本文是PyTorch入门的第二篇文章,后续将会持续更新,作为PyTorch系列文章。
本文将会介绍如何使用PyTorch来搭建简单的MLP(Multi-layer Perceptron,多层感知机)模型,来实现二分类及多分类任务。
二分类数据集为
ionosphere.csv
(电离层数据集),是
UCI机器学习数据集
中的经典二分类数据集。它一共有351个观测值,34个自变量,1个因变量(类别),类别取值为
g
(good)和
b
(bad)。在
ionosphere.csv
文件中,共351行,前34列作为自变量(输入的X),最后一列作为类别值(输出的y)。
多分类数据集为
iris.csv
(鸢尾花数据集),是
UCI机器学习数据集
中的经典多分类数据集。它一共有150个观测值,4个自变量(萼片长度,萼片宽度,花瓣长度,花瓣宽度),1个因变量(类别),类别取值为
Iris-setosa
,
Iris-versicolour
,
Iris-virginica
。在
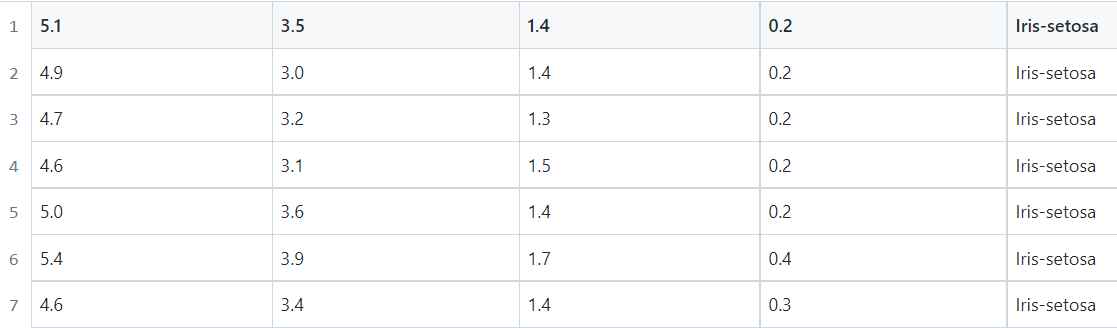
iris.csv
文件中,共150行,前4列作为自变量(输入的X),最后一列作为类别值(输出的y)。前几行数据如下图:
使用PyTorch构建神经网络模型来解决分类问题的基本流程如下:
其中
加载数据集
和
划分数据集
为数据处理部分,
构建模型
和
选择损失函数及优化器
为创建模型部分,
模型训练
的目标是选择合适的优化器及训练步长使得损失函数的值很小,
模型预测
是在模型测试集或新数据上的预测。
使用PyTorch构建MLP模型来实现二分类任务,模型结果图如下:
实现MLP模型的Python代码如下:
from numpy import vstack
from pandas import read_csv
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from torch import Tensor
from torch.optim import SGD
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader, random_split
from torch.nn import Linear, ReLU, Sigmoid, Module, BCELoss
from torch.nn.init import kaiming_uniform_, xavier_uniform_
class CSVDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, path):
df = read_csv(path, header=None)
self.X = df.values[:, :-1]
self.y = df.values[:, -1]
self.X = self.X.astype('float32')
self.y = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(self.y)
self.y = self.y.astype('float32')
self.y = self.y.reshape((len(self.y), 1))
def __len__(self):
return len(self.X)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return [self.X[idx], self.y[idx]]
def get_splits(self, n_test=0.3):
test_size = round(n_test * len(self.X))
train_size = len(self.X) - test_size
return random_split(self, [train_size, test_size])
class MLP(Module):
def __init__(self, n_inputs):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
self.hidden1 = Linear(n_inputs, 10)
kaiming_uniform_(self.hidden1.weight, nonlinearity='relu')
self.act1 = ReLU()
self.hidden2 = Linear(10, 8)
kaiming_uniform_(self.hidden2.weight, nonlinearity='relu')
self.act2 = ReLU()
self.hidden3 = Linear(8, 1)
xavier_uniform_(self.hidden3.weight)
self.act3 = Sigmoid()
def forward(self, X):
X = self.hidden1(X)
X = self.act1(X)
X = self.hidden2(X)
X = self.act2(X)
X = self.hidden3(X)
X = self.act3(X)
return X
def prepare_data(path):
dataset = CSVDataset(path)
train, test = dataset.get_splits()
train_dl = DataLoader(train, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
test_dl = DataLoader(test, batch_size=1024, shuffle=False)
return train_dl, test_dl
def train_model(train_dl, model):
criterion = BCELoss()
optimizer = SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.9)
for epoch in range(100):
for i, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(train_dl):
optimizer.zero_grad()
yhat = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(yhat, targets)
loss.backward()
print("epoch: {}, batch: {}, loss: {}".format(epoch, i, loss.data))
optimizer.step()
def evaluate_model(test_dl, model):
predictions, actuals = [], []
for i, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(test_dl):
yhat = model(inputs)
yhat = yhat.detach().numpy()
actual = targets.numpy()
actual = actual.reshape((len(actual), 1))
yhat = yhat.round()
predictions.append(yhat)
actuals.append(actual)
predictions, actuals = vstack(predictions), vstack(actuals)
acc = accuracy_score(actuals, predictions)
return acc
def predict(row, model):
row = Tensor([row])
yhat = model(row)
yhat = yhat.detach().numpy()
return yhat
path = './data/ionosphere.csv'
train_dl, test_dl = prepare_data(path)
print(len(train_dl.dataset), len(test_dl.dataset))
model = MLP(34)
print(model)
train_model(train_dl, model)
acc = evaluate_model(test_dl, model)
print('Accuracy: %.3f' % acc)
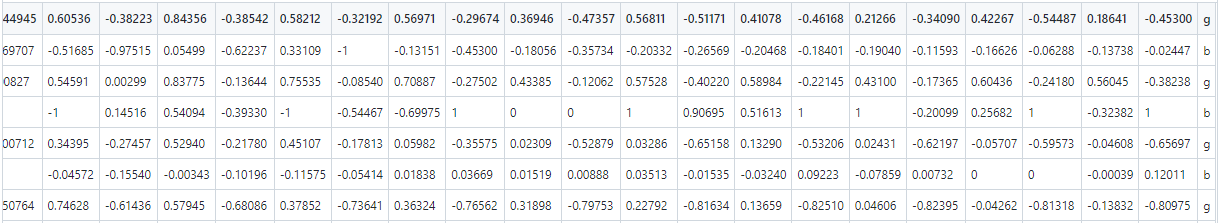
row = [1, 0, 0.99539, -0.05889, 0.85243, 0.02306, 0.83398, -0.37708, 1, 0.03760, 0.85243, -0.17755, 0.59755, -0.44945,
0.60536, -0.38223, 0.84356, -0.38542, 0.58212, -0.32192, 0.56971, -0.29674, 0.36946, -0.47357, 0.56811, -0.51171,
0.41078, -0.46168, 0.21266, -0.34090, 0.42267, -0.54487, 0.18641, -0.45300]
yhat = predict(row, model)
print('Predicted: %.3f (class=%d)' % (yhat, yhat.round()))
在上面代码中,CSVDataset类为csv数据集加载类,处理成模型适合的数据格式,并划分训练集和测试集比例为7:3。MLP类为MLP模型,模型输出层采用Sigmoid函数,损失函数采用BCELoss,优化器采用SGD,共训练100次。evaluate_model函数是模型在测试集上的表现,predict函数为在新数据上的预测结果。MLP模型的PyTorch输出如下:
(hidden1): Linear(in_features=34, out_features=10, bias=True)
(act1): ReLU()
(hidden2): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=8, bias=True)
(act2): ReLU()
(hidden3): Linear(in_features=8, out_features=1, bias=True)
(act3): Sigmoid()
运行上述代码,输出结果如下:
epoch: 0, batch: 0, loss: 0.7491992712020874
epoch: 0, batch: 1, loss: 0.750106692314148
epoch: 0, batch: 2, loss: 0.7033759355545044
......
epoch: 99, batch: 5, loss: 0.020291464403271675
epoch: 99, batch: 6, loss: 0.02309396117925644
epoch: 99, batch: 7, loss: 0.0278386902064085
Accuracy: 0.924
Predicted: 0.989 (class=1)
可以看到,该MLP模型的最终训练loss值为0.02784,在测试集上的Accuracy为0.924,在新数据上预测完全正确。
接着我们来创建MLP模型实现iris数据集的三分类任务,Python代码如下:
from numpy import vstack
from numpy import argmax
from pandas import read_csv
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder, LabelBinarizer
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from torch import Tensor
from torch.optim import SGD, Adam
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader, random_split
from torch.nn import Linear, ReLU, Softmax, Module, CrossEntropyLoss
from torch.nn.init import kaiming_uniform_, xavier_uniform_
class CSVDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, path):
df = read_csv(path, header=None)
self.X = df.values[:, :-1]
self.y = df.values[:, -1]
self.X = self.X.astype('float32')
self.y = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(self.y)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.X)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return [self.X[idx], self.y[idx]]
def get_splits(self, n_test=0.3):
test_size = round(n_test * len(self.X))
train_size = len(self.X) - test_size
return random_split(self, [train_size, test_size])
class MLP(Module):
def __init__(self, n_inputs):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
self.hidden1 = Linear(n_inputs, 5)
kaiming_uniform_(self.hidden1.weight, nonlinearity='relu')
self.act1 = ReLU()
self.hidden2 = Linear(5, 6)
kaiming_uniform_(self.hidden2.weight, nonlinearity='relu')
self.act2 = ReLU()
self.hidden3 = Linear(6, 3)
xavier_uniform_(self.hidden3.weight)
self.act3 = Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, X):
X = self.hidden1(X)
X = self.act1(X)
X = self.hidden2(X)
X = self.act2(X)
X = self.hidden3(X)
X = self.act3(X)
return X
def prepare_data(path):
dataset = CSVDataset(path)
train, test = dataset.get_splits()
train_dl = DataLoader(train, batch_size=1, shuffle=True)
test_dl = DataLoader(test, batch_size=1024, shuffle=False)
return train_dl, test_dl
def train_model(train_dl, model):
criterion = CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters())
for epoch in range(100):
for i, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(train_dl):
targets = targets.long()
optimizer.zero_grad()
yhat = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(yhat, targets)
loss.backward()
print("epoch: {}, batch: {}, loss: {}".format(epoch, i, loss.data))
optimizer.step()
def evaluate_model(test_dl, model):
predictions, actuals = [], []
for i, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(test_dl):
yhat = model(inputs)
yhat = yhat.detach().numpy()
actual = targets.numpy()
yhat = argmax(yhat, axis=1)
actual = actual.reshape((len(actual), 1))
yhat = yhat.reshape((len(yhat), 1))
predictions.append(yhat)
actuals.append(actual)
predictions, actuals = vstack(predictions), vstack(actuals)
acc = accuracy_score(actuals, predictions)
return acc
def predict(row, model):
row = Tensor([row])
yhat = model(row)
yhat = yhat.detach().numpy()
return yhat
path = './data/iris.csv'
train_dl, test_dl = prepare_data(path)
print(len(train_dl.dataset), len(test_dl.dataset))
model = MLP(4)
print(model)
train_model(train_dl, model)
acc = evaluate_model(test_dl, model)
print('Accuracy: %.3f' % acc)
row = [5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2]
yhat = predict(row, model)
print('Predicted: %s (class=%d)' % (yhat, argmax(yhat)))
可以看到,多分类代码与二分类代码大同小异,在加载数据集、模型结构、模型训练(训练batch值取1)代码上略有不同。运行上述代码,输出结果如下:
105 45
(hidden1): Linear(in_features=4, out_features=5, bias=True)
(act1): ReLU()
(hidden2): Linear(in_features=5, out_features=6, bias=True)
(act2): ReLU()
(hidden3): Linear(in_features=6, out_features=3, bias=True)
(act3): Softmax(dim=1)
epoch: 0, batch: 0, loss: 1.4808106422424316
epoch: 0, batch: 1, loss: 1.4769641160964966
epoch: 0, batch: 2, loss: 0.654313325881958
......
epoch: 99, batch: 102, loss: 0.5514447093009949
epoch: 99, batch: 103, loss: 0.620153546333313
epoch: 99, batch: 104, loss: 0.5514482855796814
Accuracy: 0.933
Predicted: [[9.9999809e-01 1.8837408e-06 2.4509615e-19]] (class=0)
可以看到,该MLP模型的最终训练loss值为0.5514,在测试集上的Accuracy为0.933,在新数据上预测完全正确。
本文介绍的模型代码已开源,Github地址为:https://github.com/percent4/PyTorch_Learning。后续将持续介绍PyTorch内容,欢迎大家关注~
多层感知机(MLP,Multilayer Perceptron)也叫人工神经网络(ANN,Artificial Neural Network),除了输入输出层,它中间可以有多个隐层,最简单的MLP只含一个隐层,即三层的结构,如下图最简单的MLP:
上图模型pyTorch代码:
import torch
from torch.nn import functional as F
x = torch.randn(1, 10) # 输入x的特征有10个
w = torch.randn(3, 10, requires_grad=True) # 一个隐藏层,节点个数为3
b = torch.rand
pytorch 实现多层感知机,主要使用torch.nn.Linear(in_features,out_features),因为torch.nn.Linear是全连接的层,就代表
MLP的全连接层
本文实例MNIST数据,输入层28×28=784个节点,2个隐含层,隐含层各100个,输出层10个节点
开发平台,windows 平台,python 3.8.5,torch版本1.8.1+cpu
#minist 用
MLP实现,
MLP也是使用
pytorch实现的
import torchvision
1、MLP模型
多层感知机(MLP,Multilayer Perceptron)也叫人工神经网络(ANN,Artificial Neural Network),除了输入输出层,它中间可以有多个隐层,最简单的MLP只含一个隐层,即三层的结构。
多层感知器(multilayer Perceptron,MLP)是指可以是感知器的人工神经元组成的多个层次。MPL的层次结构是一个有向无环图。通常,每一层都全连接到下一层,某一层上的每个人工神经元的输出成为下一层若干人工神经元的输入。MLP至少有三层人工神经元,如下图所
sklearn.neural_network.
MLPClassifier
前提警告:
MLP实现不适用于大规模应用程序。特别是,scikit-learn不提供GPU支持。关于更快的,基于gpu的
实现,以及提供更多灵活性来构建深度学习架构的框架,请参阅相关项目。官方网站:1.17. Neural network models (supervised)
Multi-layer Perceptron (
MLP)多层感知机
多层感知机是一种机器学习算法,通过在数据集上进行训练后,学习得到


