations(f1, f2):
if f1 == -1 or f2 == -1:
# Factorization failed in this case
return -1
f = []
i = j = 0
while i < len(f1) and j < len(f2):
if f1[i][0] < f2[j][0]:
f.append(f1[i])
i += 1
elif f1[i][0] > f2[j][0]:
f.append(f2[j])
j += 1
else:
f.append((f1[i][0], f1[i][1] + f2[j][1]))
i += 1
j += 1
if i < len(f1):
f.extend(f1[i:])
elif j < len(f2):
f.extend(f2[j:])
return f
def factorize_bf(n):
sn = int(math.sqrt(n))
f = []
for p in small_primes:
if p > sn:
if n > 1:
f.append((n, 1))
n = 1
break
i = 0
while n % p == 0:
n //= p
i += 1
if i > 0:
f.append((p, i))
sn = int(math.sqrt(n))
return f, n
def print_factoring_routine(n, routine_name):
return
# print "Factoring", str(n), "with", routine_name + "..."
# TODO: Incorporate Pollard (p-1) into this - ignoring it for now
def factorize(n, verbose=False, level=3):
# if verbose:
# if n != 1:
# print "Factoring", str(n) + "..."
# print "Number of digits:", len(str(n))
if n == 1:
return []
if is_prime(n):
# if verbose:
# print str(n), "is prime!"
return [(n, 1)]
else:
f, f1 = [], []
if level > 2:
# Try brute force for small prime factors
# if verbose:
# print "Finding small prime factors..."
f, n = factorize_bf(n)
# if verbose:
# if not f:
# print "Found no small prime factors... :("
# else:
# print "Prime factors found:", reduce(lambda x, y: x + y, [str(i[0]) + ", " for i in f])[:-2]
if level > 1 and n <= SIZE_THRESHOLD_RHO and n > 1:
# Try Pollard rho
if verbose:
print_factoring_routine(n, NAME_RHO)
g = factorize_rho(n, verbose=verbose)
if g != -1:
if verbose:
# print "Found factor", str(g)
f1 = merge_factorizations(factorize(g, verbose=verbose, level=2), \
factorize(n // g, verbose=verbose, level=2))
if f1 != -1:
f.extend(f1)
if level > 0 and (f1 == -1 or n > SIZE_THRESHOLD_RHO) and n > 1:
# If Pollard rho fails try ECM
if verbose:
print_factoring_routine(n, NAME_ECM)
g = factorize_ecm(n, verbose=verbose)
if g != -1:
if verbose:
# print "Found factor", str(g)
f1 = merge_factorizations(factorize(g, verbose=verbose, level=2),
factorize(n // g, verbose=verbose, level=2))
if f1 != -1:
f.extend(f1)
else:
f = -1
return f
def print_factorization(n, f):
if n == 1:
return "1^1"
s = ""
# s = str(n) + " = "
for i in range(len(f) - 1):
pf, exp = f[i][0], f[i][1]
s += str(pf) + "^" + str(exp) + " "
s += str(f[-1][0]) + "^" + str(f[-1][1])
return s
if __name__ == "__main__":
# sys.stdin = open('input.txt', 'r')
# sys.stdout = open('output.txt', 'w')
# input = sys.stdin.readline
# logfile = open('mylog.txt', 'a')
while True:
n = int(input())
if n == 0:
break
# print ""
t = time.time()
f = factorize(n, verbose=True)
t1 = time.time()
if n < 1:
print("invalid test case")
