很重要的收集 --- 关于c++的各种输入(包括istream_iterator结合逗号分隔)
最近又开始刷题了,在这个过程中,我不断地发现一个问题,就是不同的题目会有不同的输入要求,而如果用c++这么繁复的语言在刷题的时候,有时候光是一个输入就会把所有的时间都消耗得一干二净,因此我在这里设立一篇文章用来记录不同的输入方式,本篇文章采取迭代更新的方式,一旦看到新的或者更好的输入方式我就会对这篇文章进行更新,同时也希望大家能对我的错误进行指出~
- 读取文件内容
用C++读取目录下的123.txt文件内容,文件内容为:
023,456,789,012,345,678
234,567,890,123,456,789
345,678,901,234,567,890
这种一般用在读取一个邻接表,网络之类的
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
ifstream inf;
inf.open("123.txt", ifstream::in);
const int cnt = 6;
string line;
//int i = 0;
int j = 0;
size_t comma = 0;
size_t comma2 = 0;
while (!inf.eof())
getline(inf,line);
comma = line.find(',',0);
cout<<line.substr(0,comma).c_str()<<' ';
while (comma < line.size() && j != cnt-1)
comma2 = line.find(',',comma + 1);
cout<<line.substr(comma + 1,comma2-comma-1).c_str()<<' ';
comma = comma2;
cout<<endl;
j = 0;
inf.close();
return 0;
}
以上的方式中inf.eof()的判断方式会出现一些问题!!!问题原因可以参考 C++之EOF() ,主要关系到eof判断到最后一个字符的逻辑。
所以,有网友建议使用 istream_iterator。
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
ifstream in_file("input_file.txt");
ofstream out_file("output_file.txt");
if(!in_file || !out_file)
cout<<"filesopen failed!\n";
return -1;
istream_iterator<string> is(in_file); // 自动按照空格分隔
istream_iterator<string> eof;
vector<string> text;
copy(is,eof,back_inserter(text));
sort(text.begin(),text.end());
ostream_iterator<string> os(out_file," ");
copy(text.begin(),text.end(),os);
return 0;
}但是这个样子,没有逗号分隔,要逗号分隔会比较麻烦一点,我这里写了一种方法可以做到。
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#include <locale>
struct csv_reader: std::ctype<char> {
csv_reader(): std::ctype<char>(get_table()) {}
static std::ctype_base::mask const* get_table() {
static std::vector<std::ctype_base::mask> rc(table_size, std::ctype_base::mask());
rc[','] = std::ctype_base::space;
rc['\n'] = std::ctype_base::space;
rc[' '] = std::ctype_base::space;
return &rc[0];
int main()
ifstream in_file("input_file.txt");
in_file.imbue(locale(locale(), new csv_reader()));
ofstream out_file("output_file.txt");
if(!in_file || !out_file)
cout<<"filesopen failed!\n";
return -1;
istream_iterator<string> is(in_file);
istream_iterator<string> eof;
vector<string> text;
copy(is,eof,back_inserter(text));
sort(text.begin(),text.end());
ostream_iterator<string> os(out_file," ");
copy(text.begin(),text.end(),os);
return 0;
}istream_iterator是个很有意思的输入工具,也可以用来读取到set里。
fruits.txt:
banana
apple
strawberry
blueberry
peach
apple
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include <algorithm>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <set>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
ifstream file("fruits.txt");
set<string> M;
copy(istream_iterator<string>(file),
istream_iterator<string>(),
inserter(M, M.end()));
for (auto const& val : M)
cout << val << ", ";
}
- 读取输入(不确定个数)
输入的每个整数之间用空格隔开,个数不确定。
输入:3 4 1 2
int a;
vector<int> array;
while(cin.get() != '\n'){
cin >> a;
array.push_back(a);
}也可以另一种
int a;
vector<int> array;
while(cin>>a){
array.push_back(a);
}还可以用istream_iterator。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<iterator>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
string text;
istream_iterator<int> is(cin);//绑定标准输入装置
istream_iterator<int> eof;//定义输入结束位置
copy(is,eof,back_inserter(text));
sort(text.begin(),text.end());
ostream_iterator<int> os(cout,", ");//绑定标准输出装置
copy(text.begin(),text.end(),os);
}逗号分隔!!!(输入的字符串是逗号分开的)
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
int main()
std::string str ="1,2,3,4,5,6";
std::vector<int> vect;
std::stringstream ss(str);
int i;
while (ss >> i)
vect.push_back(i);
if (ss.peek() == ',')
ss.ignore();
for (i=0; i< vect.size(); i++)
std::cout << vect.at(i)<<std::endl;
~或者,更简洁的办法~
stringstream ss("1,1,1,1, or something else ,1,1,1,0" );
vector<string> result;
while( ss.good() )
string substr;
getline( ss, substr, ',' );
result.push_back( substr );
}- 读取输入(确定个数)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
vector<int> array;
int n; int a;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> a;
array.push_back(a);
//这里对数组进行操作
return 0;
}有时候题目会给你一个二维的数组,m*n
比如:
4 4
*000
00*0
00**
0*00
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//打印二维vector
void printVec(vector<vector<char> > vec)
vector<char> vec_tmp;
for (vector<vector<char> >::iterator iter = vec.begin(); iter != vec.end(); iter++)
vec_tmp = *iter;
for (vector<char>::iterator it = vec_tmp.begin(); it != vec_tmp.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
int m,n;
cin>>m>>n;
//给定行数、列数的二维vector初始化
vector<vector<char> > a(m,vector<char>(n));
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
cin>>a[i][j];
printVec(a);
return 0;
}- 字符串输入
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
getline(cin, s);
cout << s << endl;
}接受一个字符串,遇“空格”、“Tab”、“回车”都结束
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
main ()
char a[20];
cin>>a;
cout<<a<<endl;
输入:jkljkljkl
输出:jkljkljkl
输入:jkljkl jkljkl //遇空格结束,所以不能输入多个单词cin.get(字符变量名)可以用来接收字符
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
main ()
char ch;
ch=cin.get(); //或者cin.get(ch);只能获取一个字符
cout<<ch<<endl;
输入:jljkljkl
输出:jcin.get(字符数组名,接收字符数)用来接收一行字符串,可以接收空格
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
main ()
char a[20];
cin.get(a,20); //有些类似getline。可以输入多个单词,中间空格隔开。
cout<<a<<endl;
输入:jkl jkl jkl
输出:jkl jkl jkl
输入:abcdeabcdeabcdeabcdeabcde (输入25个字符)
输出:abcdeabcdeabcdeabcd (接收19个字符+1个'\0')cin.get(无参数)没有参数主要是用于舍弃输入流中的不需要的字符,或者舍弃回车,弥补cin.get(字符数组名,接收字符数目)的不足.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
char arr[10];
cin.get(arr,10);
cin.get();//用于吃掉回车,相当于getchar();
cout<<arr<<endl;
cin.get(arr,5);
cout<<arr<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
输入abcdefghi
输出abcdefghi
输入abcde
输出abcdcin.getline() // 接受一个字符串,可以接收空格并输出
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
main ()
char m[20];
cin.getline(m,5); //与上面基本相同。
cout<<m<<endl;
输入:jkljkljkl
输出:jklj
接受5个字符到m中,其中最后一个为'\0',所以只看到4个字符输出;getline() // 接受一个字符串,可以接收空格并输出,需包含“#include<string>”
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
main ()
string str;
getline(cin,str);
cout<<str<<endl;
输入:jkljkljkl //VC6中有个bug,需要输入两次回车。
输出:jkljkljkl
输入:jkl jfksldfj jklsjfl
输出:jkl jfksldfj jklsjfl
和cin.getline()类似,但是cin.getline()属于istream流,而getline()属于string流,是不一样的两个函数gets()// 接受一个字符串,可以接收空格并输出,需包含“#include<string>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
main ()
char m[20];
gets(m); //不能写成m=gets();
cout<<m<<endl;
输入:jkljkljkl
输出:jkljkljkl
输入:jkl jkl jkl
输出:jkl jkl jkl
类似cin.getline()里面的一个例子,gets()同样可以用在多维数组里面:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
main ()
char m[3][20];
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
cout<<"\n请输入第"<<i+1<<"个字符串:"<<endl;
gets(m[i]);
cout<<endl;
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
cout<<"输出m["<<j<<"]的值:"<<m[j]<<endl;
请输入第1个字符串:
kskr1
请输入第2个字符串:
kskr2
请输入第3个字符串:
kskr3
输出m[0]的值:kskr1
输出m[1]的值:kskr2
输出m[2]的值:kskr3getchar()//接受一个字符,需包含“#include<string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
main ()
char ch;
ch=getchar(); //不能写成getchar(ch);
cout<<ch<<endl;
输入:jkljkljkl
输出:j
补充:stringstream的使用方法
stringstream类同时可以支持C风格的串流的输入输出操作。
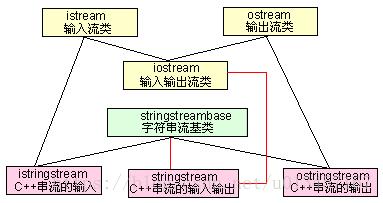
istringstream是由一个string对象构造而来,从一个string对象读取字符。
ostringstream同样是有一个string对象构造而来,向一个string对象插入字符。
stringstream则是用于C++风格的字符串的输入输出的。
#include<iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string test = "-123 9.87 welcome to, 989, test!";
istringstream iss;//istringstream提供读 string 的功能
iss.str(test);//将 string 类型的 test 复制给 iss,返回 void
string s;
cout << "按照空格读取字符串:" << endl;
while (iss >> s){
cout << s << endl;//按空格读取string
cout << "*********************" << endl;
istringstream strm(test);
//创建存储 test 的副本的 stringstream 对象
int i;
float f;
char c;
char buff[1024];
strm >> i;
cout <<"读取int类型:"<< i << endl;
strm >> f;
cout <<"读取float类型:"<<f << endl;
strm >> c;
cout <<"读取char类型:"<< c << endl;
strm >> buff;
cout <<"读取buffer类型:"<< buff << endl;
strm.ignore(100, ',');
int j;
strm >> j;
cout <<"忽略‘,’读取int类型:"<< j << endl;
return 0;
